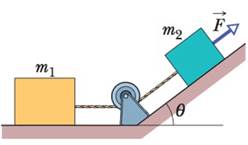
Problem 1Q: Figure 5-19 gives the free-body diagram for four situations in which an object is pulled by several... Problem 2Q: Two horizontal forces, F1=(3N)i (4N)jandF2=(1N)i (2N)j pull a banana split across a friction- less... Problem 3Q: In Fig. 5-21, forces F1 and F2 are applied to a lunchbox as it slides at constant velocity over a... Problem 4Q: At time t = 0, constant F begins to act on a rock moving through deep space in the x direction. a... Problem 5Q: Figure 5-22 shows overhead views of four situations in which forces act on a block that lies on a... Problem 6Q: Figure 5-23 shows the same breadbox in four situations where horizontal forces are applied. Rank the... Problem 7Q: July 17, 1981, Kansas City: The newly opened Hyatt Regency is packed with people listening and... Problem 8Q: Figure 5-25 gives three graphs of velocity component vxt and three graphs of velocity component vyt.... Problem 9Q: Figure 5-26 shows a train of four blocks being pulled across a frictionless floor by force F. What... Problem 10Q: Figure 5-27 shows three blocks being pushed across a frictionless floor by horizontal force F. What... Problem 11Q: A vertical force F is applied to a block of mass m that lies on a floor. What happens to the... Problem 12Q: Figure 5-28 shows four choices for the direction of a force of magnitude F to be applied to a block... Problem 1P: Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body that can move over a frictionless floor. One force... Problem 2P: Two horizontal forces act on a 2.0 kg chopping block that can slide over a frictionless kitchen... Problem 3P: If the 1 kg standard body has an acceleration of 2.00 m/s2 at 20.0 to the positive direction of an x... Problem 4P: While two forces act on it, a particle is to move at the constant velocity v=(3m/s)i(4m/s)j.One of... Problem 5P: GO Three astronauts, propelled by jet backpacks, push and guide a 120 kg asteroid toward a... Problem 6P: In a two-dimensional tug-of-war, Alex, Betty, and Charles pull horizontally on an automobile tire at... Problem 7P: SSM There are two forces on the 2.00 kg box in the overhead view of Fig. 5-31, but only one is... Problem 8P: A 2.00 kg object is subjected to three forces that give it an acceleration... Problem 9P: A 0.340 kg particle moves in an xy plane according to xt = 15.00 2.00t 4.00t3 and yt = 25.00 ... Problem 10P: GO A 0.150 kg particle moves along an x axis according to xt = 13.00 2.00t 4.00t2 3.00t3, with x... Problem 11P: A 2.0 kg particle moves along an x axis, being propelled by a variable force directed along that... Problem 12P: GO Two horizontal forces F1 and F2 act on a 4.0 kg disk that slides over frictionless ice, on which... Problem 13P: Figure 5-33 shows an arrangement in which four disks are suspended by cords. The longer, top cord... Problem 14P: A block with a weight of 3.0 N is at rest on a horizontal surface. A 1.0 N upward force is applied... Problem 15P: SSM a An 11.0 kg salami is supported by a cord that runs to a spring scale, which is supported by a... Problem 16P: Some insects can walk below a thin rod such as a twig by hanging from it. Suppose that such an... Problem 17P: SSM WWW In Fig. 5-36, let the mass of the block be 8.5 kg and the angle be 30. Find a the tension... Problem 18P: In April 1974, John Massis of Belgium managed to move two passenger railroad cars. He did so by... Problem 19P: SSM A 500 kg rocket sled can be accelerated at a constant rate from rest to 1600 km/h in 1.8 s. What... Problem 20P: A car traveling at 53 km/h hits a bridge abutment. A passenger in the car moves forward a distance... Problem 21P: A constant horizontal force Fa pushes a 2.00 kg FedEx package across a frictionless floor on which... Problem 22P: A customer sits in an amusement park ride in which the compartment is to be pulled downward in the... Problem 23P: Tarzan, who weighs 820 N, swings from a cliff at the end of a 20.0 m vine that hangs from a high... Problem 24P: 24 There are two horizontal forces on the 2.0 kg box in the overhead view of Fig. 5-38 but only one... Problem 25P: Sunjamming. A sun yacht is a spacecraft with a large sail that is pushed by sunlight. Although such... Problem 26P: The tension at which a fishing line snaps is commonly called the lines strength. What minimum... Problem 27P: SSM An electron with a speed of 1.2 107 m/s moves horizontally into a region where a constant... Problem 28P: A car that weighs 1.30 104 N is initially moving at 40 km/h when the brakes are applied and the car... Problem 29P: A firefighter who weighs 712 N slides down a vertical pole with an acceleration of 3.00 m/s2,... Problem 30P: The high-speed winds around a tornado can drive projectiles into trees, building walls, and even... Problem 31P: SSM WWW A block is projected up a frictionless inclined plane with initial speed v0 = 3.50 m/s. The... Problem 32P: Figure 5-39 shows an overhead view of a 0.0250 kg lemon half and two of the three horizontal forces... Problem 33P: An elevator cab and its load have a combined mass of 1600 kg. Find the tension in the supporting... Problem 34P: GO In Fig. 5-40, a crate of mass m = 100 kg is pushed at constant speed up a frictionless ramp =... Problem 35P: The velocity of a 3.00 kg particle is given by v=(8.00ti +3.00t2j) m/s, with time t in seconds. At... Problem 36P: Holding on to a towrope moving parallel to a frictionless ski slope, a 50 kg skier is pulled up the... Problem 37P: A 40 kg girl and an 8.4 kg sled are on the frictionless ice of a frozen lake, 15 m apart but... Problem 38P: A 40 kg skier skis directly down a frictionless slope angled at 10 to the horizontal. Assume the... Problem 39P: ILW A sphere of mass 3.0 104 kg is suspended from a cord. A steady horizontal breeze pushes the... Problem 40P: GO A dated box of dates, of mass 5.00 kg, is sent sliding up a frictionless ramp at an angle of to... Problem 41P: Using a rope that will snap if the tension in it exceeds 387 N, you need to lower a bundle of old... Problem 42P: GO In earlier days, horses pulled barges down canals in the manner shown in Fig. 5-42. Suppose the... Problem 43P: SSM In Fig. 5-43, a chain consisting of five links, each of mass 0.100 kg, is lifted vertically with... Problem 44P: A lamp hangs vertically from a cord in a de scending elevator that decelerates at 2.4 m/s2, a If the... Problem 45P: An elevator cab that weighs 27.8 kN moves upward. What is the tension in the cable if the cabs speed... Problem 46P: An elevator cab is pulled upward by a cable. The cab and its single occupant have a combined mass of... Problem 47P: GO The Zacchini family was renowned for their human-cannonball act in which a family member was shot... Problem 48P: GO In Fig. 5-44, elevator cabs A and B are connected by a short cable and can be pulled upward or... Problem 49P: In Fig. 5-45, a block of mass m = 5.00 kg is pulled along a horizontal frictionless floor by a cord... Problem 50P: GO Fig. 5-46, three ballot boxes are connected by cords, one of which wraps over a pulley having... Problem 51P: GO Figure 5-47 shows two blocks connected by a cord of negligible mass that passes over a... Problem 52P: An 85 kg man lowers himself to the ground from a height of 10.0 m by holding onto a rope that runs... Problem 53P: In Fig. 5-48, three connected blocks are pulled to the right on a horizontal frictionless table by a... Problem 54P: GO Figure 5-49 shows four penguins that are being playfully pulled along very slippery frictionless... Problem 55P: SSM ILW WWW Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. A horizontal force is applied to the... Problem 56P: GO In Fig. 5-51a, a constant horizontal force Fa is applied to block A, which pushes against block B... Problem 57P: ILW A block of mass m1 = 3.70 kg on a frictionless plane inclined at angle = 30.0 is connected by a... Problem 58P: Figure 5-53 shows a man sitting in a bosuns chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over... Problem 59P: SSM A 10 kg monkey climbs up a massless rope that runs over a frictionless tree limb and back down... Problem 60P: Figure 5-45 shows a 5.00 kg block being pulled along a friction- less floor by a cord that applies a... Problem 61P: SSM ILW A hot-air balloon of mass M is descending vertically with downward acceleration of magnitude... Problem 62P: In shot putting, many athletes elect to launch the shot at an angle that is smaller than the... Problem 63P: GO Figure 5-55 gives, as a function of time t, the force component Fx that acts on a 3.00 kg ice... Problem 64P: GO Figure 5-56 shows a box of mass m2 = 1.0 kg on a frictionless plane inclined at angle = 30. It... Problem 65P: GO Figure 5-47 shows Atwoods machine, in which two containers are connected by a cord of negligible... Problem 66P: GO Figure 5-57 shows a section of a cable-car system. The maximum permissible mass of each car with... Problem 67P: Figure 5-58 shows three blocks attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block B lies... Problem 68P: A shot putter launches a 7.260 kg shot by pushing it along a straight line of length 1.650 m and at... Problem 69P: In Fig. 5-59, 4.0 kg block A and 6.0 kg block B are connected by a string of negligible mass. Force... Problem 70P: An 80 kg man drops to a concrete patio from a window 0.50 m above the patio. He neglects to bend his... Problem 71P: SSM Figure 5-60 shows a box of dirty money mass m1 = 3.0 kg on a frictionless plane inclined at... Problem 72P: Three forces act on a particle that moves with unchanging velocity v=(2m/s)i (7m/s)j. Two of the... Problem 73P: SSM In Fig. 5-61, a tin of antioxidants m1 = 1.0 kg on a fric tionless inclined surface is connected... Problem 74P: The only two forces acting on a body have magnitudes of 20 N and 35 N and directions that differ by... Problem 75P: Figure 5-62 is an overhead view of a 12 kg tire that is to be pulled by three horizontal ropes. One... Problem 76P: A block of mass M is pulled along a horizontal frictionless sur face by a rope of mass m, as shown... Problem 77P: SSM A worker drags a crate across a factory floor by pulling on a rope tied to the crate. The worker... Problem 78P: In Fig. 5-64, a force F of magnitude 12 N is applied to a FedEx box of mass m2 = 1.0 kg. The force... Problem 79P: A certain particle has a weight of 22 N at a point where g = 9.8 m/s2. What are its a weight and b... Problem 80P: An 80 kg person is parachuting and experiencing a downward acceleration of 2.5 m/s2. The mass of the... Problem 81P: A spaceship lifts off vertically from the Moon, where g = 1.6 m/s2. If the ship has an upward... Problem 82P: In the overhead view of Fig. 5-65, five forces pull on a box of mass m = 4.0 kg. The force... Problem 83P: SSM A certain force gives an object of mass m1 an acceleration of 12.0 m/s2 and an object of mass m2... Problem 84P Problem 85P: A 52 kg circus performer is to slide down a rope that will break if the tension exceeds 425 N. a... Problem 86P: Compute the weight of a 75 kg space ranger a on Earth, b on Mars, where g = 3.7 m/s2, and c in... Problem 87P: An object is hung from a spring balance attached to the ceiling of an elevator cab. The balance... Problem 88P: Imagine a landing craft approaching the surface of Callisto, one of Jupiters moons. If the engine... Problem 89P: A 1400 kg jet engine is fastened to the fuselage of a passenger jet by just three bolts this is the... Problem 90P: An interstellar ship has a mass of 1.20 106 kg and is initially at rest relative to a star system.... Problem 91P: SSM A motorcycle and 60.0 kg rider accelerate at 3.0 m/s2 up a ramp inclined 10 above the... Problem 92P Problem 93P: SSM Figure 5-66a shows a mobile hanging from a ceiling; it consists of two metal pieces m1 = 3.5 kg... Problem 94P: For sport, a 12 kg armadillo runs onto a large pond of level, frictionless ice. The armadillos... Problem 95P: Suppose that in Fig. 5-12, the masses of the blocks are 2.0 kg and 4.0 kg. a Which mass should the... Problem 96P: A nucleus that captures a stray neutron must bring the neutron to a stop within the diameter of the... Problem 97P: If the 1 kg standard body is accelerated by only F1=(3.0N)i +(4.0N)j and F2=(2.0N)i +(6.0N)j, then... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




