
Concept explainers
The expected angle of refraction in the sheet
Answer to Problem 31P
The expected angle of refraction in the sheet
Explanation of Solution
Assume
The following figure shows the refraction of the laser beam when the sheet
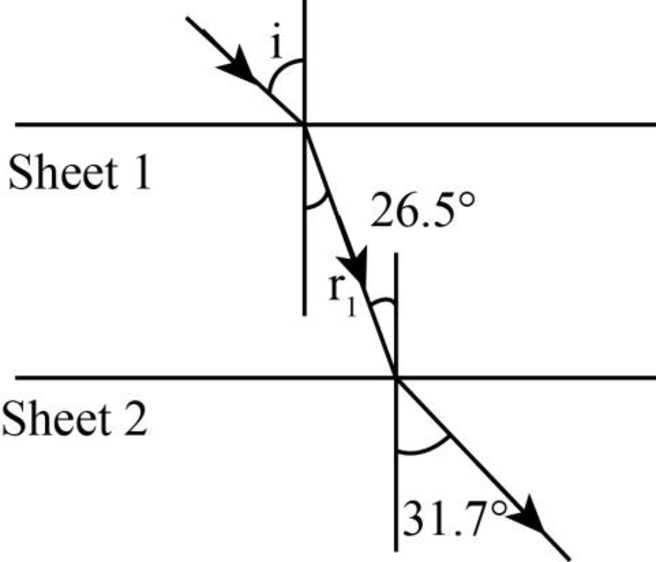
Figure-(1)
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the above figure.
Here,
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the figure-(1).
The following figure shows the refraction of the laser beam when the sheet
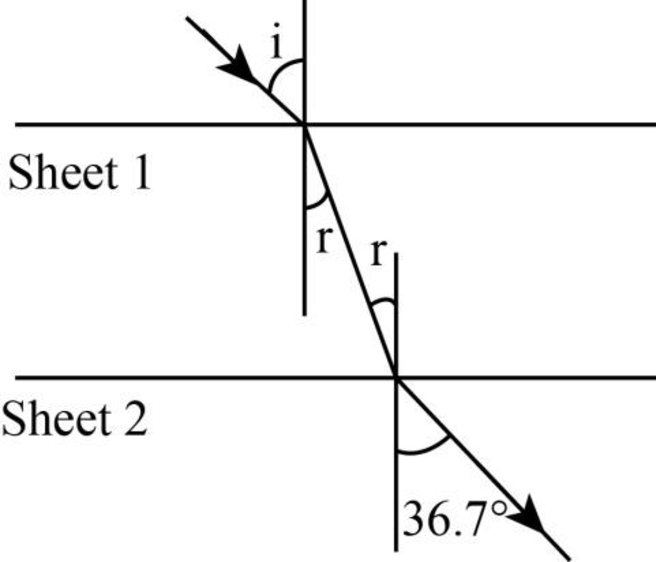
Figure-(2)
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the above figure.
Here,
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the figure-(2).
Compare the equations (III) and (IV).
The following figure shows the refraction of the laser beam when the sheet
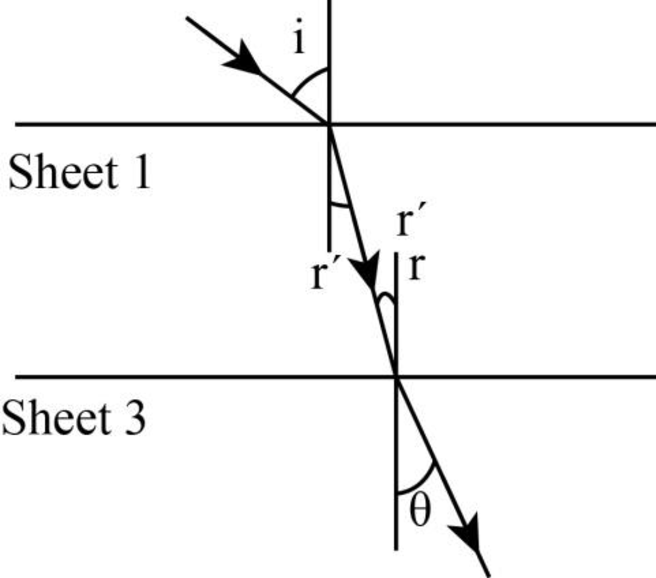
Figure-(3)
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the above figure.
Here,
Write the equation using Snell’s law in the figure-(2).
Here,
Compare the equations (VI) and (VII).
The angle of refraction in the sheet
The angle of refraction in the sheet
Rewrite the equation (IV).
Rewrite the equation (II).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the expected angle of refraction in the sheet
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- The rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forwardA particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward
- 3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward1. Explain the difference between electrical field, potential difference, and electrical potential differencearrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward9. When an electron moves into a uniform and perpendicular magnetic field, it will.. a. Accelerate parallel to the magnetic Field until it leaves b. Accelerate in a circular path c. Accelerate perpendicular to both the magnetic field and its original direction d. Repel back into the electric field 10. If a proton at rest is placed in a uniform magnetic field with no electric or gravitational field around, the proton will…….. a. Accelerate in the direction of the magnetic field b. Accelerate in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field c. Move in a circular path d. Not acceleratearrow_forward7. The electric field at a distance of 1.0 mfrom a charged sphere is 100 N/C. At what distance from thesphere will the electric field be 50 N/C? a. 1.1 m b. 1.4 m c. 2.0 m d. 4.0 m 8. The electric potential due to a point charge at a point depends on a. The direction of the electric field b. The distance from the point charge c. The velocity of the point charge d. The mass of the point chargearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





