
Concept explainers
Projectile Motion The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air resistance) is given by the equation
where is the initial velocity of the projectile, is the angle of elevation, and is acceleration due to gravity ( meters per second squared).
a. If you can throw a baseball with an initial speed of meters per second, at what angle of elevation should you direct the throw so that the ball travels a distance of 107 meters before striking the ground?
b. Determine the maximum distance that you can throw the ball.
c. Graph , with meters per second.
d. Verify the results obtained in parts (a) and (b) using a graphing utility.
To find:
a. If you can throw a baseball with an initial speed of meters per second, at what angle of elevation should you direct the throw so that the ball travels a distance of 107 meters before striking the ground?
Answer to Problem 109AYU
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air resistance) is given by the equation
where is the initial velocity of the projectile, is the angle of elevation, and is acceleration due to gravity ( meters per second squared).
Calculation:
a.
To find:
b. Determine the maximum distance that you can throw the ball.
Answer to Problem 109AYU
b. m.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air resistance) is given by the equation
where is the initial velocity of the projectile, is the angle of elevation, and is acceleration due to gravity ( meters per second squared).
Calculation:
b. Maximum range .
To find:
c. Graph , with meters per second.
Answer to Problem 109AYU
c.
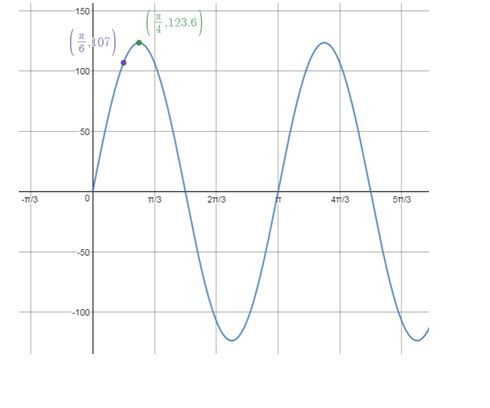
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air resistance) is given by the equation
where is the initial velocity of the projectile, is the angle of elevation, and is acceleration due to gravity ( meters per second squared).
Calculation:
c.

To find:
d. Verify the results obtained in parts (a) and (b) using a graphing utility.
Answer to Problem 109AYU
The results of (a) and (b) verified in (c).
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air resistance) is given by the equation
where is the initial velocity of the projectile, is the angle of elevation, and is acceleration due to gravity ( meters per second squared).
Calculation:
d. The results of (a) and (b) verified in (c).
Chapter 7 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
- a -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forwardEvaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forward
- I need help in ensuring that I explain it propleryy in the simplifest way as possiblearrow_forwardI need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





