
What is the difference between an atom’s ground state and an excited state?
Interpretation:
Difference between atoms’ ground state and an excited state.
Concept introduction:
Atoms have different energy states. The ground state and exited state, define energy level of the electrons present in atom.
Answer to Problem 61A
| Sr. No. | Difference between ground state and exited state of an atom | |
| Ground state | Exited state | |
| 1. | Ground state is the state in which all electrons in an atom are present in lowest possible energy level. | Exited state is the state in which electrons in an atom are present in higher energy level. |
| 2. | The electron in this state have zero energy | The electron in this state have high energy |
| 3. | The electrons of the atom are highly stable | The electrons of the atom are highly unstable |
| 4. | The distance between electrons and nucleus of the atom is least possible distance | The distance between electrons and nucleus of the atom is higher than ground state |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
ground state and excited state of atom
The ground state is the lowest possible energy level that the electrons of an atom can have. The energy states for electrons are unique means that they have specific values only. The electrons of an atom can only move to another energy level after emitting or absorbing a particular amount of energy which is equal to the difference between two energy states. An excited state is an energy state of an atom in which the electrons of an atom is said to be at a higher energy level as compared to ground state.
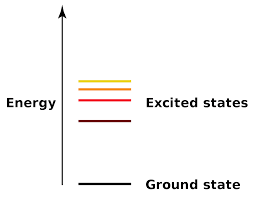
The ground state is the lowest possible energy level that an atom can have. An excited state is state where the electrons of an atom have higher energy.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Look the image attaarrow_forwardPart C: Communication (/9) 17. Compare and contrast the Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr models of the atom using the chart below. You can use words and/or diagrams in your answers. (9) What was the experiment that led to the model? Where is positive charge in the atom located in the model? Where are electrons located in the molecule? Thomson Model Rutherford Model Bohr Model 2arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. Mg(s) ∣ Mg2+(aq, 2.74 M) || Cu2+(aq, 0.0033 M) ∣ Cu(s)arrow_forward
- Calculate E° for Ni(glycine)2 + 2e– D Ni + 2 glycine– given Ni2+ + 2 glycine– D Ni(glycine)2 K = 1.2×1011 Ni2+ + 2 e– D Ni E° = -0.236 Varrow_forwardOne method for the analysis of Fe3+, which is used with a variety of sample matrices, is to form the highly colored Fe3+–thioglycolic acid complex. The complex absorbs strongly at 535 nm. Standardizing the method is accomplished using external standards. A 10.00-ppm Fe3+ working standard is prepared by transferring a 10-mL aliquot of a 100.0 ppm stock solution of Fe3+ to a 100-mL volumetric flask and diluting to volume. Calibration standards of 1.00, 2.00, 3.00, 4.00, and 5.00 ppm are prepared by transferring appropriate amounts of the 10.0 ppm working solution into separate 50-mL volumetric flasks, each of which contains 5 mL of thioglycolic acid, 2 mL of 20% w/v ammonium citrate, and 5 mL of 0.22 M NH3. After diluting to volume and mixing, the absorbances of the external standards are measured against an appropriate blank. Samples are prepared for analysis by taking a portion known to contain approximately 0.1 g of Fe3+, dissolving it in a minimum amount of HNO3, and diluting to…arrow_forwardAbsorbance and transmittance are related by: A = -log(T) A solution has a transmittance of 35% in a 1-cm-pathlength cell at a certain wavelength. Calculate the transmittance if you dilute 25.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL? (A = εbc) What is the transmittance of the original solution if the pathlength is increased to 10 cm?arrow_forward
- Under what conditions will Beer’s Law most likely NO LONGER be linear? When the absorbing species is very dilute. When the absorbing species participates in a concentration-dependent equilibrium. When the solution being studied contains a mixture of ions.arrow_forwardCompared to incident (exciting) radiation, fluorescence emission will have a: Higher energy Higher frequency Longer wavelengtharrow_forwardLin and Brown described a quantitative method for methanol based on its effect on the visible spectrum of methylene blue. In the absence of methanol, methylene blue has two prominent absorption bands at 610 nm and 663 nm, which correspond to the monomer and the dimer, respectively. In the presence of methanol, the intensity of the dimer’s absorption band decreases, while that for the monomer increases. For concentrations of methanol between 0 and 30% v/v, the ratio of the two absorbance, A663/ A610, is a linear function of the amount of methanol. Use the following standardization data to determine the %v/v methanol in a sample if A610 is 0.75 and A663 is 1.07.arrow_forward
- The crystal field splitting energy, Δ, of a complex is determined to be 2.9 × 10-19 What wavelength of light would this complex absorb? What color of light is this? What color would the compound be in solution?arrow_forwardA key component of a monochromator is the exit slit. As the exit slit is narrowed, the bandwidth of light (i.e., the range of wavelengths) exiting the slit gets smaller, leading to higher resolution. What is a possible disadvantage of narrowing the exit slit? (Hint: why might a narrower slit lower the sensitivity of the measurement?).arrow_forwardAn x-ray has a frequency of 3.33 × 1018 What is the wavelength of this light?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





