
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 109P
The experiment shown next and discussed in Section 8.13 shows that the proximity of the chloride ion to C-2 in the transition state causes the 1,2·addition product to form more rapidly than the 1,4-addition product.
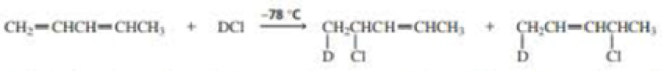
- a. Why was it important for the investigators to know that the preceding reaction was being carried out under kinetic control?
- b. How could the investigators know that the reaction was being carried out under kinetic control?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The table includes macrostates characterized by 4 energy levels (&) that are
equally spaced but with different degrees of occupation.
a) Calculate the energy of all the macrostates (in joules). See if they all have
the same energy and number of particles.
b) Calculate the macrostate that is most likely to exist. For this macrostate,
show that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann
distribution.
macrostate 1 macrostate 2 macrostate 3
ε/k (K) Populations
Populations
Populations
300
5
3
4
200
7
9
8
100
15
17
16
0
33
31
32
DATO: k = 1,38×10-23 J K-1
Don't used Ai solution
In an experiment, the viscosity of water was measured at different
temperatures and the table was constructed from the data obtained.
a) Calculate the activation energy of viscous flow (kJ/mol).
b) Calculate the viscosity at 30°C.
T/°C
0
20
40
60
80
η/cpoise 1,972 1,005 0,656 0,469 0,356
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 3PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 6PCh. 8.6 - a. Predict the relative bond lengths of the three...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 8PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 10PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger acid?Ch. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger base? a....Ch. 8.9 - Rank the following compounds from strongest acid...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.10 - Which acid in each of the following pairs is...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 29PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 30PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 31PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 32PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 33PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 34PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 35PCh. 8.13 - What are the major 1,2- and 1,4-addition products...Ch. 8.13 - Prob. 38PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 39PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 40PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 41PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 42PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 43PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 44PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.15 - Prob. 47PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 48PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 49PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 50PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 53PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 54PCh. 8.19 - Prob. 55PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 56PCh. 8.20 - What orbitals contain the electrons represented as...Ch. 8.20 - Prob. 59PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - Prob. 65PCh. 8 - Prob. 66PCh. 8 - Prob. 67PCh. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Prob. 69PCh. 8 - Prob. 70PCh. 8 - Prob. 71PCh. 8 - Prob. 72PCh. 8 - Prob. 73PCh. 8 - Which compound is the strongest base?Ch. 8 - Prob. 75PCh. 8 - Prob. 76PCh. 8 - a. The A ring (Section 3.16) of cortisone (a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 78PCh. 8 - Prob. 79PCh. 8 - Prob. 80PCh. 8 - Prob. 81PCh. 8 - Purine is a heterocyclic compound with four...Ch. 8 - Prob. 83PCh. 8 - Why is the delocalization energy of pyrrole (21...Ch. 8 - Prob. 85PCh. 8 - Prob. 86PCh. 8 - Prob. 87PCh. 8 - A student obtained two products from the reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 89PCh. 8 - a. How could each of the following compounds be...Ch. 8 - Draw the products obtained from the reaction of...Ch. 8 - How would the following substituents affect the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 93PCh. 8 - The acid dissociation constant (Ka) for loss of a...Ch. 8 - Protonated cyclohexylamine has a Ka = 1 1011...Ch. 8 - Draw the product or products that would be...Ch. 8 - Prob. 97PCh. 8 - Prob. 98PCh. 8 - Prob. 99PCh. 8 - Prob. 100PCh. 8 - Prob. 101PCh. 8 - a. Propose n mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 8 - Prob. 103PCh. 8 - As many as 18 different Diels-Alder products can...Ch. 8 - Prob. 105PCh. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - Prob. 107PCh. 8 - Prob. 108PCh. 8 - The experiment shown next and discussed in Section...Ch. 8 - Prob. 110PCh. 8 - Prob. 111PCh. 8 - Prob. 112PCh. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - Prob. 2PCh. 8 - Prob. 3PCh. 8 - Prob. 4PCh. 8 - Prob. 5PCh. 8 - Prob. 6PCh. 8 - Prob. 7PCh. 8 - Prob. 8PCh. 8 - Prob. 9PCh. 8 - Prob. 10PCh. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - Prob. 12P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forward
- A laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardThe number of microstates corresponding to each macrostate is given by N. The dominant macrostate or configuration of a system is the macrostate with the greatest weight W. Are both statements correct?arrow_forwardFor the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License