
Identify the catalyst in each equation.
a.
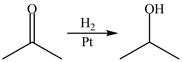
b.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaH (20°C) 2. CH3Br ? Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G Crarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardPlease draw the structuresarrow_forward
- Draw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forward
- What is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





