
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118912652
Author: Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 43P
Water flows from a very large tank through a 5 cm diameter tube. The dark liquid in the manometer is mercury. Estimate the velocity in the pipe and the rate of discharge from the tank. Assume the flow is frictionless.
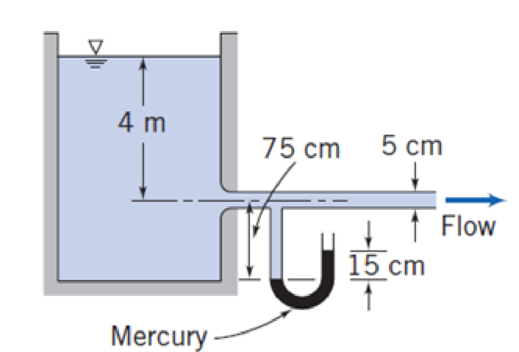
P6.43
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. Two links made of heat treated 6061 aluminum (Sy = 276 MPa, Sys = 160 MPa) are pinned
together using a steel dowel pin (Sy = 1398 MPa, Sys = 806 MPa) as shown below. The
links are to support a load P with a factor of safety of at least 2.0. Determine if the link will
fail first by tearout, direct shear of the pin, bearing stress on the link, or tensile stress at
section AA. (Hint: find the load P for each case and choose the case that gives the smallest
load.)
P
8 mm
P
8 mm
¡+A
3 mm
→A
10 mm
P
1. For a feature other than a sphere, circularity is where:
A. The axis is a straight line
B. The modifier is specified with a size dimension
C. All points of the surface intersected by any plane
perpendicular to an axis or spine (curved line) are
equidistant from that axis or spine
D. All points of the surface intersected by any plane
passing through a common center are equidistant
from that center
2. What type of variation is limited by a circularity toler-
ance zone?
A. Ovality
B. Tapering
C. Bending
D. Warping
3. How does the Rule #1 boundary affect the application
of a circularity tolerance?
A. The modifier must be used.
B. The feature control frame must be placed next to
the size dimension.
C. The circularity tolerance value must be less than
the limits of size tolerance.
D. Circularity cannot be applied where a Rule #1
boundary exists.
4. A circularity tolerance may use a
modifier.
A. Ø
B. F
C. M
D. ℗
5. A real-world application for a circularity tolerance is:
A. Assembly (i.e.,…
3. A steel bar is pinned to a vertical support column by a 10 mm diameter hardened dowel pin,
Figure 1. For P = 7500 N, find:
a. the shear stress in the pin,
b. the direct bearing stress on the hole in the bar,
c. the minimum value of d to prevent tearout failure if the steel bar has a shear strength of
175 MPa.
support column
pin
bar
thickness of bar = 8 mm
h
d
150 mm
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 6 - An incompressible frictionless flow field is given...Ch. 6 - A velocity field in a fluid with density of 1000...Ch. 6 - The x component of velocity in an incompressible...Ch. 6 - Consider the flow field with the velocity given by...Ch. 6 - Consider the flow field with the velocity given by...Ch. 6 - The velocity field for a plane source located...Ch. 6 - In a two-dimensional frictionless, incompressible...Ch. 6 - Consider a two-dimensional incompressible flow...Ch. 6 - An incompressible liquid with a density of 900...Ch. 6 - Consider a flow of water in pipe. What is the...
Ch. 6 - The velocity field for a plane vortex sink is...Ch. 6 - An incompressible liquid with negligible viscosity...Ch. 6 - Consider water flowing in a circular section of a...Ch. 6 - Consider a tornado as air moving in a circular...Ch. 6 - A nozzle for an incompressible, inviscid fluid of...Ch. 6 - A diffuser for an incompressible, inviscid fluid...Ch. 6 - A liquid layer separates two plane surfaces as...Ch. 6 - Consider Problem 6.15 with the nozzle directed...Ch. 6 - Consider Problem 6.16 with the diffuser directed...Ch. 6 - A rectangular computer chip floats on a thin layer...Ch. 6 - Heavy weights can be moved with relative ease on...Ch. 6 - The y component of velocity in a two-dimensional...Ch. 6 - The velocity field for a plane doublet is given in...Ch. 6 - Tomodel the velocity distribution in the curved...Ch. 6 - Repeat Example 6.1, but with the somewhat more...Ch. 6 - Using the analyses of Example 6.1 and Problem...Ch. 6 - Water flows at a speed of 25 ft/s. Calculate the...Ch. 6 - Plot the speed of air versus the dynamic pressure...Ch. 6 - Water flows in a pipeline. At a point in the line...Ch. 6 - In a pipe 0.3 m in diameter, 0.3 m3/s of water are...Ch. 6 - A jet of air from a nozzle is blown at right...Ch. 6 - The inlet contraction and test section of a...Ch. 6 - Maintenance work on high-pressure hydraulic...Ch. 6 - An open-circuit wind tunnel draws in air from the...Ch. 6 - Water is flowing. Calculate H(m) and p(kPa). P6.36Ch. 6 - If each gauge shows the same reading for a flow...Ch. 6 - Derive a relation between A1 and A2 so that for a...Ch. 6 - Water flows steadily up the vertical 1...Ch. 6 - Your car runs out of gas unexpectedly and you...Ch. 6 - A tank at a pressure of 50 kPa gage gets a pinhole...Ch. 6 - The water flow rate through the siphon is 5 L/s,...Ch. 6 - Water flows from a very large tank through a 5 cm...Ch. 6 - Consider frictionless, incompressible flow of air...Ch. 6 - A closed tank contains water with air above it....Ch. 6 - Water jets upward through a 3-in.-diameter nozzle...Ch. 6 - Calculate the rate of flow through this pipeline...Ch. 6 - A mercury barometer is carried in a car on a day...Ch. 6 - A racing car travels at 235 mph along a...Ch. 6 - The velocity field for a plane source at a...Ch. 6 - A smoothly contoured nozzle, with outlet diameter...Ch. 6 - Water flows steadily through a 3.25-in.-diameter...Ch. 6 - A flow nozzle is a device for measuring the flow...Ch. 6 - The head of water on a 50 mm diameter smooth...Ch. 6 - Water flows from one reservoir in a 200-mm pipe,...Ch. 6 - Barometric pressure is 14.0 psia. What is the...Ch. 6 - A spray system is shown in the diagram. Water is...Ch. 6 - Water flows out of a kitchen faucet of...Ch. 6 - A horizontal axisymmetric jet of air with...Ch. 6 - The water level in a large tank is maintained at...Ch. 6 - Many recreation facilities use inflatable bubble...Ch. 6 - Water flows at low speed through a circular tube...Ch. 6 - Describe the pressure distribution on the exterior...Ch. 6 - An aspirator provides suction by using a stream of...Ch. 6 - Carefully sketch the energy grade lines (EGL) and...Ch. 6 - Carefully sketch the energy grade lines (EGL) and...Ch. 6 - Water is being pumped from the lower reservoir...Ch. 6 - The turbine extracts power from the water flowing...Ch. 6 - Consider a two-dimensional fluid flow: u = ax + by...Ch. 6 - The velocity field for a two-dimensional flow is...Ch. 6 - A flow field is characterized by the stream...Ch. 6 - The flow field for a plane source at a distance h...Ch. 6 - The stream function of a flow field is = Ax2y ...Ch. 6 - A flow field is characterized by the stream...Ch. 6 - A flow field is characterized by the stream...Ch. 6 - The stream function of a flow field is = Ax3 ...Ch. 6 - A flow field is represented by the stream function...Ch. 6 - Consider the flow field represented by the...Ch. 6 - Show by expanding and collecting real and...Ch. 6 - Consider the flow field represented by the...Ch. 6 - An incompressible flow field is characterized by...Ch. 6 - Consider an air flow over a flat wall with an...Ch. 6 - A source with a strength of q = 3 m2/s and a sink...Ch. 6 - The velocity distribution in a two-dimensional,...Ch. 6 - Consider the flow past a circular cylinder, of...Ch. 6 - The flow in a corner with an angle can be...Ch. 6 - Consider the two-dimensional flow against a flat...Ch. 6 - A source and a sink with strengths of equal...Ch. 6 - A flow field is formed by combining a uniform flow...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob. F2-15
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
What does the following code print? System.out.print(""); System.out.print(""); System.out.print(""); System.ou...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
_____ is the only language computers can process directly, without any conversion required.
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Fill in the blanks in each of the following statements: A relation that has no partial functional dependencies ...
Modern Database Management
2-1 List the five types of measurements that form the
basis of traditional ptane surveying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
What features or properties are provided or enhanced by adhesive additives?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A press that delivers 115 strokes per minute, each stroke providing a force of 7826 N throughout a distance of 18 mm. The press efficiency is 90% and is driven by a 1749-rpm motor. Determine average torque that must be provided by the motor in the units of N-m.arrow_forward·3) find the force (P) for the figures (1) and (2) 15cm 10cm 15 h=10mm h2=6mm // Call = 90 N/2 P Agate Fig (i) Ans: 1)P=112614N 2) P=1956.5 N 25cm 25 cm الفترة أو الحجم تمر بالتي عثر اكو تورشن (ک Fig (2) h₁ = 10mm 42=6mm Cmarrow_forwardI want a human solutionarrow_forward
- (Read Image)arrow_forward47 14 16 12 34 10 12 12 33arrow_forward3. A steam power plant has an average monthly net power delivery of 740 MW over the course of a year. This power delivery is accomplished by burning coal in the boiler. The coal has a heating value of 9150 Btu/lbm. The cost of the coal is $14.20/ton. The overall thermal efficiency of the plant is, nth = Wnet Qboiler = 0.26 = 26% Determine the annual cost of the coal required to deliver the given average monthly power.arrow_forward
- 47 14 16 12 34 10 12 12 33arrow_forward= The forces F₁ = 590 lb, F₂ = 380 lb, F3 = 240 lb and F 330 lb. Determine the forces in each member of the truss. Use positive values to indicate tension and negative values to indicate compression. a a a D b F₁ A 000 B. 779977 F₂V H G E F4 b BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 6 ft b 10.1 ft The force in member AB is lb. The force in member AH is lb. The force in member GH is lb. The force in member BH is lb. The force in member BC is lb. The force in member BG is lb. The force in member EG is lb. The force in member CD is lb. The force in member DE is lb. The force in member CE is lb. The force in member CG is lb.arrow_forwardMultiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which type of surface deviation is controlled by a cy- lindricity tolerance but not by a circularity tolerance? A. B. C. Ovality Taper Lobing D. None of the above 2. When verifying a cylindricity tolerance, the inspec- tion method must be able to collect a set of points and determine the: A. Distance between two coaxial cylinders that con- tain the set of points B. Cylinder that circumscribes the set of points C. Cylinder that inscribes the set of points D. Distance between two coaxial circles that contain the set of points 3. Where Rule #1 applies to a cylindrical regular feature of size, the tolerance value of a cylindricity tolerance applied to the feature of size must be tolerance. A. Less than B. Equal to C. Greater than D. None of the above the size 4. Which of the following modifiers may be applied with a cylindricity tolerance? A. M B. C. ℗ D. Ø 5. Which geometric tolerance can provide an indirect cylindricity…arrow_forward
- The beam AB is attached to the wall in the xz plane by a fixed support at A. A force of F = (−129î + 69.0ĵ + 3591) N is applied to the end of the beam at B. The weight of the beam can be modeled with a uniform distributed load of intensity w = 85.0 N/m acting in the negative z direction along its entire length. Find the support reactions at A. Z с A b a B F y Cc 10 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl X Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following. table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 5.60 m b 5.00 m C 3.70 m A II = MA = ( m 2.> ~.> + + k) N k) N-arrow_forwardneed help?arrow_forwardA bent pipe is attached to a wall with brackets as shown. A force of F = 180 lb is applied to the end of the tube with direction indicated by the dimensions in the figure. Determine the support reactions at the brackets B, C, and D. Model these brackets as journal bearings (only force reactions perpendicular to the axis of the tube) and neglect couple moment reactions. Assume the distance between the supports at B and C and the tube bends nearby are negligible such that the support at C is directly above the support at D and the dimension g gives the distance between supports B and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. 2013 Michael Swanbom cc 10 BY NC SA g h א B 8° У A C x каж Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 6.72 in b 11.8 in с 14.8 in d 42.0 in h 26.6 in g 28.0 in → The reaction at B is B = lb. The reaction at C is C = lb. The reaction at D is D = lb. + << + + 2. + + 557 〈んarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY