
To determine: The new placement of departments that will minimize the total transportation costs.
Introduction:
Product layouts:
Product layout is a production system where the equipment and workstations are placed along the production and assembly lines. A conveyor is used to move the production units along the line. Product layouts have specialized labor to perform specific functions with the help of equipment (programmed to do a specific tasks in a repetitive manner). The layout is mostly based on the processing sequence.
Process layouts:
Process layout is a production system where the equipment is placed in a system based on their functions. The production line is planned to eliminate wastes. In certain process layouts, the machineries and work settings are not arranged as per the standardized production sequence. However, there would be an assembly having similar machineries and operational activities depending on the requirement. For example, paint department.
Answer to Problem 15P
Arrangement:
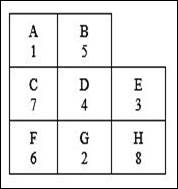
The total transportation cost for the arrangement is $143, 650 per day.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- Work centers 1 and 3 are assigned in two locations and cannot be moved.
- There are 8 work centers.
- Cost is $1 per load per meter.
- The departments are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- The locations are A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
Distances between locations (meters):
| To | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| From | ||||||||
| A | 40 | 40 | 60 | 120 | 80 | 100 | 110 | |
| B | 60 | 40 | 60 | 140 | 120 | 130 | ||
| C | 45 | 85 | 40 | 70 | 90 | |||
| D | 40 | 50 | 40 | 45 | ||||
| E | 90 | 50 | 40 | |||||
| F | 40 | 60 | ||||||
| G | 40 | |||||||
| H |
Number of load per day between departments:
| To | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| From | ||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 5 | 90 | 370 | 135 | 125 | 0 | |
| 2 | 360 | 120 | 40 | 115 | 45 | 120 | ||
| 3 | 350 | 110 | 40 | 20 | 190 | |||
| 4 | 190 | 70 | 50 | 200 | ||||
| 5 | 10 | 40 | 10 | |||||
| 6 | 50 | 20 | ||||||
| 7 | 20 | |||||||
| 8 |
Locations:
Arrangement of departments:
The numbers of trips between work centers is shown and are ranked from high to low.
| Work centers pair | Number of loads | Ranking |
| 1–2 | 10 | |
| 1–3 | 5 | |
| 1–4 | 90 | 11 |
| 1–5 | 370 | 1 |
| 1–6 | 135 | 6 |
| 1–7 | 125 | 7 |
| 1–8 | 0 | |
| 2–3 | 360 | 2 |
| 2–4 | 120 | 8 (Tied) |
| 2–5 | 40 | |
| 2–6 | 115 | 9 |
| 2–7 | 45 | |
| 2–8 | 120 | 8 (Tied) |
| 3–4 | 350 | 3 |
| 3–5 | 110 | 10 |
| 3–6 | 40 | |
| 3–7 | 20 | |
| 3–8 | 200 | 4 |
| 4–5 | 190 | 5 (Tied) |
| 4–6 | 70 | 12 |
| 4–7 | 50 | |
| 4–8 | 190 | 5 (Tied) |
| 5–6 | 10 | |
| 5–7 | 40 | |
| 5–8 | 10 | |
| 6–7 | 50 | |
| 6–8 | 20 | |
| 7–8 | 20 |
The table clearly indicates that work centers 1-5 have the highest number of trips between them. After that the following work centers have the most number of trips: 2-3, 3-4, 3-8, 4-5, 4-8, 1-6, 1-7, 2-4, 2-8 and others. After continuous trial and error method the following assignment is reached. It is to be noted that, except the pre assigned work centers, slight variations are reasonable in the assignment as long as work centers 2,4 and 8 are nearer to 3, 4 is nearer to 5 and 5 is nearer to 1.
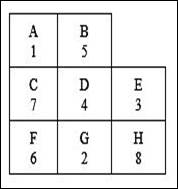
Calculation of cost for each work center pair:
The cost for each department pair is calculated by multiplying the number of loads with the distance with the cost per load per meter.
Department 1-2:
Cost=10×100×1=$1,000
Department 1-3:
Cost=5×120×1=$600
Department 1-4:
Cost=90×60×1=$5,400
Department 1-5:
Cost=370×40×1=$14,800
Department 1-6:
Cost=135×80×1=$10,800
Department 1-7:
Cost=125×40×1=$5,000
Department 2-3:
Cost=360×50×1=$18,000
Department 2-4:
Cost=120×40×1=$4,800
Department 2-5:
Cost=40×120×1=$4,800
Department 2-6:
Cost=115×40×1=$4,600
Department 2-7:
Cost=45×70×1=$3,150
Department 2-8:
Cost=120×40×1=$4,800
Department 3-4:
Cost=350×40×1=$14,000
Department 3-5:
Cost=110×60×1=$6,600
Department 3-6:
Cost=40×90×1=$3,600
Department 3-7:
Cost=20×85×1=$1,700
Department 3-8:
Cost=200×40×1=$8,000
Department 4-5:
Cost=190×40×1=$7,600
Department 4-6:
Cost=70×50×1=$3,500
Department 4-7:
Cost=50×45×1=$2,250
Department 4-8:
Cost=190×45×1=$8,550
Department 5-6:
Cost=10×140×1=$1,400
Department 5-7:
Cost=40×60×1=$2,400
Department 5-8:
Cost=10×130×1=$1,300
Department 6-7:
Cost=50×40×1=$2,000
Department 6-8:
Cost=20×60×1=$1,200
Department 7-8:
Cost=20×90×1=$1,800
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the cost of individual work center pairs.
Cost=1,000+600+5,400+14,800+10,800+5,000+18,000+4,800+4,800+4,600+3,150+4,800+14,000+6,600+3,600+1,700+8,000+7,600+3,500+2,250+8,550+1,400+2,400+1,300+2,000+1,200+1,800=$143,650
The total transportation cost for the arrangement is $143,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Operations Management
- How does rework hurt a process? Give examples on how rework can hurt a process. Please provide a referencearrow_forwardHow does rework hurt a process? Give examples on how rework can hurt a process. Please provide a referencearrow_forwardWhat the different between a near miss and hazard 1. movement and contact 2. Contact 3. movementarrow_forward
- The fixed and variable costs for three potential manufacturing plant sites for a rattan chair weaver are shown: Site Fixed Cost Per Year Variable Cost per Unit 1 $700 $12.00 2 $1,000 $7.00 $2,200 $5.00 a) After rounding to the nearest whole number, site 1 is best below After rounding to the nearest whole number, site 2 is best between After rounding to the nearest whole number, site 3 is best above b) If the demand is 590 units, then the best location for the potent 3 units. and units. 600 0 60 units. g plant isarrow_forwardRefer to Table S6.1 - Factors for Computing Control Chart Limits (3 sigma) for this problem. Sampling 4 pieces of precision-cut wire (to be used in computer assembly) every hour for the past 24 hours has produced the following results: Hour R Hour X R Hour X R Hour X R 1 3.25" 0.71" 7 3.15" 0.58" 13 3.11" 0.85" 19 4.51" 1.56" 2 3.20 1.18 8 2.65 1.08 14 2.83 1.31 20 2.79 1.14 3 3.12 1.38 9 15 4. 3.39 1.31 10 5 2.97 1.17 6 2.76 0.32 3.02 0.71 3.12 1.01 2.75 1.33 16 2.74 0.50 22 11 2.73 1.17 17 2.76 1.43 23 12 2.87 0.45 18 2.64 1.24 21 2.75 1.03 3.18 0.46 2.94 1.53 24 2.54 0.97 Based on the sampling done, the control limits for 3-sigma x chart are (round all intermediate calculations to three decimal places before proceeding with further calculations): Upper Control Limit (UCL) = inches (round your response to three decimal places). Lower Control Limit (LCL) = inches (round your response to three decimal places). Based on the x-chart, the wire cutting process has been The control limits…arrow_forwardChoose a specific cars company. E.g Toyota, Volkswagen, Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Honda, Ford, Audi, Tesla Define a list of required machinery, equipment, workstations, offices, rest areas, materials, etc. Develop and define the location of machinery, equipment, workstations, offices, rest areas, materials. Make the distribution in the manufacturing facility the most efficient way possible. Develop a process distribution for one specific product. Explain why you consider this is the most efficient distribution for this specific manufacturing facility. demonstrate the benefits of optimizing a production line with the best distribution of its equipment and spaces. To be more productive and profitable.arrow_forward
- Provide a Synposis of the Articlearrow_forwardThe goal of understanding personality in negotiation is to better predict behavior, such as the counterparty's acceptance or rejection of a negotiation offer. One investigation used acoustic and visual cues to predict the likely behavior of a counterparty to a proposal. The best visual cue predictor of the counterparty (55%) was whether they _____. A. tilted their head B. had their arms and legs crossed C. steepled their fingers D. tapped a penarrow_forwardWomen who ask for what they want in negotiation are less well-liked than women who do not self-advocate. However, nonassertive, other-advocating women suffer a leadership backlash and are regarded as less competent because their behavior is regarded to be _____ and _____. A. high-negative feminine; low-positive masculine B. high-positive feminine; high-positive masculine C. high-negative masculine; low-negative feminine D. low-positive masculine; low-positive femininearrow_forward
- There are five most recognized personality traits that can reliably be measured and predict negotiator behavior in a number of different situations. All of the following are one of those "Big 5" personality traits except _____. A. conscientiousness B. introversion C. agreeableness D. openness to experiencearrow_forwardWith regard to reputation in negotiation, negotiators who use adversarial, stubborn, and ethically questionable behavior often have the effect of _____. A. improving their business relationships B. decreasing their effectiveness as a negotiator C. improving their business relationships D. decreasing their group statusarrow_forwardWhen it comes to assertiveness, there is only a modest link between negotiators' self-views and how the counterparty sees them. Many negotiators come away from a negotiation thinking they came on too strong with the counterparty. The _____ refers to the fact that negotiators believe they are coming on too strong with the counterparty, but they actually are not. A. Collective trap illusion B. Attribution error C. Aggressive anchoring bias D. Line-crossing illusionarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,

