
(a)
Interpretation:
The products for the given reactions should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds that results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
The curved arrows are generally used to indicate the flow of electrons present in the reaction.
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Oxidizing Reagents: The chemical agents used to add oxygen or remove hydrogen to other compound which finally reduced on oxidizing the other compound.
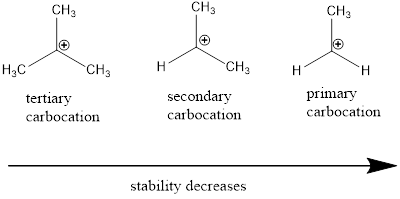
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given two reactions the one with higher free energy activation should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Free energy activation is the energy difference between the transition state and the ground state of the reactants present in a reaction.
Transition State: The state which defines the highest potential energy with respect to reaction co-ordinate between reactant and product. It is usually denoted by using the symbol ‘≠’.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reactivity for given set of compounds towards
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. and two equivalents of CH2=O draw structure ...arrow_forwardH-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





