
Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780073529592
Author: Giorgio Rizzoni Professor of Mechanical Engineering, James A. Kearns Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.28HP
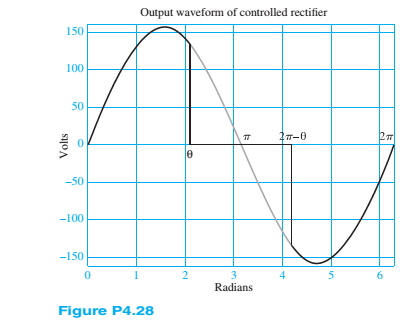
The output voltage waveform of a controlled rectifier is shown in Figure P4.28. The input voltage waveform was a sinusoid of amplitude 110 V rms.Find the average and rms voltages of the output waveform in terms of the firing angle
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An evening meal is being prepared in a home kitchen containing an electric oven and a microwave oven. The cost for electricity in the home's neighborhood is $0.15 per kilowatt hour. The microwave oven is specified as a 1000 watt unit, while the oven requires 240 volts and uses a current of 30 amperes to cook at 350 degrees Fahrenheit. A frozen meal can be cooked in the microwave oven set on full power in 10 minutes. The same frozen meal cooked in the electric oven set for 350 degrees F takes 40 minutes.
(a) How much energy does it take to cook the frozen meal in the microwave at full power and how much does it cost?
(b) How much energy does it take to cook the frozen meal in the electric oven at 350 degrees Fahrenheit and how much does it cost?
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
An electrical substation had a sudden discharge arc event lasting 0.005 seconds. The event produced 768,000 volts that conducted 500 amperes to a nearby grounded metal strap and opened a 500 ampere protective breaker.
(a) How much power was produced by the electrical discharge?
(b) How much energy was in the discharge?
(c) How long could a 75 watt light bulb stay lit, if all the energy in the arc was used to operate it?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering
Ch. 4 - The current through a 0.8-H inductor is given by...Ch. 4 - For each case shown below, derive the expression...Ch. 4 - Derive the expression for the voltage across...Ch. 4 - In the circuit shown in Figure P4.4, assume R=1...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.5HPCh. 4 - In the circuit shown in Figure P4.4, assume R=2...Ch. 4 - In the circuit shown in Figure P4.7, assume R=2...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.8HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.9HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.10HP
Ch. 4 - The voltage waveform shown in Figure P4.10 is...Ch. 4 - The voltage across a 0.5-mH inductor, Plotted as a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.13HPCh. 4 - The current through a 16-H inductor is zero at t=0...Ch. 4 - The voltage across a generic element X has the...Ch. 4 - The plots shown in Figure P4.16 are the voltage...Ch. 4 - The plots shown in Figure P4.17 are the voltage...Ch. 4 - The plots shown in Figure P4.18 are the voltage...Ch. 4 - The plots shown in Figure P4.19 are the voltage...Ch. 4 - The voltage vL(t) across a 10-mH inductor is shown...Ch. 4 - The current through a 2-H inductor is p1otted in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.22HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.23HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.24HPCh. 4 - The voltage vC(t) across a capacitor is shown in...Ch. 4 - The voltage vL(t) across an inductor is shown in...Ch. 4 - Find the average and rms values of x(t) when:...Ch. 4 - The output voltage waveform of a controlled...Ch. 4 - Refer to Problem 4.28 and find the angle + that...Ch. 4 - Find the ratio between the average and rms value...Ch. 4 - The current through a 1- resistor is shown in...Ch. 4 - Derive the ratio between the average and rms value...Ch. 4 - Find the rms value of the current waveform shown...Ch. 4 - Determine the rms (or effective) value of...Ch. 4 - Assume steady-state conditions and find the energy...Ch. 4 - Assume steady-state conditions and find the energy...Ch. 4 - Find the phasor form of the following functions:...Ch. 4 - Convert the following complex numbers to...Ch. 4 - Convert the rectangular factors to polar form and...Ch. 4 - Complete the following exercises in complex...Ch. 4 - Convert the following expressions to rectangular...Ch. 4 - Find v(t)=v1(t)+v2(t) where...Ch. 4 - The current through and the voltage across a...Ch. 4 - Express the sinusoidal waveform shown in Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.45HPCh. 4 - Convert the following pairs of voltage and current...Ch. 4 - Determine the equivalent impedance seen by the...Ch. 4 - Determine the equivalent impedance seen by the...Ch. 4 - The generalized version of Ohm’s law for impedance...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.50HPCh. 4 - Determine the voltage v2(t) across R2 in the...Ch. 4 - Determine the frequency so that the current Ii...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.53HPCh. 4 - Use phasor techniques to solve for the current...Ch. 4 - Use phasor techniques to solve for the voltage...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.56HPCh. 4 - Solve for VR shown in Figure P4.57. Assume:...Ch. 4 - With reference to Problem 4.55, find the value of ...Ch. 4 - Find the current iR(t) through the resistor shown...Ch. 4 - Find vout(t) shown in Figure P4.60.Ch. 4 - Find the impedance Z shown in Figure...Ch. 4 - Find the sinusoidal steady-state output vout(t)...Ch. 4 - Determine the voltage vL(t) across the inductor...Ch. 4 - Determine the current iR(t) through the resistor...Ch. 4 - Find the frequency that causes the equivalent...Ch. 4 - a. Find the equivalent impedance Zo seen by the...Ch. 4 - A common model for a practical capacitor has...Ch. 4 - Using phasor techniques, solve for vR2 shown in...Ch. 4 - Using phasor techniques to solve for iL in the...Ch. 4 - Determine the Thévenin equivalent network seen by...Ch. 4 - Determine the Norton equivalent network seen by...Ch. 4 - Use phasor techniques to solve for iL(t) in...Ch. 4 - Use mesh analysis to determine the currents i1(t)...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.74HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.75HPCh. 4 - Find the Thévenin equivalent network seen by the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.77HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.78HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.79HPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.80HPCh. 4 - Use mesh analysis to find the phasor mesh current...Ch. 4 - Write the node equations required to solve for all...Ch. 4 - Determine Vo in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.84HP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardFind Rth at open terminals using a 1V test source.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- How many atoms are there in a simple cubic unit cell? in a bcc unit cell? in a fcc unit cell? in the unit cell characterizing the diamond lattice?arrow_forwardConsider the homogeneous RLC circuit (no voltage source) shown in the diagram below. Before the switch is closed, the capacitor has an initial charge go and the circuit has an initial current go- R 9(1) i(t)↓ After the switches closes, current flows through the circuit and the capacitor begins to discharge. The equation that describes the total voltage in the loop comes from Kirchoff's voltage law: L di(t) + Ri(t)+(0) = 0, (1) where i(t) and q(t) are the current and capacitor charge as a function of time, L is the inductance, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance. Using the fact that the current equals the rate of change of the capacitor charge, and dividing by L, we can write the following homogeneous (no input source) differential equation for the charge on the capacitor: 4(1) +29(1)+w79(1)=0, ཀྱི where a= R 2L and The solution to this second order linear differential equation can be written as: 9(1) =Aent - Beat, where (3) (4) (5) A= (81+20)90 +90 (82+20)90 +90 and B= (6)…arrow_forwardConsider the homogeneous RLC circuit (no voltage source) shown in the diagram below. Before the switch is closed, the capacitor has an initial charge go and the circuit has an initial current go. R w i(t) q(t) C н After the switches closes, current flows through the circuit and the capacitor begins to discharge. The equation that describes the total voltage in the loop comes from Kirchoff's voltage law: di(t) L + Ri(t) + (t) = 0, dt (1) where i(t) and q(t) are the current and capacitor charge as a function of time, L is the inductance, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance. Using the fact that the current equals the rate of change of the capacitor charge, and dividing by L, we can write the following homogeneous (no input source) differential equation for the charge on the capacitor: ä(t)+2ag(t)+wg(t) = 0, (2) where R a 2L and w₁ = C LC The solution to this second order linear differential equation can be written as: where 81= q(t) = Ae³¹- Bel 82 = (3) (4) (5)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardFind Rth at open terminals using a 1V test source.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
19 Power Diodes | Power Electronics; Author: Walid Issa Plus;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_E-4bIYlNYQ;License: Standard Youtube License