
Interpretation:
The products of the given reactions have to be determined and if the products can exist as stereoisomers, then those have to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of phi bonds between carbon-carbon multiple bonds and addition of alcohol to more substituted position of carbon in the molecule.
First step is the acid donates proton to the alkene which leads to the formation of more stable carbo cation.
Then, the water is added to the given alkene through acid catalyzed reaction where the water gets added to the carbo cation finally, the removal of one proton from oxonium ion (oxygen with one positive charge) using water results in the formation of product.
Halogen addition to an alkene:
The addition reaction of halides to
Mainly
In general, the reaction can be shown as below.
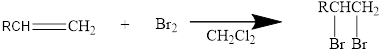
When the bromine approaches the alkene, one bromine accepts the electrons from alkene and give them to the other bromine and a cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed.
The formed unstable intermediate reacts with
Lindlar reduction: The alkenes or
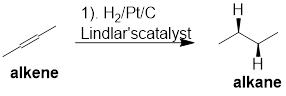
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- Draw the principal organic product of the following reaction.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided structures, draw the curved arrows that epict the mechanistic steps for the proton transfer between a hydronium ion and a pi bond. Draw any missing organic structures in the empty boxes. Be sure to account for all lone-pairs and charges as well as bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 2 56°F Mostly cloudy F1 Drawing Arrows > Q Search F2 F3 F4 ▷11 H. H : CI: H + Undo Reset Done DELLarrow_forwardCalculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbons. Draw out the benzene ring structure when doing itarrow_forward
- 1) Calculate the longest and shortest wavelengths in the Lyman and Paschen series. 2) Calculate the ionization energy of He* and L2+ ions in their ground states. 3) Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron emitted upon irradiation of a H-atom in ground state by a 50-nm radiation.arrow_forwardCalculate the ionization energy of He+ and Li²+ ions in their ground states. Thannnxxxxx sirrr Ahehehehehejh27278283-4;*; shebehebbw $+$;$-;$-28283773838 hahhehdvaarrow_forwardPlleeaasseee solllveeee question 3 andd thankss sirr, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee don't use AIarrow_forward
- Calculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseeearrow_forward
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

