
(a)
Cost matrix with 20% off on 10 MP cameras and 10% off on other models.
(a)
Answer to Problem 44PPS
Cost matrix after discount:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Digital cameras prices based on features like optical zoom, digital zoom, and megapixels:
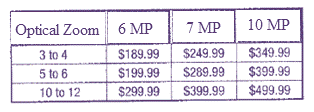
Matrix representing the actual prices of digital cameras:
According to the statement,
There is 20% off on 10 MP cameras.
And
There is 10% off on other models.
Such that
From the table,
For 10 MP cameras:
The cost of 10 MP cameras with optical zoom of 3 to 4 is $349.99.
After 20% off,
The cost of 10 MP cameras with optical zoom of 3 to 4 is $279.99.
For other models:
The cost of 6 MP cameras with optical zoom of 3 to 4 is $189.99.
After 10% off,
The cost of 6 MP cameras with optical zoom of 3 to 4 is $170.99.
Thus,
After discount,
The cost matrix becomes
(b)
Matrix allowing 6.25% sales tax on the discounted prices.
(b)
Answer to Problem 44PPS
After 6.25% sales tax:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Digital cameras prices based on features like optical zoom, digital zoom, and megapixels:
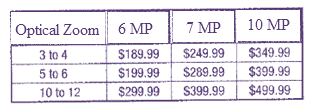
While adding the sales tax of 6.25% on the discounted prices,
Each amount to be multiplied by 1.0625:
Simplify:
Thus,
After allowing 6.25% sales tax on discounted prices,
The matrix becomes
(c)
Discuss the difference in matrices from Part (a) and Part (b) represent.
(c)
Answer to Problem 44PPS
Difference matrix:
This matrix represents the difference after sales tax was imposed on discounted prices.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Digital cameras prices based on features like optical zoom, digital zoom, and megapixels:
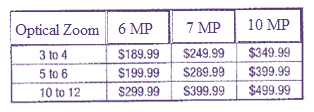
Matrix from Part (a) result:
Matrix from Part (b) result:
Difference between the two matrices:
Subtract the corresponding values:
Simplify:
Thus,
The difference matrix:
This matrix represents the difference after sales tax was imposed on discounted prices.
The prices for the one that does include tax are of course greater.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- please Solve questions by Course Name( Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardInThe Northern Lights are bright flashes of colored light between 50 and 200 miles above Earth. Suppose a flash occurs 150 miles above Earth. What is the measure of arc BD, the portion of Earth from which the flash is visible? (Earth’s radius is approximately 4000 miles.)arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- Suppose you flip a fair two-sided coin four times and record the result. a). List the sample space of this experiment. That is, list all possible outcomes that could occur when flipping a fair two-sided coin four total times. Assume the two sides of the coin are Heads (H) and Tails (T).arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardEvaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





