
Concept explainers
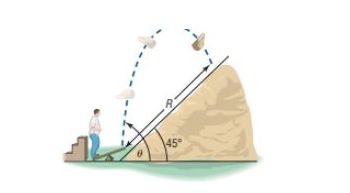
Projectile Motion An object is propelled upward at an angle , to the horizontal with an initial velocity feet per second from the base of a plane that makes an angle of with the horizontal. See the illustration. If air resistance is ignored, the distance that it travels up the inclined plane is given by the function
Show that
In calculus, you will be asked to find the angle that maximizes by solving the equation
solve the equation for .
What is the maximum distance if feet per second?
Graph , and find the angle that maximizes the distance . Also find the maximum distance. Use feet per second. Compare the results with the answers found in parts (b) and (c).
To show:
a.
Answer to Problem 97AYU
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is propelled upward at an angle , , to the horizontal with an initial velocity of feet per second from the base of a plane that makes an angle of with the horizontal. See the illustration. If air resistance is ignored, the distance that it travels up the inclined plane is given by the function .

Calculation:
a.
To show:
b. In calculus, you will be asked to find the angle that maximizes by solving the equation . Solve this equation for .
Answer to Problem 97AYU
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is propelled upward at an angle , , to the horizontal with an initial velocity of feet per second from the base of a plane that makes an angle of with the horizontal. See the illustration. If air resistance is ignored, the distance that it travels up the inclined plane is given by the function .

Calculation:
b.
To show:
c. What is the maximum distance if feet per second?
Answer to Problem 97AYU
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is propelled upward at an angle , , to the horizontal with an initial velocity of feet per second from the base of a plane that makes an angle of with the horizontal. See the illustration. If air resistance is ignored, the distance that it travels up the inclined plane is given by the function .

Calculation:
c.
To show:
d. Graph , and find the angle that maximizes the distance . Also find the maximum distance. Use feet per second. Compare the results with the answers found in parts (b) and (c).
Answer to Problem 97AYU
d.

Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is propelled upward at an angle , , to the horizontal with an initial velocity of feet per second from the base of a plane that makes an angle of with the horizontal. See the illustration. If air resistance is ignored, the distance that it travels up the inclined plane is given by the function .

Calculation:
d.

Chapter 7 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- 1. A bicyclist is riding their bike along the Chicago Lakefront Trail. The velocity (in feet per second) of the bicyclist is recorded below. Use (a) Simpson's Rule, and (b) the Trapezoidal Rule to estimate the total distance the bicyclist traveled during the 8-second period. t 0 2 4 6 8 V 10 15 12 10 16 2. Find the midpoint rule approximation for (a) n = 4 +5 x²dx using n subintervals. 1° 2 (b) n = 8 36 32 28 36 32 28 24 24 20 20 16 16 12 8- 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 12 8 4 1 2 3 4 5 6arrow_forward= 5 37 A 4 8 0.5 06 9arrow_forwardConsider the following system of equations, Ax=b : x+2y+3z - w = 2 2x4z2w = 3 -x+6y+17z7w = 0 -9x-2y+13z7w = -14 a. Find the solution to the system. Write it as a parametric equation. You can use a computer to do the row reduction. b. What is a geometric description of the solution? Explain how you know. c. Write the solution in vector form? d. What is the solution to the homogeneous system, Ax=0?arrow_forward
- 2. Find a matrix A with the following qualities a. A is 3 x 3. b. The matrix A is not lower triangular and is not upper triangular. c. At least one value in each row is not a 1, 2,-1, -2, or 0 d. A is invertible.arrow_forwardFind the exact area inside r=2sin(2\theta ) and outside r=\sqrt(3)arrow_forwardA 20 foot ladder rests on level ground; its head (top) is against a vertical wall. The bottom of the ladder begins by being 12 feet from the wall but begins moving away at the rate of 0.1 feet per second. At what rate is the top of the ladder slipping down the wall? You may use a calculator.arrow_forward
- Explain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forwarduse Cauchy Mean-Value Theorem to derive Corollary 12.6.2, and then derive 12.6.3arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





