
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780133858501
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.10, Problem 16P
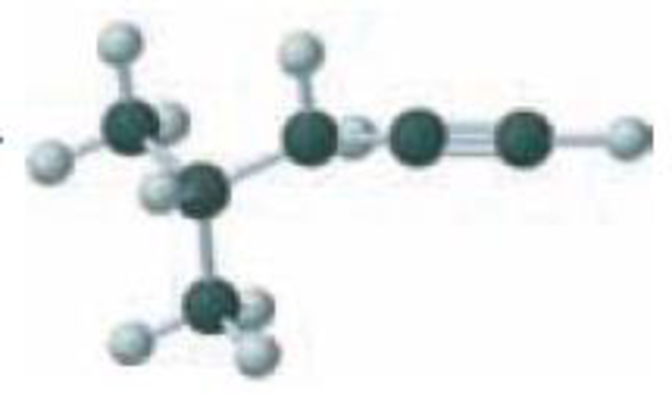
Name the following:

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Assign all the Protons in HNMR
Provide the missing information
HO
NO2
Br2
FeBr3
to
CI
HO
H₂N
NO2
AICI3
Zn(Hg), HCI
1. NBS
2. t-BuONa
1. Br₂, FeBr3
2. CH3CI, AC13
3. Na2Cr2O7
Br
NH2
SO3H
HO
H₂N
Br
Assign the carbon numbered on CNMR
Chapter 6 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
Ch. 6.1 - Draw the mechanism for the reaction of cyclohexene...Ch. 6.2 - a. How many bond orbitals are available for...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 9PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 10PCh. 6.5 - a. What is the major product of each of the...
Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 6.6 - What stereoisomers are obtained from each of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 14PCh. 6.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.10 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 6.10 - Draw the structures for and name the seven alkynes...Ch. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.11 - What hybrid orbitals are used to form the...Ch. 6.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 6.14 - Prob. 23PCh. 6.14 - Which alkyne would be the best one to use for the...Ch. 6.14 - Prob. 25PCh. 6.14 - Prob. 26PCh. 6.15 - Describe the alkyne you would start with and the...Ch. 6.15 - What are products of the following reactions?Ch. 6 - Prob. 29PCh. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - Prob. 32PCh. 6 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - What reagents could be used to carry out the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 37PCh. 6 - Prob. 38PCh. 6 - Prob. 39PCh. 6 - Prob. 40PCh. 6 - Prob. 41PCh. 6 - Prob. 42PCh. 6 - Answer Problem 42 using 2-butyne as the starting...Ch. 6 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 6 - Prob. 45PCh. 6 - Prob. 46PCh. 6 - Prob. 47PCh. 6 - Prob. 48PCh. 6 - Prob. 49PCh. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Draw the keto tautomer for each of the following:Ch. 6 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction...Ch. 6 - Prob. 53PCh. 6 - Prob. 54PCh. 6 - Prob. 55PCh. 6 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 6 - Prob. 57PCh. 6 - Prob. 58PCh. 6 - Prob. 59PCh. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - Prob. 61PCh. 6 - Prob. 62P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 N2H4 (l) + 3 O2(g) > 2 NO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) If 75.0 kg of hydrazine are reacted with 75.0 kg of oxygen, which is the limiting reactant?arrow_forwardPQ-10. What is the major product of this reaction? (A) (C) 930 Me HO O=S=O O-8-CF, C 어 Me H+ OH 270 O 0-5-0 O=S=O O-S-CF CF3 2arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain.arrow_forward
- Q2: Explain why epoxides that react in an SN1 manner will not show any stereochemical inversion in the product. Q3: Rationalize why Alcohol B will react under the indicated reaction conditions, but Alcohol A will not. A ☑ OH B OH PBr3 R-Brarrow_forwardQ1: Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain. 1.) LDA, THF 2.) СОН CI OH H2SO4, heat OH m...... OH 1.) PCC, CH2Cl2 2.) CH3CH2MgBr, THF 3.) H3O+ 4.) TsCl, pyr 5.) tBuOK, tBuOH 1.) SOCI 2, CHCI 3 2.) CH3CH2ONA, DMF OH 1.) HBr 2.) Mg, THF 3.) H₂CO, THE 4.) H3O+ OH NaH, THFarrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reactionarrow_forwardPlease provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown herearrow_forwardProblem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY