
Operations Management
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781259667473
Author: William J Stevenson
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 2P
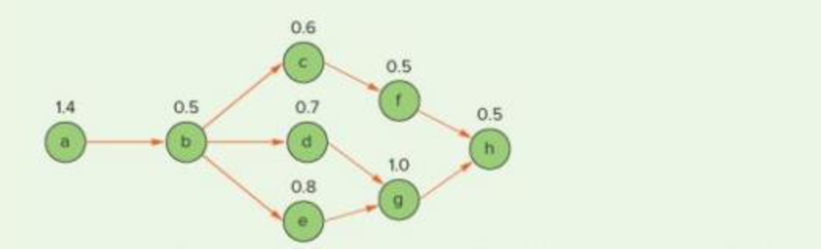
A manager wants to assign tasks to workstations as efficiently as possible and achieve an hourly output of
a. In order of most following tasks Tiebreaker: greatest positional weight.
b. In order of greatest positional weight Tiebreaker: most following tasks.
c. What is the efficiency?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Purchasing, Receiving, Storage, and Inventory Instructions- Dietary management in a nursing home in ABQ NM
What workers are involved in the purchasing, receiving, storage and inventory process. Complete the table below:
Position
Description of their job duties
Date/ What did they do?
Answer the questions below:
PURCHASING:
1. Is there a centralized purchasing department for the facility? If yes, observe someone in that department for a half day if possible, if no write N/A
2. What kinds of items are required to go out for formal bid?
3. What about capital purchases? What is the dollar amount at which an item must go on the capital rather than the operating budget?
4. Does the facility participate with a group to cooperatively purchase items?
5. Is there a Prime Vendor? If yes, how often is the contract renegotiated?
6. Is informal or open-market buying used for any items? Which ones?
7. Who orders…
Critical Incident Report- Dietary Mangement
Critical incidences involve critical thinking and problem solving techniques. This exercise is the opportunity to analyze and decide on the appropriateness of the action and
to determine better ways to solve problems, approach employees and get the job done. This exercise should help in doing it better the next time. As you observe or become
more involved in the situations that require problem solving or critical thinking use this exercise to identify the what, who, and when and determine how the actions
taken or not taken affected the outcome. You must write up two or more experiences. The summary is to include two parts:
1.
Objective data of what occurred and how it occurred:
2.
Analysis of what happened and what we could or would have done to make the outcome better.
Prepare a graph of the monthly forecasts and average forecast demand for Chicago Paint Corp., a manufacturer of specialized paint for artists.
Compute the demand per day for each month (round your responses to one decimal place).
Month
B
Production Days
Demand Forecast
Demand per Day
January
21
950
February
19
1,150
March
21
1,150
April
20
1,250
May
23
1,200
June
22
1,000'
July
20
1,350
August
21
1,250
September
21
1,050
October
21
1,050
November
21
December
225
950
19
850
Chapter 6 Solutions
Operations Management
Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.2 - MORTON SALT Introduction Morton Salt is a...Ch. 6.3 - FOXCONN SHIFTS ITS FOCUS TO AUTOMATION Foxconn...Ch. 6.3 - FOXCONN SHIFTS ITS FOCUS TO AUTOMATION Foxconn...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 2.1RQCh. 6.3 - Prob. 2.2RQ
Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 1.1RQCh. 6.5 - Prob. 1.2RQCh. 6 - Explain the importance of process selection in...Ch. 6 - Briefly describe the five process types, and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 3DRQCh. 6 - Briefly describe computer-assisted approaches to...Ch. 6 - What is a flexible manufacturing system, and under...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6DRQCh. 6 - Why might the choice of equipment that provides...Ch. 6 - Prob. 8DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 9DRQCh. 6 - Briefly describe the two main layout types.Ch. 6 - Prob. 11DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 12DRQCh. 6 - What is the goal of Line balancing? What happens...Ch. 6 - Why are routing and scheduling continual problems...Ch. 6 - Prob. 15DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 16DRQCh. 6 - The City Transportation Planning Committee must...Ch. 6 - Identify the fixed-path and variable-path...Ch. 6 - Prob. 19DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 20DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 21DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 22DRQCh. 6 - What is cellular manufacturing? What are its main...Ch. 6 - Prob. 24DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 25DRQCh. 6 - Prob. 1TSCh. 6 - What trade-offs are involved when deciding how...Ch. 6 - Who needs to be involved in process selection?Ch. 6 - Prob. 4TSCh. 6 - Prob. 5TSCh. 6 - Prob. 1CTECh. 6 - Prob. 2CTECh. 6 - What are the risks of automating a production...Ch. 6 - Consider an assembly line such as the burrito...Ch. 6 - Prob. 1PCh. 6 - A manager wants to assign tasks to workstations as...Ch. 6 - A manager wants to assign tasks to workstations as...Ch. 6 - A producer of inkjet printer is planning to add a...Ch. 6 - As part of a major plant renovation project, the...Ch. 6 - Twelve tasks, with times and precedence...Ch. 6 - For the given set of tasks, do the following: a....Ch. 6 - A shop works a 400-minute day. The manager of the...Ch. 6 - Arrange six departments into a 2 3 grid so that...Ch. 6 - Using the information given in the preceding...Ch. 6 - Using the information in the following grid,...Ch. 6 - Arrange the eight departments shown in the...Ch. 6 - Arrange the departments so they satisfy the...Ch. 6 - a. Determine the placement of departments fix a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 15PCh. 6 - Develop a process layout that will minimize the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 17PCh. 6 - Rebalance the assembly line in Problem 7. This...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The president of Hill Enterprises, Terri Hill, projects the firm's aggregate demand requirements over the next 8 months as follows: 2,300 January 1,500 May February 1,700 June 2,100 March April 1,700 1,700 July August 1,900 1,500 Her operations manager is considering a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units of inventory on hand. Stockout cost of lost sales is $125 per unit. Inventory holding cost is $25 per unit per month. Ignore any idle-time costs. The plan is called plan C. Plan C: Keep a stable workforce by maintaining a constant production rate equal to the average gross requirements excluding initial inventory and allow varying inventory levels. Conduct your analysis for January through August. The average monthly demand requirement = units. (Enter your response as a whole number.) In order to arrive at the costs, first compute the ending inventory and stockout units for each month by filling in the table below (enter your responses as whole numbers). Ending E Period…arrow_forwardMention four early warning indicators that a business may be at risk.arrow_forward6. Identify and describe any four hazard-based risks.arrow_forward
- 2. Describe three types of risks commonly faced by entrepreneurs.arrow_forwardDefine risk management and explain its importance in a small business.arrow_forward1. Define risk management and explain its importance in a small business. 2. Describe three types of risks commonly faced by entrepreneurs. 3. Explain the purpose of a risk register. 4. List and briefly describe four risk response strategies. (5 marks) (6 marks) (4 marks) (8 marks) 5. Explain how social media can pose a risk to small businesses. (5 marks) 6. Identify and describe any four hazard-based risks. (8 marks) 7. Mention four early warning indicators that a business may be at risk. (4 marks)arrow_forward
- State whether each of the following statements is TRUE or FALSE. 1. Risk management involves identifying, analysing, and mitigating risks. 2. Hazard risks include interest rate fluctuations. 3. Entrepreneurs should avoid all forms of risks. 4. SWOT analysis is a tool for risk identification. 5. Scenario building helps visualise risk responses. 6. Risk appetite defines how much risk an organisation is willing to accept. 7. Diversification is a risk reduction strategy. 8. A risk management framework must align with business goals. 9. Political risk is only relevant in unstable countries. 10. All risks can be eliminated through insurance.arrow_forward9. A hazard-based risk includes A. Political instability B. Ergonomic issues C. Market demand D. Taxation changesarrow_forward8. Early warning indicators help businesses to A. Avoid legal actions B. Grow rapidly C. Detect potential risks D. Hire employees 9. A hazard-based risk includes A. Political instability B. Ergonomic issues C. Market demand D. Taxation changesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Marketing
Marketing
ISBN:9780357033791
Author:Pride, William M
Publisher:South Western Educational Publishing

Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781285869681
Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Management, Loose-Leaf Version
Management
ISBN:9781305969308
Author:Richard L. Daft
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Inventory Management | Concepts, Examples and Solved Problems; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2n9NLZTIlz8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY