
(a)
Interpretation: The explanation for poor nucleophilicity of the solvent should be suggested.
Concept introduction:Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from
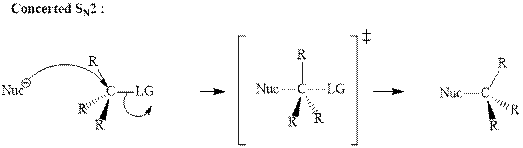
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

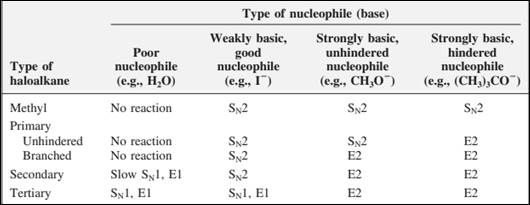
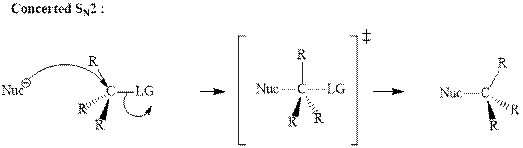
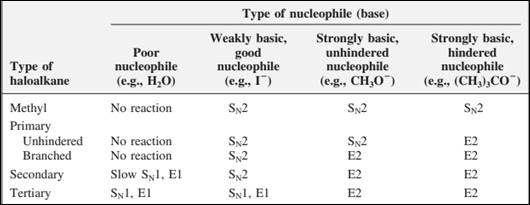
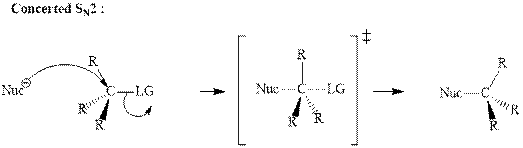
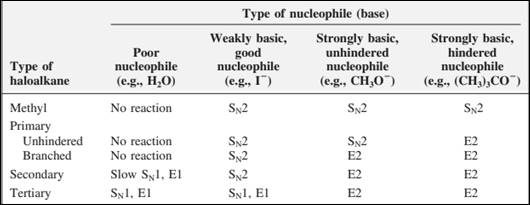
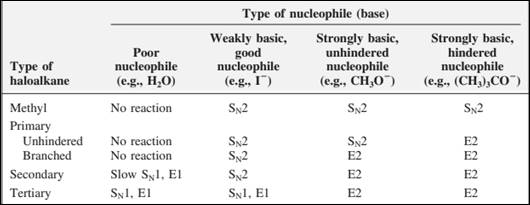
The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The relative rates of the two steps should be found and compared to usual
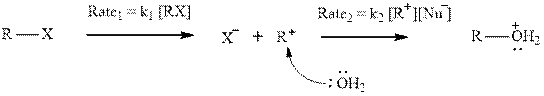
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The manner carbocation stability and decreasing solvent nucleophilicity might affect the relative magnitudes of
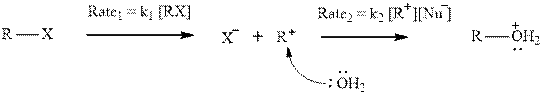
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(d)
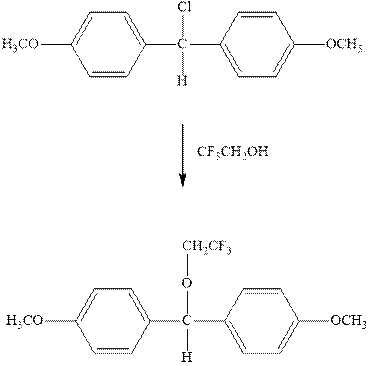
Interpretation: The complete mechanism for the indicated reaction should be written.
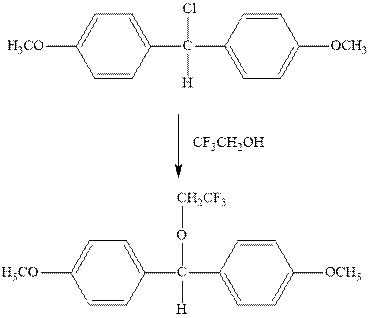
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- (10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward
- Q3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forwardQ5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardQ4: Circle the substrate that gives a single alkene product in a E2 elimination. CI CI Br Brarrow_forward
- Please calculate the chemical shift of each protonsarrow_forwardQ1: Answer the questions for the reaction below: ..!! Br OH a) Predict the product(s) of the reaction. b) Is the substrate optically active? Are the product(s) optically active as a mix? c) Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. d) What happens to the SN1 reaction rate in each of these instances: 1. Change the substrate to Br 'CI 2. Change the substrate to 3. Change the solvent from 100% CH3CH2OH to 10% CH3CH2OH + 90% DMF 4. Increase the substrate concentration by 3-fold.arrow_forwardQ6: Provide the reagents and conditions for the following reactions to make the product with a good yield. Br Br CI она CIarrow_forward
- Q2: We would not expect the following primary alkyl halide to go through an SN1 reaction. However, it can go through an SN1 mechanism. Explain why. Hint: Think about what happens when the leaving group leaves. CI NaO EtOH H བྱིས་ Harrow_forwardI performed this experiment, but I'm so confused. How do I find the first two blank columns using the data provided. What is the [I^-] mol/L and [S2O8^-2] mol/L. How do I find this? Please help!arrow_forwardExample 3 A molecule is achiral if it has a plane of symmetry in any conformation. The given conformation of 2,3-dibromobutane below does not have a plane of symmetry. Will rotation around the C2-C3 bond form a conformation with a plane of symmetry? Draw the conformation to find out. DIY: Do the same for: H3C Brill rotate H CH3 OH HO Brarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

