
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between
(a)
Answer to Problem 6.134EP
Carboxylic acid that is required was,
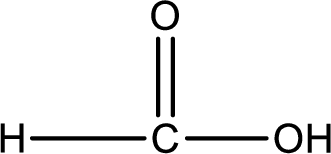
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
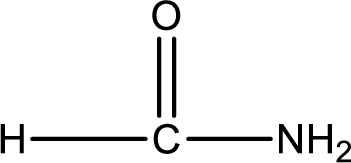
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The “parent” carboxylic acid can be identified as shown below,
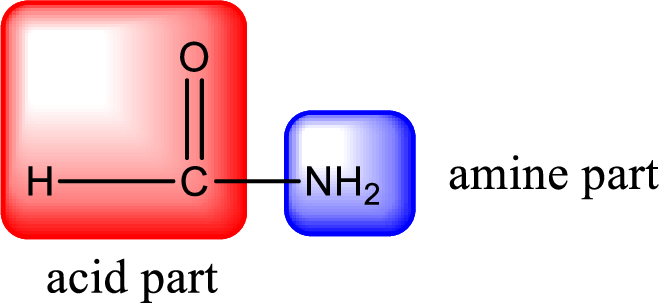
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
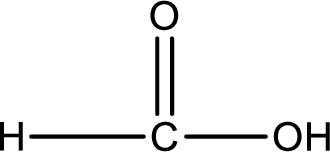
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(b)
Answer to Problem 6.134EP
Carboxylic acid that is required was,
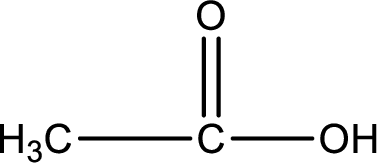
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
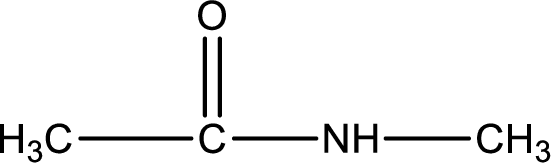
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The “parent” carboxylic acid can be identified as shown below,
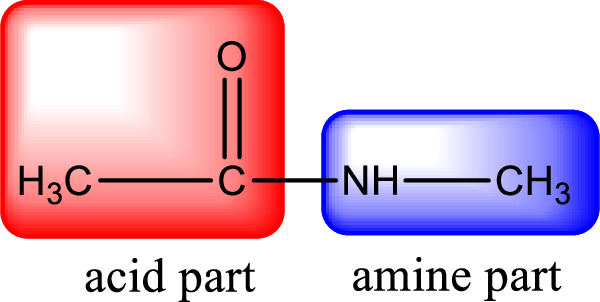
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
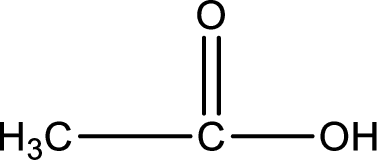
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(c)
Answer to Problem 6.134EP
Carboxylic acid that is required was,
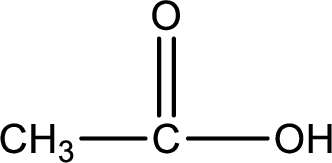
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
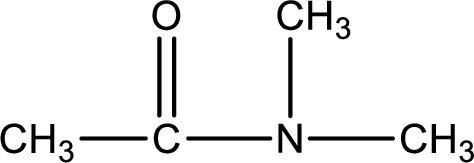
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The “parent” carboxylic acid can be identified as shown below,
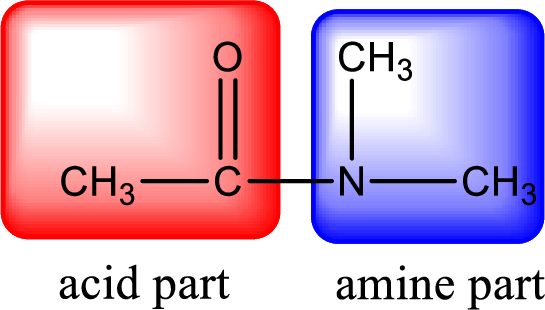
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
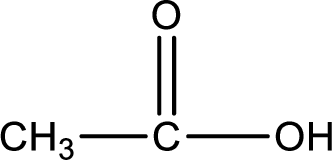
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(d)
Answer to Problem 6.134EP
Carboxylic acid that is required was,
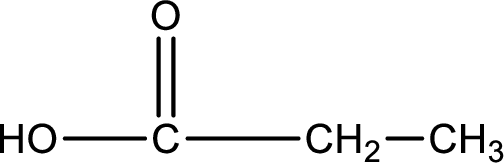
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
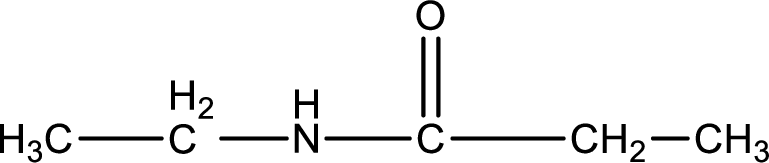
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The “parent” carboxylic acid can be identified as shown below,
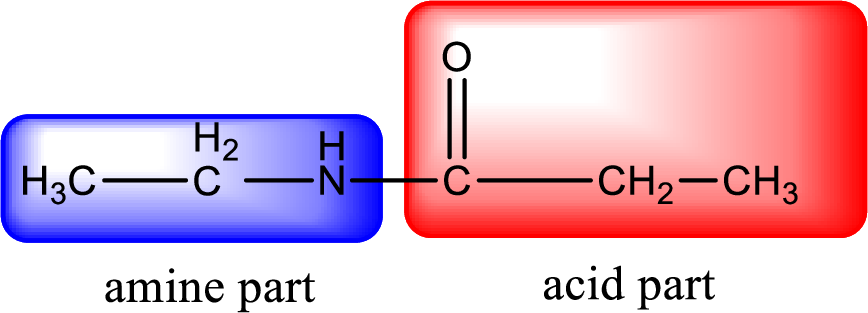
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
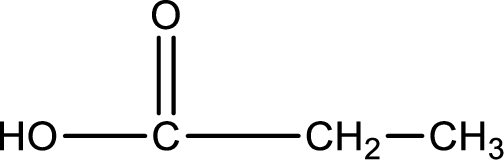
Structure of carboxylic acid that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forward35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward21) The rate of reaction depends upon: a. the concentration and nature of reactants b. the temperature of the reaction C. whether or not a catalyst was used d. all of the above 22) A Maxwell-Boltzmann curve shows the distribution of molecular energies in a reaction system. When the temperature in this system is increased, the peak is a. higher and further to the right. b. higher and further to the left. c. lower and further to the right. d. lower and further to the left. 23) Which of the following correctly describes the reaction represented by the reaction below? CaCO3 (s) + energy → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) a. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the reactants than the products. b. c. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. It is endothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. d. It is endothermic and the potential energy is equal for the products and reactants.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



