
Concept explainers
A producer of inkjet printer is planning to add a new line of printers, and you have been asked to balance the process, given the following task time and precedence relationship. Assume that cycle time is to be the minimum possible.
a. Do each of the following:
(1) Draw the precedence diagram.
(2) Assign tasks to stations in order of most following tasks. Tiebreaker, greatest positional weight.
(3) Determine the percentage of idle time.
(4) Compute the late of output in printers per day that could be expected for that line assuming a 420-minute working day.
b. Answer these questions:
(1) What it the shortest cycle tone that will permit use of only two workstations? Is this cycle time feasible? Identify the tasks you would assign to each station.
(2) Determine the percentage of idle time that would results if two stations were used.
(3) What is the daily output under this arrangement?
(4) Determine the output rate that would be associated with the maximum cycle time.
a) 1
To draw: The precedence diagram.
Answer to Problem 4P
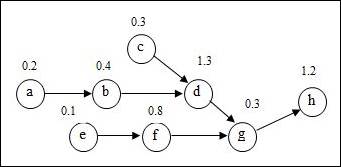
Answer: Precedence diagram:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
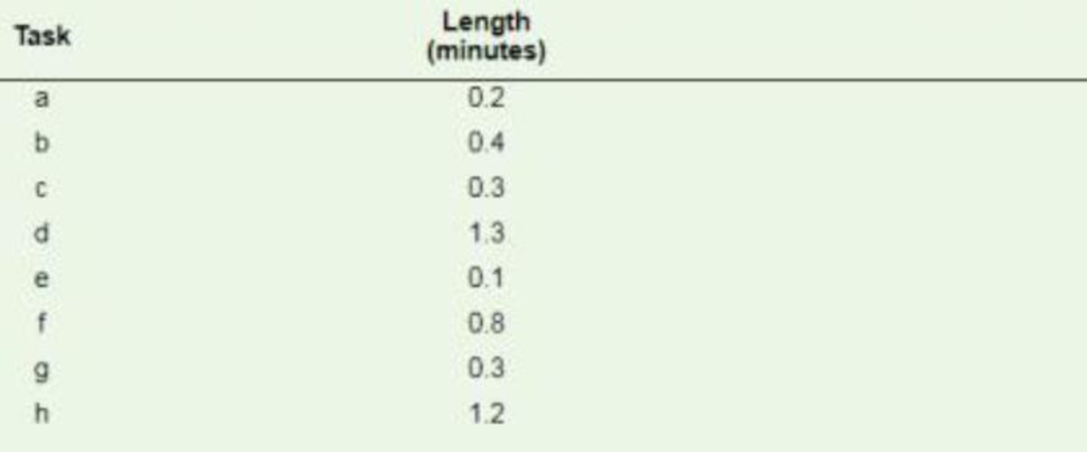
| Task | Length (minutes) | Immediate (Predecessor) |
| a | 0.2 | Nil |
| b | 0.4 | a |
| c | 0.3 | Nil |
| d | 1.3 | b, c |
| e | 0.1 | Nil |
| f | 0.8 | e |
| g | 0.3 | d, f |
| h | 1.2 | g |
Precedence diagram:

The precedence diagram is drawn circles and arrows. The tasks are represented in circles and weights for each task are represented outside the circle. The arrows are represented to show which task is preceding the other task and so on.
2)
To assign: Tasks to workstations in the order of most following tasks.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Task | Length (minutes) | Immediate (Predecessor) |
| a | 0.2 | Nil |
| b | 0.4 | a |
| c | 0.3 | Nil |
| d | 1.3 | b, c |
| e | 0.1 | Nil |
| f | 0.8 | e |
| g | 0.3 | d, f |
| h | 1.2 | g |
The positional weight of a task is the sum of the task times of the task itself and all of the following tasks.
| Task | Following tasks | Number of following tasks | Calculation of positional weight | Positional weight |
| a | b, d, g, h | 4 | 0.2 + 0.4 + 1.3 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 3.4 |
| b | d, g, h | 3 | 0.4 + 1.3 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 3.2 |
| c | d, g, h | 3 | 0.3 + 1.3 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 3.1 |
| d | g, h | 2 | 1.3 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 2.8 |
| e | f, g, h | 3 | 0.1 + 0.8 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 2.4 |
| f | g, h | 2 | 0.8 + 0.3 + 1.2 | 2.3 |
| g | h | 1 | 0.3 + 1.2 | 1.5 |
| h | Nil | 0 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
Calculation of cycle time:
The cycle is said to be the minimum time possible.
Therefore, the cycle time is 1.3 minutes / unit.
Assigning tasks to workstations:
| Workstation number | Eligible task | Assigned task | Task time | Unassigned cycle time | Reason |
| 1.3 | |||||
| 1 | a, c, e | a | 0.2 | 1.1 | Task 'a' has more number of following tasks |
| b, c , e | b | 0.4 | 0.7 | Task 'b' has greatest positional weight | |
| c, e | c | 0.3 | 0.4 | Task 'c' has greatest positional weight | |
| d, e | e | 0.1 | 0.3 | Task 'e' has greatest positional weight | |
| d, f | None | 0.3 (Idle time) | The task time is greater than the unassigned cycle time. | ||
| 1.3 | |||||
| 2 | d, f | d | 1.3 | 0 | Task 'd' has greatest positional weight |
| 1.3 | |||||
| 3 | f | f | 0.8 | 0.5 | Task 'f' is the only eligible task available |
| g | g | 0.3 | 0.2 | Task 'g' is the only eligible task available | |
| h | None | 0.2 (Idle time) | The task time is greater than the unassigned cycle time. | ||
| 1.3 | |||||
| 4 | h | h | 1.2 | 0.1 | Task 'h' is the only task remaining |
| 0.1 (Idle time) | All tasks completed |
Overview of tasks assignment:
| Workstation | Assigned tasks | Total cycle time used | Idle time |
| 1 | a, b, c, e | 1 | 0.3 |
| 2 | d | 1.3 | 0 |
| 3 | f, g | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| 4 | h | 1.2 | 0.1 |
3)
To determine: The percentage of idle time.
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate percentage of idle time:
Calculation of percentage of idle time:
The percentage of idle time is 11.54%.
4)
To determine: The rate of output printers per day.
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Operating time per day = 420 minutes
Formula to calculate output printers per day:
Calculation of output printers per day:
The rate of output printers per day is 323.08 printers / day.
b) 1
To determine: The shortest cycle time that will permit the use of only 2 workstations and to check if it is feasible.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Task | Length (minutes) | Immediate (Predecessor) |
| a | 0.2 | Nil |
| b | 0.4 | a |
| c | 0.3 | Nil |
| d | 1.3 | b, c |
| e | 0.1 | Nil |
| f | 0.8 | e |
| g | 0.3 | d, f |
| h | 1.2 | g |
Calculation of shortest cycle time:
The shortest cycle time is calculated by summing all the task times and dividing the resultant value by 2 workstations.
The obtained shortest cycle time is feasible based on the task times. Every task time is either equal to or less than 2.3 minutes. The feasibility is checked by assigning the tasks to the 2 workstations.
Assigning tasks to workstations:
| Workstation number | Eligible task | Assigned task | Task time | Unassigned cycle time | Reason |
| 2.3 | |||||
| 1 | a, c, e | a | 0.2 | 2.1 | Task 'a' has more number of following tasks |
| b, c , e | b | 0.4 | 1.7 | Task 'b' has greatest positional weight | |
| c, e | c | 0.3 | 1.4 | Task 'c' has greatest positional weight | |
| d, e | e | 0.1 | 1.3 | Task 'e' has more number of following tasks | |
| d, f | d | 1.3 | 0 | Task 'd' has greatest positional weight | |
| 2.3 | |||||
| 2 | f | f | 0.8 | 1.5 | Task 'f' is the only eligible task available |
| g | g | 0.3 | 1.2 | Task 'g' is the only eligible task available | |
| h | h | 1.2 | 1.2 | Task 'h' is the only task available |
Overview of tasks assignment:
| Workstation | Assigned tasks | Total cycle time used | Idle time |
| 1 | a, b, c, e, d | 2.3 | 0 |
| 2 | f, g, h | 2.3 | 0 |
The shortest cycle time of 2.3 minutes is feasible.
2)
To determine: The percentage of idle time.
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate percentage of idle time:
Calculation of percentage of idle time:
The percentage of idle time is 0.00%.
3)
To determine: The daily output under this arrangement.
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Operating time per day = 420 minutes
Formula to calculate output under this arrangement:
Calculation of output under this arrangement:
The rate of output under this arrangement is 182.61 units / day.
4)
To determine: The output rate associated with cycle time.
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Operating time per day = 420 minutes
Formula to calculate output under this arrangement:
Calculation of output under this arrangement:
The maximum cycle time is the sum of all task times.
The sum of all task times is:
The rate of output under this arrangement is 91.30 units / day.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Operations Management
- Prepare a report on the following: Part 1: Discuss the role of the corporate secretary in facilitating effective governance in a limited liability company. Include the relationships with directors, shareholders, and other officers. Part 2: Compare and contrast two characteristics of different business entities (sole trader, partnership, and limited liability company). Use examples to recommend the most appropriate type of business entity for the scenario below: Scenario Background Alex, Taylor, and Jordan plan to collaborate to launch a tech startup focused on developing and selling innovative software solutions. Each individual brings unique skills and resources to the venture: Alex: A skilled software developer with technical expertise and a vision for the product. Taylor: A marketing professional with extensive connections in the technology industry, aiming to drive sales and build the brand. Jordan: An investor willing to contribute significant financial resources but…arrow_forwardProblem 1 (20 Points) Davison Electronics manufactures three LED television monitors, identified as Model A, Model B, and Model C. Davison Electronics four manufacturing plants. Each model has its lowest possible production cost when produced at Plant 1. However, Plant 1 does not have the capacity to handle the total production of all three models. As a result, at least some of the production must be routed to the other manufacturing plants. The following table shows the minimum production requirements for next month, the plant capacities in units per month, and the production cost per unit at each plant: Model Production Cost per Unit Minimum Production Requirements Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 A $25 $28 $37 $34 48,000 B $26 $35 $36 $41 75,000 C $20 $31 $26 $23 60,000 Production Capacity 65,000 50,000 32,000 43,000 Davison’s objective is to determine the cost-minimizing production plan. Without…arrow_forwardSECTION B: TOPIC STRUCTURE CAPSTONE PROJECT TOPIC SUBMISSION TEMPLATE SECTION A: STUDENT DETAILS Student number Title (Mr/Miss/Ms/Mrs) Surname First name/s Title of research Date and year of registration Work Home Contact details Cell Region Date submitted Email 1.1 Title Insert title of the research. Choose a title that captures the essence of your proposed project. 1.2 Background to the Problem This section will be used to create the readers' interest. It can include a specific description of the topic that is to be investigated. A brief preview of the topic and the foundation of the problem should also be given. The researcher can achieve this through building up a detailed background of circumstances that lead to the problem being examined. Therefore, the background helps the reader understand the specific problem addressed by the researcher. This section should not include the background/history of the organisation. The background to the problem should not be more than ½ a page.…arrow_forward
- Does Nike Corporation's emphasis on lean operations help the Vietnamese workforce that still earns $150.00 minimum wage a month since 2014?arrow_forwardInformation Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment All organisations using computers need to consider the security of information they keep. Many organisations utilise Websites for their core business functions and this results in monetary transactions being carried out on the Websites.arrow_forwardPlease help with a complete research report on the topic below: "Information Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment " The format of the report should follow this below.arrow_forward
- 7. Wireless Infrastructure in the Cloud Wireless devices have changed the way organisations and their customers interact. Wireless enabled devices have driven the mindset that wireless networks must be ubiquitous, fast, and constantly available. These are demands that have traditionally put organisations and their user communities in direct conflict with their IT departments, as constructing and maintaining wireless infrastructures are typically time-consuming, complex, and costly endeavours.arrow_forwardIM.54 A growing online retailer sells thousands of items yet has has one specialty product category with just 30 items. They want to classify these thirty items according to the annual dollar volume (revenue) generated by each item. The table below lists each item number, Annual Sales (in units), and Price per unit: Item # Annual Sales Price 1 221 $25.85 2 446 $14.15 3 8,940 $168.19 4 2,965 $15.99 5 1,322 $29.37 6 2,575 $12.77 7 767 $28.43 8 5,803 $163.01 9 2,673 $20.51 10 642 $14.71 11 4,168 $54.53 12 1,881 $22.55 13 2,417 $29.63 14 5,207 $36.41 15 1,381 $20.55 16 9,635 $173.69 17 17,406 $27.07 18 1,573 $25.99 19 6,471 $64.99 20 6,047 $29.83 21 433 $20.89 22 2,279 $53.59 23 15,532 $106.91 24 1,585 $4.09 25 5,376 $65.23 26 2,965 $37.93 27 2,048 $28.51 28 1,174 $22.99 29 381 $5.57 30 2,930 $3.43 Which item in the table above has the highest annual dollar volume? In the answer field below, write the ITEM # that…arrow_forwardIM.84 An outdoor equipment manufacturer sells a rugged water bottle to complement its product line. They sell this item to a variety of sporting goods stores and other retailers. The manufacturer offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Price A 1 - 2,199 $5.00 B 2,200 - 3,699 $4.55 C 3,700+ $3.90 A large big-box retailer expects to sell 9,200 units this year. This retailer estimates that it incurs an internal administrative cost of $235 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding cost for the retailer is $60 per case per year. (There are 52 units or water bottles per case.)Based on this information, and not taking into account any quantity discount offers, what is the calculated EOQ (in units)? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) Based on this information, sort each quantity discount plan from left to right by dragging the MOST preferred option plan to the left, and the LEAST preferred option…arrow_forward
- Please provide detailed solutions to the following problems/exercises (4 problems/exercises x 9 points each): 1) View the video ON Unveils ‘Lightspray’ Technology (4.55 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and The Secret of Lightspray (8.27 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjmeaC-wlZs a) What is new about the design of ON’s shoes? b) How will ON’s new manufacturing technique affect location planning for footwear firms? c) How does ON focus on it sustainability strategy? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Unimed Hospital currently processes patient admissions through three admitting clerks who are set up to work in series, with respective reliabilities of 0.96, 0.95, and 0.90 (see figure below). a) Find the reliability of the current admission process. Due to rising patient complaints, the hospital administrator, Chimeg…arrow_forward3) A startup firm, Pocket International, has come up with a tiny programmable computer, NerdCom Mini Air, that sells for $49.99. The firm estimates that the programmable computers have an expected life that is exponential, with a mean of 24 months. The firm wants to estimate the probability that the NerdCom Mini Air will have a life that ends: a) after the initial 24 months of service. b) before the 24 months of service is completed. c) not before 48 months of service. Note: You could work out the problem by hand or use excel; in chapter 4S, section 4S.2 of the Stevenson text, reliability (finding the probability of functioning for a specified length of time) is covered with examples; chapters 4 & 4S Stevenson lecture power point slides 33 to 38 (chapters 4 & 4S lecture: 32.30 mins to 38.56 mins) cover reliability over time with examples.arrow_forwardDiscuss how training and development programs can be best presented to ultimately change the behavior of employees, often without their knowledge or awareness.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing


