
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
In addition reaction of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but differ in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves from a substrate with a pair of electrons via
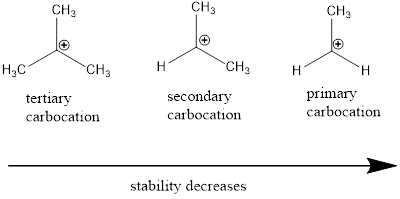
Carbocation stability order:
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation stability order:

(c)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation stability order:

(d)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation stability order:

(e)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation stability order:

(f)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained after reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Carbocation stability order:

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forwardIndicate characteristics of oxodec acid.arrow_forward
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



