
Concept explainers
In Problems 33-56, graph each function using transformations or the method of key points. Be sure to label key points and show at least two cycles. Use the graph to determine the domain and the range of each function.
To find: The graph of each function using method of key points. Also find domain and range.
Answer to Problem 54AYU
Domain: Range: .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
If , the amplitude and period of and are given by
Amplitude Period .
Comparing: to , and .
Amplitude .
Period .
Because the amplitude is , the graph of will lie between and on the . Because the period is , one cycle will begin at and end at .
Divide the interval into four subintervals, each of length . The of the five key points are .
To obtain the of the five key points of: , multiply the of the five key points of by . The five key points are
A vertical shift up units gives the graph of .
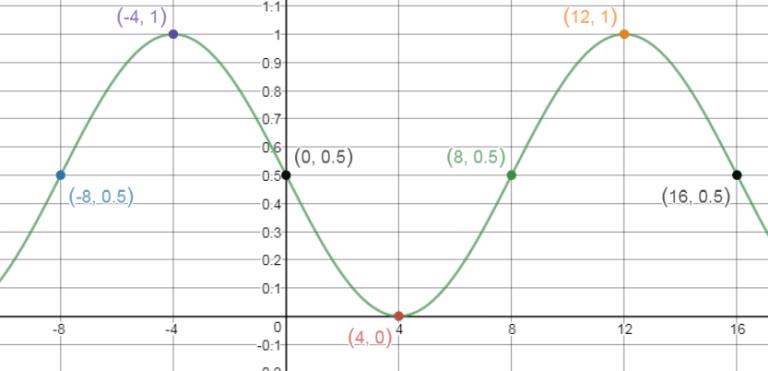
Domain: Range: .
Chapter 6 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Consider the function f(x) = x²-1. (a) Find the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x=1 using the definition of the derivative. Show all your steps clearly. (b) Sketch the graph of f(x) around x = 1. Draw the secant line passing through the points on the graph where x 1 and x-> 1+h (for a small positive value of h, illustrate conceptually). Then, draw the tangent line to the graph at x=1. Explain how the slope of the tangent line relates to the value you found in part (a). (c) In a few sentences, explain what the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = 1 represents in the context of the graph of f(x). How does the rate of change of this function vary at different points?arrow_forward1. The graph of ƒ is given. Use the graph to evaluate each of the following values. If a value does not exist, state that fact. и (a) f'(-5) (b) f'(-3) (c) f'(0) (d) f'(5) 2. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = g(x) at x = 5 if g(5) = −3 and g'(5) = 4. - 3. If an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at the point where x 2 is y = 4x — 5, find ƒ(2) and f'(2).arrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forward
- Suppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forwardLet f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forwardplease do Q3arrow_forward
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





