
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 50P
GO Fig. 5-46, three ballot boxes are connected by cords, one of which wraps over a pulley having negligible friction on its axle and negligible mass. The three masses are mA = 30.0 kg, mB = 40.0 kg, and mC = 10.0 kg. When the assembly is released from rest, (a) what is the tension in the cord connecting B and C, and (b) how far does A move in the first 0.250 s (assuming it does not reach the pulley)?
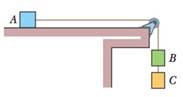
Figure 5-46 Problem 50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need help with how to solve this answer, thank you !
I need help with how to solve this answer, thank you !
I need help with how to solve this answer, thank you !
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 5 - Figure 5-19 gives the free-body diagram for four...Ch. 5 - Two horizontal forces, F1=(3N)i (4N)jandF2=(1N)i...Ch. 5 - In Fig. 5-21, forces F1 and F2 are applied to a...Ch. 5 - At time t = 0, constant F begins to act on a rock...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-22 shows overhead views of four...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-23 shows the same breadbox in four...Ch. 5 - July 17, 1981, Kansas City: The newly opened Hyatt...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-25 gives three graphs of velocity...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-26 shows a train of four blocks being...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-27 shows three blocks being pushed across...
Ch. 5 - A vertical force F is applied to a block of mass m...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-28 shows four choices for the direction...Ch. 5 - Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body...Ch. 5 - Two horizontal forces act on a 2.0 kg chopping...Ch. 5 - If the 1 kg standard body has an acceleration of...Ch. 5 - While two forces act on it, a particle is to move...Ch. 5 - GO Three astronauts, propelled by jet backpacks,...Ch. 5 - In a two-dimensional tug-of-war, Alex, Betty, and...Ch. 5 - SSM There are two forces on the 2.00 kg box in the...Ch. 5 - A 2.00 kg object is subjected to three forces that...Ch. 5 - A 0.340 kg particle moves in an xy plane according...Ch. 5 - GO A 0.150 kg particle moves along an x axis...Ch. 5 - A 2.0 kg particle moves along an x axis, being...Ch. 5 - GO Two horizontal forces F1 and F2 act on a 4.0 kg...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-33 shows an arrangement in which four...Ch. 5 - A block with a weight of 3.0 N is at rest on a...Ch. 5 - SSM a An 11.0 kg salami is supported by a cord...Ch. 5 - Some insects can walk below a thin rod such as a...Ch. 5 - SSM WWW In Fig. 5-36, let the mass of the block be...Ch. 5 - In April 1974, John Massis of Belgium managed to...Ch. 5 - SSM A 500 kg rocket sled can be accelerated at a...Ch. 5 - A car traveling at 53 km/h hits a bridge abutment....Ch. 5 - A constant horizontal force Fa pushes a 2.00 kg...Ch. 5 - A customer sits in an amusement park ride in which...Ch. 5 - Tarzan, who weighs 820 N, swings from a cliff at...Ch. 5 - 24 There are two horizontal forces on the 2.0 kg...Ch. 5 - Sunjamming. A sun yacht is a spacecraft with a...Ch. 5 - The tension at which a fishing line snaps is...Ch. 5 - SSM An electron with a speed of 1.2 107 m/s moves...Ch. 5 - A car that weighs 1.30 104 N is initially moving...Ch. 5 - A firefighter who weighs 712 N slides down a...Ch. 5 - The high-speed winds around a tornado can drive...Ch. 5 - SSM WWW A block is projected up a frictionless...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-39 shows an overhead view of a 0.0250 kg...Ch. 5 - An elevator cab and its load have a combined mass...Ch. 5 - GO In Fig. 5-40, a crate of mass m = 100 kg is...Ch. 5 - The velocity of a 3.00 kg particle is given by...Ch. 5 - Holding on to a towrope moving parallel to a...Ch. 5 - A 40 kg girl and an 8.4 kg sled are on the...Ch. 5 - A 40 kg skier skis directly down a frictionless...Ch. 5 - ILW A sphere of mass 3.0 104 kg is suspended from...Ch. 5 - GO A dated box of dates, of mass 5.00 kg, is sent...Ch. 5 - Using a rope that will snap if the tension in it...Ch. 5 - GO In earlier days, horses pulled barges down...Ch. 5 - SSM In Fig. 5-43, a chain consisting of five...Ch. 5 - A lamp hangs vertically from a cord in a de...Ch. 5 - An elevator cab that weighs 27.8 kN moves upward....Ch. 5 - An elevator cab is pulled upward by a cable. The...Ch. 5 - GO The Zacchini family was renowned for their...Ch. 5 - GO In Fig. 5-44, elevator cabs A and B are...Ch. 5 - In Fig. 5-45, a block of mass m = 5.00 kg is...Ch. 5 - GO Fig. 5-46, three ballot boxes are connected by...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-47 shows two blocks connected by a...Ch. 5 - An 85 kg man lowers himself to the ground from a...Ch. 5 - In Fig. 5-48, three connected blocks are pulled to...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-49 shows four penguins that are being...Ch. 5 - SSM ILW WWW Two blocks are in contact on a...Ch. 5 - GO In Fig. 5-51a, a constant horizontal force Fa...Ch. 5 - ILW A block of mass m1 = 3.70 kg on a frictionless...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-53 shows a man sitting in a bosuns chair...Ch. 5 - SSM A 10 kg monkey climbs up a massless rope that...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-45 shows a 5.00 kg block being pulled...Ch. 5 - SSM ILW A hot-air balloon of mass M is descending...Ch. 5 - In shot putting, many athletes elect to launch the...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-55 gives, as a function of time t, the...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-56 shows a box of mass m2 = 1.0 kg on...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-47 shows Atwoods machine, in which two...Ch. 5 - GO Figure 5-57 shows a section of a cable-car...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-58 shows three blocks attached by cords...Ch. 5 - A shot putter launches a 7.260 kg shot by pushing...Ch. 5 - In Fig. 5-59, 4.0 kg block A and 6.0 kg block B...Ch. 5 - An 80 kg man drops to a concrete patio from a...Ch. 5 - SSM Figure 5-60 shows a box of dirty money mass m1...Ch. 5 - Three forces act on a particle that moves with...Ch. 5 - SSM In Fig. 5-61, a tin of antioxidants m1 = 1.0...Ch. 5 - The only two forces acting on a body have...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-62 is an overhead view of a 12 kg tire...Ch. 5 - A block of mass M is pulled along a horizontal...Ch. 5 - SSM A worker drags a crate across a factory floor...Ch. 5 - In Fig. 5-64, a force F of magnitude 12 N is...Ch. 5 - A certain particle has a weight of 22 N at a point...Ch. 5 - An 80 kg person is parachuting and experiencing a...Ch. 5 - A spaceship lifts off vertically from the Moon,...Ch. 5 - In the overhead view of Fig. 5-65, five forces...Ch. 5 - SSM A certain force gives an object of mass m1 an...Ch. 5 - Prob. 84PCh. 5 - A 52 kg circus performer is to slide down a rope...Ch. 5 - Compute the weight of a 75 kg space ranger a on...Ch. 5 - An object is hung from a spring balance attached...Ch. 5 - Imagine a landing craft approaching the surface of...Ch. 5 - A 1400 kg jet engine is fastened to the fuselage...Ch. 5 - An interstellar ship has a mass of 1.20 106 kg...Ch. 5 - SSM A motorcycle and 60.0 kg rider accelerate at...Ch. 5 - Prob. 92PCh. 5 - SSM Figure 5-66a shows a mobile hanging from a...Ch. 5 - For sport, a 12 kg armadillo runs onto a large...Ch. 5 - Suppose that in Fig. 5-12, the masses of the...Ch. 5 - A nucleus that captures a stray neutron must bring...Ch. 5 - If the 1 kg standard body is accelerated by only...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
PRACTICE 1.3 The melting point of table salt is 1474oF. What temperature is this on the Celsius and Kelvin scal...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Match the following cell types with their correct definition. _________Macrophage _________NK cell _________Eos...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
56. Global Positioning System. Learn more about the global positioning system and its uses. Write a short repo...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
A compressor brings nitrogen from 100kPa,290K to 2000kPa . The process has a specific work input of 450kJ/kg an...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
a. Which compound has the stretching vibration for its carbonyl group at the highest frequency: acetyl chloride...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Is work function of a metals surface related to surface energy and surface tension? What is the need to the work function component in the math of tension of metal surfaces that cannot be provided by existing equations of surface energy and surface tension? What are the key differences in each parameter and variables that allow for a differentiation of each function? What has a more significant meaning work function, surface tension or surface energy? Are there real differences and meaning? Please clarify and if possible provide examples . Does surface tension dependant on thickness of a metal or type of metal surface all having the same thickness? Clearly temperature has a profound change on surface tension what other variables besides temperature are key to surface tension. What if any is there a connection between crystal structure of the element and surface energy and tension? This is NOT a Assignment Question!!!arrow_forwardThe cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field? V/marrow_forwardConsider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...? a. Both rods have less mass b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass c. both rods have more mass d. the masses of both rods are unchanged e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe massarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY