
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305932302
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 35.5, Problem 35.2QQ
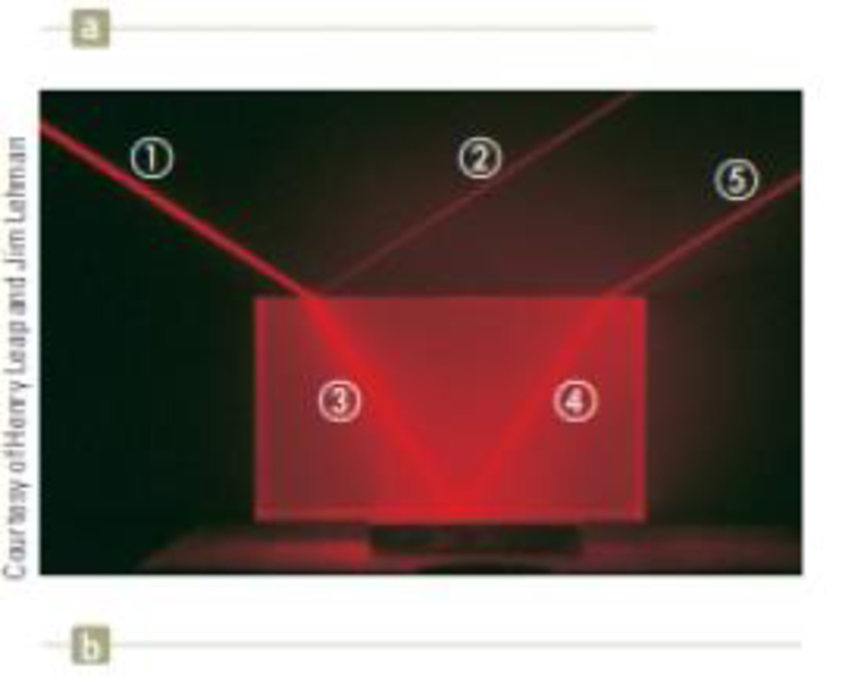
If beam ① is the incoming beam in Figure 34.10b, which of the other four red lines are reflected beams and which are refracted beams?
Figure 34.10 (a) The wave under refraction model. (b) Light incident on the Lucite block refracts both when it enters the block and when it leases the block.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A fluid with density 263 kg/m3 flows through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At location 1 the flow speed is 13.5 m/s and the diameter of the pipe is 7.4 cm down to location 2 the pipe diameter is 16.9 cm. Location 1 is 6.3 meters higher than location 2.
What is the difference in pressure P2 - P1?
Using units in Pascals and use g = 9.81 m/s2.
The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?
Water is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?
Chapter 35 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
Ch. 35.4 - Prob. 35.1QQCh. 35.5 - If beam is the incoming beam in Figure 34.10b,...Ch. 35.5 - Light passes from a material with index of...Ch. 35.7 - Prob. 35.4QQCh. 35.8 - Prob. 35.5QQCh. 35 - Prob. 1OQCh. 35 - Prob. 2OQCh. 35 - Prob. 3OQCh. 35 - Prob. 4OQCh. 35 - Prob. 5OQ
Ch. 35 - Prob. 6OQCh. 35 - Prob. 7OQCh. 35 - Prob. 8OQCh. 35 - Prob. 9OQCh. 35 - Prob. 10OQCh. 35 - Prob. 11OQCh. 35 - Prob. 12OQCh. 35 - Prob. 13OQCh. 35 - Prob. 14OQCh. 35 - Prob. 15OQCh. 35 - Prob. 1CQCh. 35 - Prob. 2CQCh. 35 - Prob. 3CQCh. 35 - Prob. 4CQCh. 35 - Prob. 5CQCh. 35 - Prob. 6CQCh. 35 - Prob. 7CQCh. 35 - Prob. 8CQCh. 35 - Prob. 9CQCh. 35 - Prob. 10CQCh. 35 - Prob. 11CQCh. 35 - (a) Under what conditions is a mirage formed?...Ch. 35 - Prob. 13CQCh. 35 - Prob. 14CQCh. 35 - Prob. 15CQCh. 35 - Prob. 16CQCh. 35 - Prob. 17CQCh. 35 - Prob. 1PCh. 35 - Prob. 2PCh. 35 - In an experiment to measure the speed of light...Ch. 35 - As a result of his observations, Ole Roemer...Ch. 35 - Prob. 5PCh. 35 - Prob. 6PCh. 35 - Prob. 7PCh. 35 - Prob. 8PCh. 35 - Prob. 9PCh. 35 - Prob. 10PCh. 35 - Prob. 11PCh. 35 - A ray of light strikes a flat block of glass (n =...Ch. 35 - Prob. 13PCh. 35 - Prob. 14PCh. 35 - Prob. 15PCh. 35 - Prob. 16PCh. 35 - Prob. 17PCh. 35 - Prob. 18PCh. 35 - When you look through a window, by what time...Ch. 35 - Two flat, rectangular mirrors, both perpendicular...Ch. 35 - Prob. 21PCh. 35 - Prob. 22PCh. 35 - Prob. 23PCh. 35 - Prob. 24PCh. 35 - Prob. 25PCh. 35 - Prob. 26PCh. 35 - Prob. 27PCh. 35 - Prob. 28PCh. 35 - Prob. 29PCh. 35 - Prob. 30PCh. 35 - Prob. 31PCh. 35 - Prob. 32PCh. 35 - Prob. 33PCh. 35 - A submarine is 300 m horizontally from the shore...Ch. 35 - Prob. 35PCh. 35 - Prob. 36PCh. 35 - Prob. 37PCh. 35 - Prob. 39PCh. 35 - Prob. 40PCh. 35 - Prob. 41PCh. 35 - Prob. 42PCh. 35 - Prob. 43PCh. 35 - Prob. 44PCh. 35 - Assume a transparent rod of diameter d = 2.00 m...Ch. 35 - Consider a light ray traveling between air and a...Ch. 35 - Prob. 47PCh. 35 - Prob. 48PCh. 35 - Prob. 49PCh. 35 - Prob. 50PCh. 35 - Prob. 51APCh. 35 - Prob. 52APCh. 35 - Prob. 53APCh. 35 - Prob. 54APCh. 35 - Prob. 55APCh. 35 - Prob. 56APCh. 35 - Prob. 57APCh. 35 - Prob. 58APCh. 35 - Prob. 59APCh. 35 - A light ray enters the atmosphere of a planet and...Ch. 35 - Prob. 61APCh. 35 - Prob. 62APCh. 35 - Prob. 63APCh. 35 - Prob. 64APCh. 35 - Prob. 65APCh. 35 - Prob. 66APCh. 35 - Prob. 67APCh. 35 - Prob. 68APCh. 35 - Prob. 69APCh. 35 - Prob. 70APCh. 35 - Prob. 71APCh. 35 - Prob. 72APCh. 35 - Prob. 73APCh. 35 - Prob. 74APCh. 35 - Prob. 75APCh. 35 - Prob. 76APCh. 35 - Prob. 77APCh. 35 - Prob. 78APCh. 35 - Prob. 79APCh. 35 - Prob. 80APCh. 35 - Prob. 81CPCh. 35 - Prob. 82CPCh. 35 - Prob. 83CPCh. 35 - Prob. 84CPCh. 35 - Prob. 85CPCh. 35 - Prob. 86CPCh. 35 - Prob. 87CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forwardWater is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forward
- Jason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. At instant 3, cars P and Q are adjacent to one another (i.e., they have the same position). In the reference frame o f the road, at instant 3 i s the speed o f car Q greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of car P? Explain.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals.arrow_forward
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forwardJust 5 and 6 don't mind 7arrow_forwardIn an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?arrow_forward
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399944
Author:Michael A. Seeds
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY