
Concept explainers
The intensity of transmitted light in terms of the fraction of the incident intensity.
Answer to Problem 87CP
The intensity of transmitted light is
Explanation of Solution
The light ray path which is perpendicular to the diamond surface is as shown in the figure below.
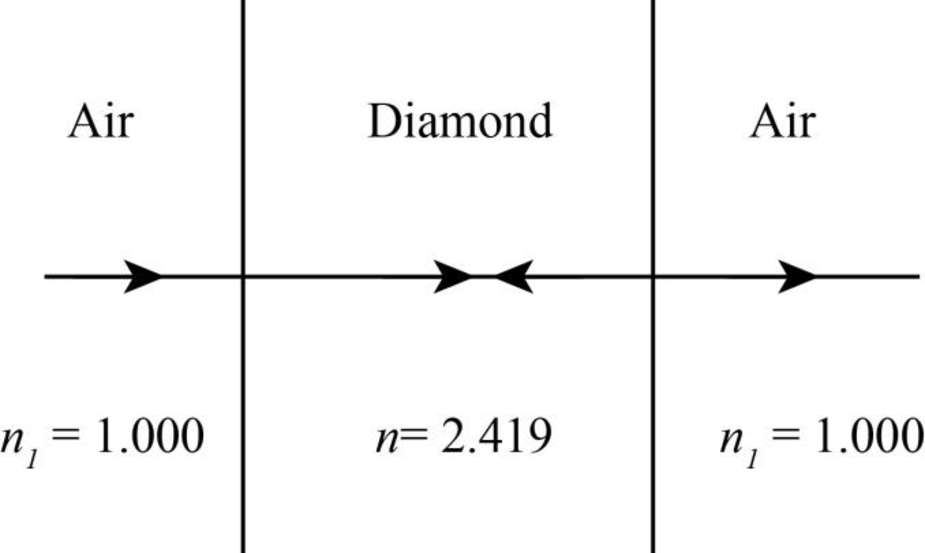
Figure-(1)
Write the expression to obtain the refracted light intensity.
Here,
Re-write the above equation.
Substitute
Here,
Write the expression to obtain the magnitude of the refracted light.
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Here,
Write the expression to obtain the resultant magnitude of the transmitted light through
Here,
Further solve the above equation.
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the intensity of transmitted light is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- You're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





