
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products of the following reaction should be drawn along with the mechanism for the formation. Whether the given transformation is faster in polar, aprotic solvent in comparison to polar, protic solvent should be determined.
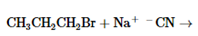
Concept Introduction:
The
The chemical reaction in which displacement of leaving group occurs by a nucleophile is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction between nucleophile (electron pair donor) and electrophile (electron pair acceptor) is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is classified as SN1 and SN2 reaction.
The solvents which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds due to the presence of at least one hydrogen linked with electronegative atom is known as polar protic solvents whereas the solvents in which no hydrogen atoms are linked with electronegative atom and also incapable of hydrogen bonding is known as
(b)
Interpretation:
The products of the following reaction should be drawn along with the mechanism for the formation. Whether the given transformation is faster in polar, aprotic solvent in comparison to polar, protic solvent should be determined.
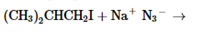
Concept Introduction:
The chemical reaction in which one functional group is substituted by another functional group is known as substitution reaction.
The chemical reaction in which displacement of leaving group occurs by a nucleophile is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction between nucleophile (electron pair donor) and electrophile (electron pair acceptor) is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is classified as SN1 and SN2 reaction.
The solvents which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds due to the presence of at least one hydrogen linked with electronegative atom is known as polar protic solvents whereas the solvents in which no hydrogen atoms are linked with electronegative atom and also incapable of hydrogen bonding is known as polar aprotic solvents
(c)
Interpretation:
The products of the following reaction should be drawn along with the mechanism for the formation. Whether the given transformation is faster in polar, aprotic solvent in comparison to polar, protic solvent should be determined.
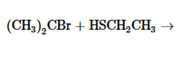
Concept Introduction:
The chemical reaction in which one functional group is substituted by another functional group is known as substitution reaction.
The chemical reaction in which displacement of leaving group occurs by a nucleophile is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction between nucleophile (electron pair donor) and electrophile (electron pair acceptor) is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is classified as SN1 and SN2 reaction.
The solvents which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds due to the presence of at least one hydrogen linked with electronegative atom is known as polar protic solvents whereas the solvents in which no hydrogen atoms are linked with electronegative atom and also incapable of hydrogen bonding is known as polar aprotic solvents
(d)
Interpretation:
The products of the following reaction should be drawn along with the mechanism for the formation. Whether the given transformation is faster in polar, aprotic solvent in comparison to polar, protic solvent should be determined.

Concept Introduction:
The chemical reaction in which one functional group is substituted by another functional group is known as substitution reaction.
The chemical reaction in which displacement of leaving group occurs by a nucleophile is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction between nucleophile (electron pair donor) and electrophile (electron pair acceptor) is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is classified as SN1 and SN2 reaction.
The solvents which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds due to the presence of at least one hydrogen linked with electronegative atom is known as polar protic solvents whereas the solvents in which no hydrogen atoms are linked with electronegative atom and also incapable of hydrogen bonding is known as polar aprotic solvents
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. (CH3)2NH, TSOH Drawingarrow_forwardSo, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
- Drawing of 3-fluro-2methylphenolarrow_forwardWhich compound(s) will be fully deprotonated (>99%) by reaction with one molar equivalent of sodium hydroxide? I, II, III I, || I, III I only II, III SH | H3C-C=C-H || III NH2arrow_forwardWill NBS (and heat or light) work for this reaction, or do we have to use Br2?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

