
(a)
Interpretation: The products formed due to elimination and most likely mechanism for below reaction should be written.
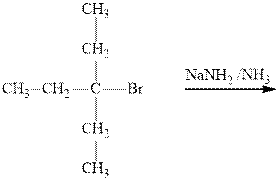
Concept introduction: Carbocations generated from
If the leaving group present eliminates along with a proton in absence of any strong nucleophile the double bond formation might occur. Such reactions are known as two-step unimolecuar elimination, abbreviated as
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed due to elimination and most likely mechanism for below reaction should be written.
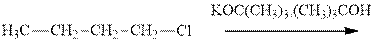
Concept introduction: Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
If the leaving group present eliminates along with a proton in absence of any strong nucleophile the double bond formation might occur. Such reactions are known as two-step unimolecuar elimination, abbreviated as
(c)
Interpretation: The products formed due to elimination and most likely mechanism for below reactionshould be written.
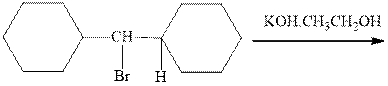
Concept introduction: Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
If the leaving group present eliminates along with a proton in absence of any strong nucleophile the double bond formation might occur. Such reactions are known as two-step unimolecuar elimination, abbreviated as
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed due to elimination and most likely mechanism should be written.
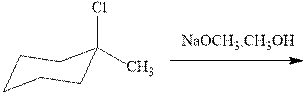
Concept introduction: Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
If the leaving group present eliminates along with a proton in absence of any strong nucleophile the double bond formation might occur. Such reactions are known as two-step unimolecuar elimination, abbreviated as
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Part I. Draw the stepwise reaction mechanism of each product (a, b, c, d, e, f) HO HO OH НОН,С HO OH Sucrose HO CH₂OH H N N HO -H H -OH KMnO4, Heat H OH CH₂OH (d) Phenyl Osatriazole OH НОН,С HO HO + Glacial HOAC HO- HO CH₂OH OH HO Fructose (a) Glucose OH (b) H₂N HN (c) CuSO4-5H2O, ethanol H N N N HO ·H H OH H OH N CH₂OH OH (f) Phenyl Osazone H (e) Carboxy phenyl osatriazole Figure 2.1. Reaction Scheme for the Total Synthesis of Fine Chemicalsarrow_forwardWhich molecule is the most stable? Please explain.arrow_forwardPlease see photoarrow_forward
- Blocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see image **NOTE: The compound on the left is the starting point, and the compound on the right is the final product. Please show the steps in between to get from start to final, please. These are not two different compounds that need to be worked.arrow_forwardI dont understand this.arrow_forwardCan you please explain this prooblem to me, show me how the conjugation is added, did I add them in the correct places and if so please show me. Thanks!arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




