
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between X and
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
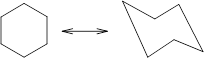
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
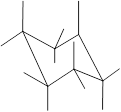
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(b)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between X and Z group needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
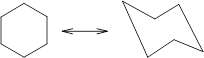
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
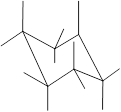
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(c)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between Y and Z group needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
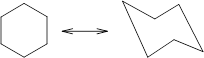
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
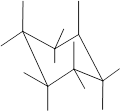
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(d)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
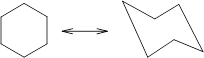
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
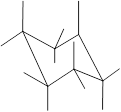
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(e)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between Z and
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
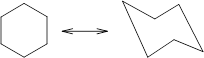
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
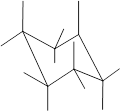
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(f)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between Z and
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
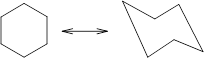
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
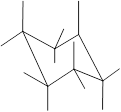
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(g)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between Y and
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
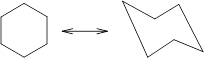
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
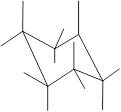
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
(h)
Interpretation: In the given structure, the relationship between
Concept Introduction: Chair conformation is the most stable conformation of cyclohexane. It is represented as follows:
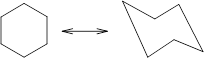
Here, the substituted groups in the chair conformation are represented as follows:
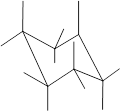
The groups showing in straight upward and downward directions are axial and the groups bend slightly right or left are equatorial.
In the chair conformation of the cyclohexane, if two groups are pointing in same direction, it is cis conformation and if the two groups are pointing in opposite direction then it is trans conformation.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Can I please get help with this question. All required information should be in data table.arrow_forwardesc For the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. Major Product: Explanation Check C ☐ + X NaOH Br F1 F2 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 1 ! @ 2 3 $ 4 % 5 Q W LU E S D A F7 * C Click and dr drawing a 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserv ►II F8 4 F9 6 7 8 9 R T Y U LL F G H Jarrow_forwardCalculate equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction:N2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇋ 2 NO (g) Kc = 0.10 at 2273K initially [N2] = 0.200M; [O2] = 0.200arrow_forward
- For each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forwardThe following reaction is run in which the initial conditions include only methane (CH4) at a concentration of0.115 M. Once equilibrium was established, the concentration of acetylene (C2H2) was measured to be 0.035M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K?2 CH4 (g) ⇋ C2H2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)arrow_forwardCalculate the equilibrium concentration of carbon dioxide for the following reaction:2 COF2 (g) ⇋ CF4 (g) + CO2 (g) Kc = 2.00 at 10.00 °C. at equilibrium [COF2] = 0.255M; [CF4] = 0.118Marrow_forward
- In a benzene derivative that has -CH2CH3, indicate how it can be substituted by -COOH.arrow_forwardIn a sulfonated derivative of benzene, indicate how -SO3H can be eliminated.arrow_forwardWhat is the equilibrium expression (law of mass action) for the following reaction:CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇋ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)arrow_forward
- Indicate the compound resulting from adding NaOH cyclopentane-CH2-CHO.arrow_forwardUse the provided information to calculate Kc for the following reaction at 550 °C: H2(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) Kc = ?CoO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Co(s) + CO2(g) Kc1 = 490CoO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Co(s) + H2O(g) Kc2 = 67arrow_forwardCalculate Kc for the reaction: I2 (g) ⇋ 2 I (g) Kp = 6.26 x 10-22 at 298Karrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

