
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305932302
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 35, Problem 45P
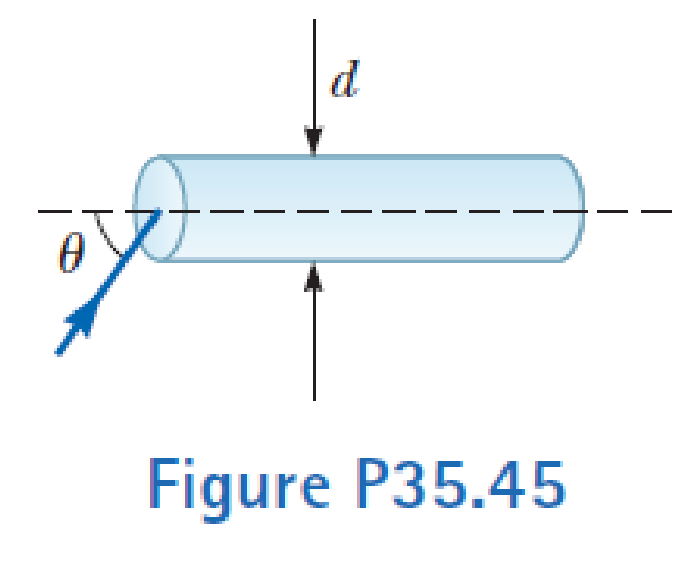
Assume a transparent rod of diameter d = 2.00 µm has an index of refraction of 1.36. Determine the maximum angle θ for which the light rays incident on the end of the rod in Figure P35.45 are subject to total internal reflection along the walls of the rod. Your answer defines the size of the cone of acceptance for the rod.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A (3.60 m)
30.0°-
70.0°
x
B (2.40 m)
In general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in
space, and then to make calculations with them using
their components. (You must first specify a coordinate
system in order to find the components of each arrow.)
This problem gives you some practice with the
components.
Let vectors A = (1,0, -3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and
C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your
answers as ordered triplets of values separated by
commas.
fine the magnitude of the vector product express in sq meters
what direction is the vector product in -z or +z
Chapter 35 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
Ch. 35.4 - Prob. 35.1QQCh. 35.5 - If beam is the incoming beam in Figure 34.10b,...Ch. 35.5 - Light passes from a material with index of...Ch. 35.7 - Prob. 35.4QQCh. 35.8 - Prob. 35.5QQCh. 35 - Prob. 1OQCh. 35 - Prob. 2OQCh. 35 - Prob. 3OQCh. 35 - Prob. 4OQCh. 35 - Prob. 5OQ
Ch. 35 - Prob. 6OQCh. 35 - Prob. 7OQCh. 35 - Prob. 8OQCh. 35 - Prob. 9OQCh. 35 - Prob. 10OQCh. 35 - Prob. 11OQCh. 35 - Prob. 12OQCh. 35 - Prob. 13OQCh. 35 - Prob. 14OQCh. 35 - Prob. 15OQCh. 35 - Prob. 1CQCh. 35 - Prob. 2CQCh. 35 - Prob. 3CQCh. 35 - Prob. 4CQCh. 35 - Prob. 5CQCh. 35 - Prob. 6CQCh. 35 - Prob. 7CQCh. 35 - Prob. 8CQCh. 35 - Prob. 9CQCh. 35 - Prob. 10CQCh. 35 - Prob. 11CQCh. 35 - (a) Under what conditions is a mirage formed?...Ch. 35 - Prob. 13CQCh. 35 - Prob. 14CQCh. 35 - Prob. 15CQCh. 35 - Prob. 16CQCh. 35 - Prob. 17CQCh. 35 - Prob. 1PCh. 35 - Prob. 2PCh. 35 - In an experiment to measure the speed of light...Ch. 35 - As a result of his observations, Ole Roemer...Ch. 35 - Prob. 5PCh. 35 - Prob. 6PCh. 35 - Prob. 7PCh. 35 - Prob. 8PCh. 35 - Prob. 9PCh. 35 - Prob. 10PCh. 35 - Prob. 11PCh. 35 - A ray of light strikes a flat block of glass (n =...Ch. 35 - Prob. 13PCh. 35 - Prob. 14PCh. 35 - Prob. 15PCh. 35 - Prob. 16PCh. 35 - Prob. 17PCh. 35 - Prob. 18PCh. 35 - When you look through a window, by what time...Ch. 35 - Two flat, rectangular mirrors, both perpendicular...Ch. 35 - Prob. 21PCh. 35 - Prob. 22PCh. 35 - Prob. 23PCh. 35 - Prob. 24PCh. 35 - Prob. 25PCh. 35 - Prob. 26PCh. 35 - Prob. 27PCh. 35 - Prob. 28PCh. 35 - Prob. 29PCh. 35 - Prob. 30PCh. 35 - Prob. 31PCh. 35 - Prob. 32PCh. 35 - Prob. 33PCh. 35 - A submarine is 300 m horizontally from the shore...Ch. 35 - Prob. 35PCh. 35 - Prob. 36PCh. 35 - Prob. 37PCh. 35 - Prob. 39PCh. 35 - Prob. 40PCh. 35 - Prob. 41PCh. 35 - Prob. 42PCh. 35 - Prob. 43PCh. 35 - Prob. 44PCh. 35 - Assume a transparent rod of diameter d = 2.00 m...Ch. 35 - Consider a light ray traveling between air and a...Ch. 35 - Prob. 47PCh. 35 - Prob. 48PCh. 35 - Prob. 49PCh. 35 - Prob. 50PCh. 35 - Prob. 51APCh. 35 - Prob. 52APCh. 35 - Prob. 53APCh. 35 - Prob. 54APCh. 35 - Prob. 55APCh. 35 - Prob. 56APCh. 35 - Prob. 57APCh. 35 - Prob. 58APCh. 35 - Prob. 59APCh. 35 - A light ray enters the atmosphere of a planet and...Ch. 35 - Prob. 61APCh. 35 - Prob. 62APCh. 35 - Prob. 63APCh. 35 - Prob. 64APCh. 35 - Prob. 65APCh. 35 - Prob. 66APCh. 35 - Prob. 67APCh. 35 - Prob. 68APCh. 35 - Prob. 69APCh. 35 - Prob. 70APCh. 35 - Prob. 71APCh. 35 - Prob. 72APCh. 35 - Prob. 73APCh. 35 - Prob. 74APCh. 35 - Prob. 75APCh. 35 - Prob. 76APCh. 35 - Prob. 77APCh. 35 - Prob. 78APCh. 35 - Prob. 79APCh. 35 - Prob. 80APCh. 35 - Prob. 81CPCh. 35 - Prob. 82CPCh. 35 - Prob. 83CPCh. 35 - Prob. 84CPCh. 35 - Prob. 85CPCh. 35 - Prob. 86CPCh. 35 - Prob. 87CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4) Three point charges of magnitude Q1 = +2.0 μC, Q2 = +3.0 μС, Q3 = = +4.0 μС are located at the corners of a triangle as shown in the figure below. Assume d = 20 cm. (a) Find the resultant force vector acting on Q3. (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the force. d Q3 60° d Q1 60° 60° Q2 darrow_forwardThree point charges of magnitudes Q₁ = +6.0 μС, Q₂ = −7.0 μС, Qз = −13.0 μC are placed on the x-axis at x = 0 cm, x = 40 cm, and x = 120 cm, respectively. What is the force on the Q3 due to the other two charges?arrow_forwardTwo point charges of +30.0 μС and -9.00 μC are separated by a distance of 20.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges?arrow_forward
- Two point charges of +7.00 μС and +10.0 μС are placed inside a cube of edge length 0.100 m. What is the net electric flux due to these charges?arrow_forwardA conducting hollow sphere has a charge density of σ = 12.2 μC/m². If the sphere has a radius of 25 cm, what net charge is on the sphere?arrow_forward9) Consider an electric field right Ĕ = 21+3ĵ. What is the magnitude of the flux of this field through a 4.0 m² square surface whose corners are located at (x,y,z) = (0, 2, 1), (2, 2, 1), (2, 2, −1), (0, 2, −1)? Ꮓ ту x (0,2,1) Surface 2 Surface (2,2,1) y Ē (0,2,-1) (2,2,-1) 2 xarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward2 聯梧桐紀 PAGENIN ERA 5 7 DOG FAMILY puppies C01: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements 4 A student wanted to measure the diameter of a cylindrical water bottle. Which of the following gives the most accurate measurement? A B CD Take three measurements of the diameter using a rule before finding the average. Take three measurements of the diameter using a digital micrometer screw gauge, resetting to zero before every measurement before finding the average. Take three measurements of the diameter using the digital calipers, resetting to zero before every measurement before finding the average. Take three measurements of the diameter using the digital calipers without resetting to zero before every measurement before finding the average. The resultant force FR acting on an object is given by, FR = ma, where m is the mass of the object in kg and a is the acceleration of the object in m/s². Which unit is equivalent to the unit for force? A B с D kg ms² kg m²s kg m/s² kg m²/s² adt to…arrow_forwardC01: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements 10 A student uses a rule to measure a thin piece of wire. wire 0 1 cm 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 (a) State two errors in the student's measurement of the length of wire. [2] The student records the length of the wire as 12.8 cm. [E] The student is asked to measure the thickness of the wire using a pencil and the same rule. Suggest how this can be done as accurately as possible. [4] (b) The student finds out that the density of the wire is 2.7 g/cm³. Express 2.7 g/cm³ in kg/m³. [2] to V emulov or worl? гавтоха [E11 The length of a sheet of plastic is measured using a 15 cm rule. eq 8 5 Imm 1 2 سيلينا 3 3 5 7 8 10 11 12 13 14 L ins 15 sem of beiupe stipib e elun olfastq e riliw bei inebulz A H com al Jari Inemundeni or ezoori (s) re the sheet of plasticarrow_forward
- tion v more m C01: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements 8 The following shows a pencil. (a) pencil sharpened section Describe how you would use a piece of string and a rule to determine the circumference c of the unsharpened section of the pencil. [3] nd pupp e e E (b) The student's value for the circumference c is 2.5 cm. Suggest a source of error in determining the circumference of the pencil. [1] ntit ble Ec et (c) Show the volume V of the unsharpened section of the pencil is V = c²x [3] ΑΠ 55 sn ar 2 72 C: or n/ el D a 7 9 (d) Express the volume VE of the sharpened section of the pencil in terms of c and y. pilasi to leeries to rignal on [3] State any assumptions made. lau besser A student is required to measure the thickness of a ream of 500 sheets of A4 size paper. He is supplied with a plastic rule, a digital micrometer screw gauge and a pair of digital calipers. (a) Choose the instrument that is most suitable to measure the thickness of the ream of paper. Give two…arrow_forward5 C01: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements 4 Complete the table by stating a suitable instrument for obtaining each of the following lengths to be measured. (6) Length to be measured (a) 12.0 cm (b) 8.880 mm (c) 4.440 cm (d) (e) internal diameter of a test tubes bas thickness of a wire (f) height of a bedroom Suitable Instrument 5 Fill in the blanks by making estimates of each of the following quantities. [5] (a) The thickness of a sheet of paper = mm (b) The time for one heartbeat = (c) The mass of 500 cm3 of water = S g (d) The height of a 4-year-old = 3 (e) The average human reaction time S hoda 6 A student has a stack of 20 identical coins. The following diagram shows the student measuring the height of the stack using a rule.uis en cm 15. 10 7 eye (6) ream of (3) emuntani na mBM (0) 5. stack of 20 coins 0 (b) With his eye at the position shown, the student's measurement of the height of the stack is 6.8 cm. (a) Suggest two reasons why the student's measurement is…arrow_forwardoutside the theory of evolution, the spontaneous emergence of complexity and information from randomness is not recognized in nature. true or falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Laws of Refraction of Light | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4l2thi5_84o;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY