
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 8.14, Problem 40P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
- The product of the given Diels-Alder reaction has to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Diels-Alder reaction:
A conjugated diene reacts with a compound containing a carbon-carbon double bond. It is a cycloaddition reaction, where two reactants form a cyclic product.
Rule: The stabilities of carbocation are,
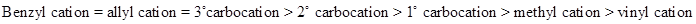
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
9. compore the Following two Venctions IN
termy Of Ronction Rate and explan in
detail the reasoning that led to your conclusion
+He p₁₂ 11-
ㅐ 15
.. +He
H #H
H
/
H
b. Compare
the Following too reactions 14
terms of reaction Rate and explain in detail
the reasoning that led to your conclusion
Н
d-C-
tłu
Na
+2446
е
-ll +2n
"H
a.
•Write all of the possible products
For the Following ronction
А
-----
H
-
H
H
+ H₂0 H+
Н
b. in Rite the complete reaction Mechaniszn
For the Formation of each product.
·C. Suggest what Reaction conditions could
Result in each product being the major
Product of the veaction:
a. Write the product For each of the
Following reactions
H
6-836-6
레
+H₂ N
A
H
A-C-C=C-C-CH + 2 Na +2 NH3 -
H H
b. Write the reaction Mechanism For.
reaction
each
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 3PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 6PCh. 8.6 - a. Predict the relative bond lengths of the three...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 8PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 10PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger acid?Ch. 8.9 - Which member of each pair is the stronger base? a....Ch. 8.9 - Rank the following compounds from strongest acid...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.10 - Which acid in each of the following pairs is...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 29PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 30PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 31PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 32PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 33PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 34PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 35PCh. 8.13 - What are the major 1,2- and 1,4-addition products...Ch. 8.13 - Prob. 38PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 39PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 40PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 41PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 42PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 43PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 44PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.15 - Prob. 47PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 48PCh. 8.17 - Prob. 49PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 50PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 53PCh. 8.18 - Prob. 54PCh. 8.19 - Prob. 55PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 56PCh. 8.20 - What orbitals contain the electrons represented as...Ch. 8.20 - Prob. 59PCh. 8.20 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - Prob. 65PCh. 8 - Prob. 66PCh. 8 - Prob. 67PCh. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Prob. 69PCh. 8 - Prob. 70PCh. 8 - Prob. 71PCh. 8 - Prob. 72PCh. 8 - Prob. 73PCh. 8 - Which compound is the strongest base?Ch. 8 - Prob. 75PCh. 8 - Prob. 76PCh. 8 - a. The A ring (Section 3.16) of cortisone (a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 78PCh. 8 - Prob. 79PCh. 8 - Prob. 80PCh. 8 - Prob. 81PCh. 8 - Purine is a heterocyclic compound with four...Ch. 8 - Prob. 83PCh. 8 - Why is the delocalization energy of pyrrole (21...Ch. 8 - Prob. 85PCh. 8 - Prob. 86PCh. 8 - Prob. 87PCh. 8 - A student obtained two products from the reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 89PCh. 8 - a. How could each of the following compounds be...Ch. 8 - Draw the products obtained from the reaction of...Ch. 8 - How would the following substituents affect the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 93PCh. 8 - The acid dissociation constant (Ka) for loss of a...Ch. 8 - Protonated cyclohexylamine has a Ka = 1 1011...Ch. 8 - Draw the product or products that would be...Ch. 8 - Prob. 97PCh. 8 - Prob. 98PCh. 8 - Prob. 99PCh. 8 - Prob. 100PCh. 8 - Prob. 101PCh. 8 - a. Propose n mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 8 - Prob. 103PCh. 8 - As many as 18 different Diels-Alder products can...Ch. 8 - Prob. 105PCh. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - Prob. 107PCh. 8 - Prob. 108PCh. 8 - The experiment shown next and discussed in Section...Ch. 8 - Prob. 110PCh. 8 - Prob. 111PCh. 8 - Prob. 112PCh. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - Prob. 2PCh. 8 - Prob. 3PCh. 8 - Prob. 4PCh. 8 - Prob. 5PCh. 8 - Prob. 6PCh. 8 - Prob. 7PCh. 8 - Prob. 8PCh. 8 - Prob. 9PCh. 8 - Prob. 10PCh. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - Prob. 12P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning