
(a)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
Concept Introduction:
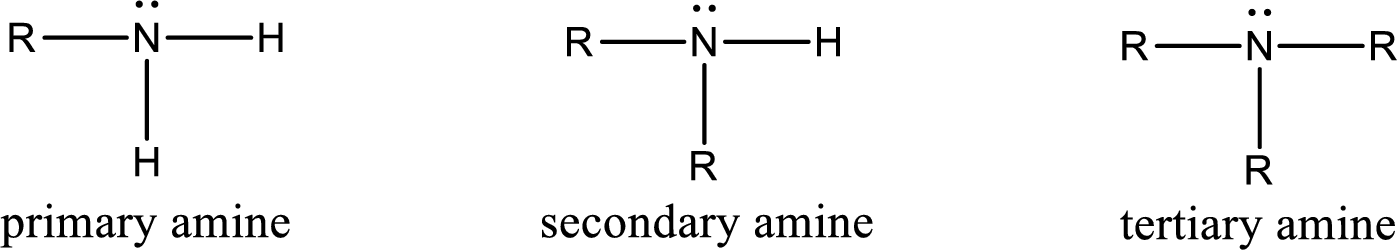
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
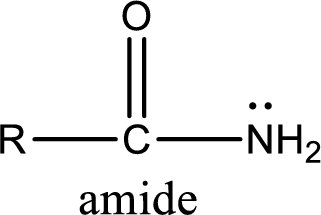
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
Concept Introduction:
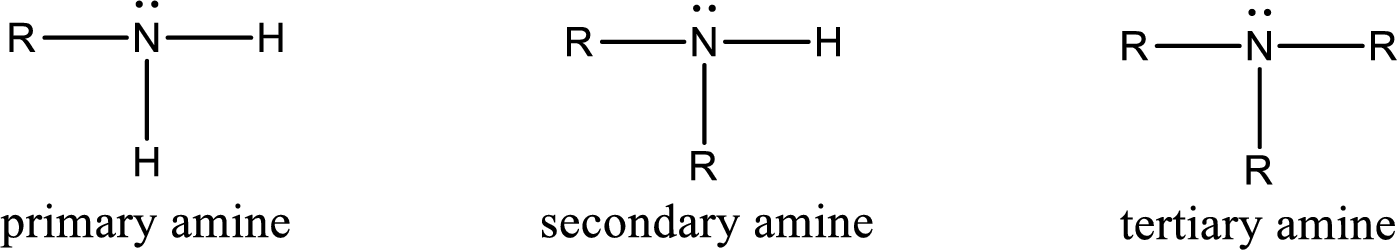
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
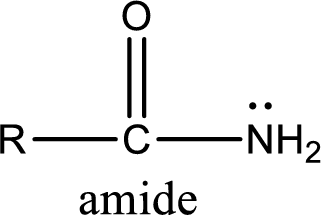
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
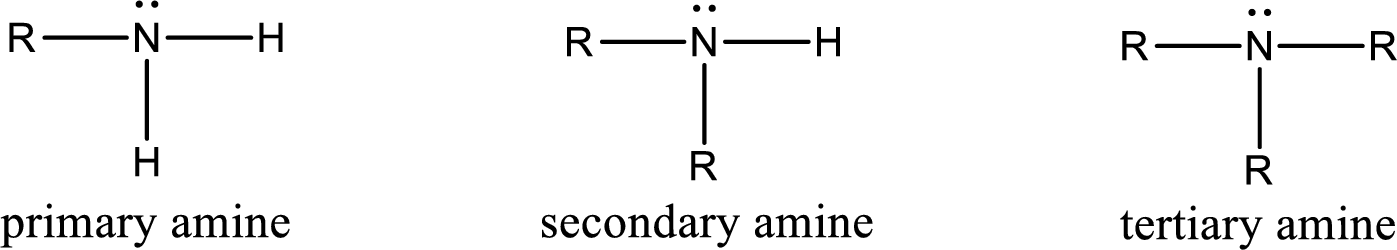
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
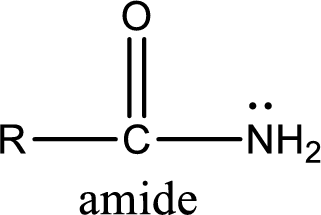
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
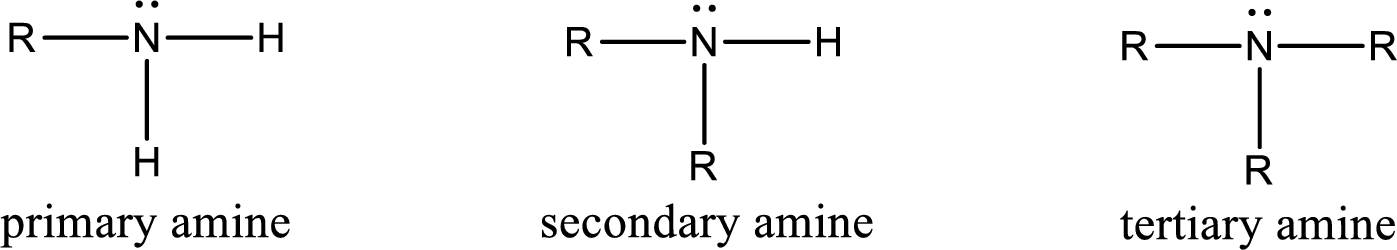
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
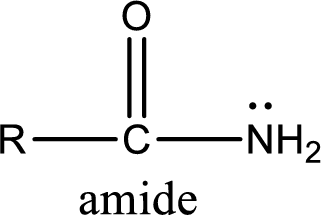
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forwardIndicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



