
a.
Sketch a
a.
Answer to Problem 3P
The scatter plot is
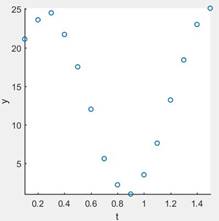
Explanation of Solution
Given: A set of the data is,
Calculation:
Let’s take a given data set sketch a scatter plot using MATLAB.
The function is using in the MATLAB to sketch a scatter plot is,
Program:
clc
clear
close all
t=[0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5];
y=[21.1 23.6 24.5 21.7 17.5 12.0 5.6 2.2 1.0 3.5 7.6 13.2 18.4 23.0 25.1];
scatter(t,y,'linewidth',1.25');
set(gca,'Linewidth',1.2,'Fontsize',12);
xlabel('t');
ylabel('y')
axis square
axis tight
Query:
- First, we have defined the given data sets.
- Then using a function “scatter (t, y)” sketch a scatter plot.
b.
Calculate the cosine function using given data set.
b.
Answer to Problem 3P
The cosine function is,
Explanation of Solution
Given: A set of the data is,
Calculation:
First, we have to write a general equation of the cosine function,
Then, calculate the vertical shifting as,
Calculate the amplitude as,
Then, Calculate the phase shift as,
The value of c is,
Put all the value into the equation (1) then,
Program:
clc clear close all t=[0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5]; y=[21.1 23.6 24.5 21.7 17.5 12.0 5.6 2.2 1.0 3.5 7.6 13.2 18.4 23.0 25.1]; b=(1/2)*(max(y)+min(y)); a=(1/2)*(max(y)-min(y)); w=2*pi/max(t); idx=find(y==max(y)); c=t(idx); f=(a*cos(w*(t-c)))+b;
Query:
- First, we have defined the given data sets.
- Then calculate the value of b, a, w, and c.
- Put all the values into the equation of cosine function and get the solution.
c.
Sketch a graph of the function which is found in part (b).
c.
Answer to Problem 3P
The solution is,
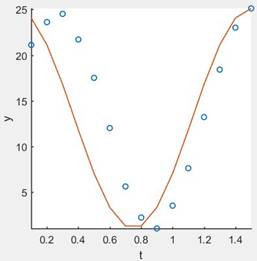
Explanation of Solution
Given: A set of the data is,
Calculation:
Sketch a graph of the cosine function in MATLAB using function “plot (f, t)”.
The function is found in part (b) is,
Program:
clc
clear
close all
t=[0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5];
y=[21.1 23.6 24.5 21.7 17.5 12.0 5.6 2.2 1.0 3.5 7.6 13.2 18.4 23.0 25.1];
b=(1/2)*(max(y)+min(y));
a=(1/2)*(max(y)-min(y));
w=2*pi/max(t);
idx=find(y==max(y));
c=t(idx);
f=(a*cos(w*(t-c)))+b;
scatter(t,y,'linewidth',1.25');
hold on
plot(t,f,'linewidth',1.25');
set(gca,'Linewidth',1.2,'Fontsize',12);
xlabel('t');
ylabel('y')
axis square
axis tight
Query:
- First, we have defined the given data sets.
- Then calculate the value of b, a, w, and c.
- Put all the values into the equation of cosine function and get the solution.
- Then sketch a graph.
d.
Calculate the sine function using given data set.
d.
Answer to Problem 3P
The cosine function is,
Explanation of Solution
Given: A set of the data is,
Calculation:
First, we have to write a general equation of the cosine function,
Then, calculate the vertical shifting as,
Calculate the amplitude as,
Then, Calculate the phase shift as,
The value of c is,
Put all the value into the equation (1) then,
Program:
clc clear close all t=[0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5]; y=[21.1 23.6 24.5 21.7 17.5 12.0 5.6 2.2 1.0 3.5 7.6 13.2 18.4 23.0 25.1]; b=(1/2)*(max(y)+min(y)); a=(1/2)*(max(y)-min(y)); w=2*pi/max(t); idx=find(y==max(y)); c=t(idx); f=(a*sin(w*(t+c)))+b;
Query:
- First, we have defined the given data sets.
- Then calculate the value of b, a, w, and c.
- Put all the values into the equation of cosine function and get the solution.
e.
Compare the results from part (b) and (c).
e.
Answer to Problem 3P
Using reduction relation, the graph of the given data is,
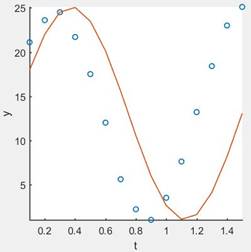
Explanation of Solution
Given: the reduction formula,
Calculation:
As we can see in part (d) the sine function is,
Where,
Then rewrite the function as,
Simplify the above function and sketch a graph.
Program:
clc
clear
close all
t=[0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 325 350];
y=[190 175 155 125 110 95 105 120 140 165 185 200 195 185 165];
b=(1/2)*(max(y)+min(y));
a=(1/2)*(max(y)-min(y));
w=2*pi/max(t);
idx=find(y==max(y));
c=t(idx);
f=(a*cos(w*(t+c)-pi/2))+b;
scatter(t,y,'linewidth',1.25');
hold on
plot(t,f,'linewidth',1.25');
set(gca,'linewidth',1.2,'fontsize',12);
xlabel('t');
ylabel('y')
axis square
axis tight
Query:
- First, we have defined the given data sets.
- Then calculate the value of b, a, w, and c.
- Then using reduction relation redefine the function.
- Sketch a graph.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus - 6th Edition
- (6 points) Let S be the surface z = 1 − x² - y², x² + y² ≤1. The boundary OS of S is the unit circle x² + y² = 1. Let F(x, y, z) = (x², y², z²). Use the Stokes' Theorem to calculate the line integral Hint: First calculate V x F. Jos F F.ds.arrow_forward(28 points) Define T: [0,1] × [−,0] → R3 by T(y, 0) = (cos 0, y, sin 0). Let S be the half-cylinder surface traced out by T. (a) (4 points) Calculate the normal field for S determined by T.arrow_forwardI need the last answer t=? I did got the answer for the first two this is just homework.arrow_forward
- 7) 8) Let R be the region bounded by the given curves as shown in the figure. If the line x = k divides R into two regions of equal area, find the value of k 7. y = 3√x, y = √x and x = 4 8. y = -2, y = 3, x = −3, and x = −1 -1 2 +1 R Rarrow_forwardSolve this question and show steps.arrow_forwardu, v and w are three coplanar vectors: ⚫ w has a magnitude of 10 and points along the positive x-axis ⚫ v has a magnitude of 3 and makes an angle of 58 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ u has a magnitude of 5 and makes an angle of 119 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ vector v is located in between u and w a) Draw a diagram of the three vectors placed tail-to-tail at the origin of an x-y plane. b) If possible, find w × (ū+v) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. c) If possible, find v. (ū⋅w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. d) If possible, find u. (vxw) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. Note: in this question you can work with the vectors in geometric form or convert them to algebraic vectors.arrow_forward
- Question 3 (6 points) u, v and w are three coplanar vectors: ⚫ w has a magnitude of 10 and points along the positive x-axis ⚫ v has a magnitude of 3 and makes an angle of 58 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ u has a magnitude of 5 and makes an angle of 119 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ vector v is located in between u and w a) Draw a diagram of the three vectors placed tail-to-tail at the origin of an x-y plane. b) If possible, find w × (u + v) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. c) If possible, find v. (ū⋅ w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. d) If possible, find u (v × w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. Note: in this question you can work with the vectors in geometric form or convert them to algebraic vectors.arrow_forwardK Find all values x = a where the function is discontinuous. For each value of x, give the limit of the function as x approaches a. Be sure to note when the limit doesn't exist. x-7 p(x) = X-7 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) within your choice. (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) OA. f is discontinuous at the single value x = OB. f is discontinuous at the single value x= OC. f is discontinuous at the two values x = OD. f is discontinuous at the two values x = The limit is The limit does not exist and is not co or - ∞. The limit for the smaller value is The limit for the larger value is The limit for the smaller value is The limit for the larger value does not exist and is not c∞ or -arrow_forwardK x3 +216 complete the table and use the results to find lim k(x). If k(x) = X+6 X-6 X -6.1 -6.01 - 6.001 - 5.999 - 5.99 -5.9 k(x) Complete the table. X -6.1 -6.01 - 6.001 - 5.999 - 5.99 - 5.9 k(x) (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the limit. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





