
Concept explainers
a.
To find the linear model 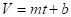
a.
Answer to Problem 35E
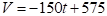
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A laptop computer that costs 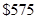 new has a book value of
new has a book value of 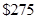 after
after 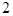 years.
years.
Calculation:
Linear model is 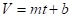
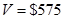 for
for 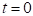
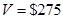 for
for 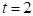
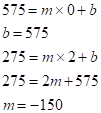
Therefore, the linear model is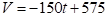 .
.
b.
To find the exponential model 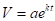
b.
Answer to Problem 35E
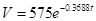
Explanation of Solution
Exponential model is 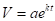
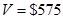 for
for 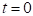
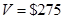 for
for 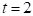
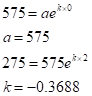
Therefore, the exponential model is 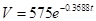
c.
To graph the two models using the graphing utility and find out which model depreciates faster in two years.
c.
Answer to Problem 35E
The exponential model depreciates faster.
Explanation of Solution
The graph for both linear and exponential models are shown below:
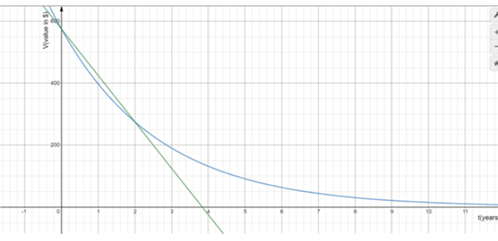
The blue color graph represents exponential model and green color graph represents linear model.
From the above graphs we can say that exponential model depreciates faster than linear model in the first 2 years.
d.
To find out the book values of the computer after one year and three years using each model.
d.
Answer to Problem 35E
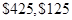 and
and 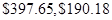
Explanation of Solution
For the linear model 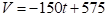
The book value after one year is;
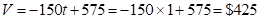
--- three years is;
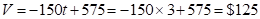
For the exponential model 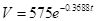
The book value after one year is;
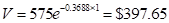
--- three years is;
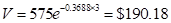
e.
To explain the advantages and disadvantages of using each model to a buyer and a seller.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Advantages to buyer:
1) The buyer can get the product for less money with exponential model in first 2 years.
2) The buyer can get the product for less money with linear model after 2 years.
Disadvantages to buyer:
1) The product will cost more for the buyer with linear model in first 2 years.
2) The product will cost more for the buyer with exponential model after 2 years.
Advantages to seller:
1) The product will be sold at more cost with linear model in first 2 years.
2) The product will be sold at more cost with exponential model after 2 years.
Disadvantages to seller:
1) The product will be sold at less cost with exponential model in first 2 years.
2) The product will be sold at less cost with linear model after 2 years.
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- For each of the following series, determine whether the absolute convergence series test determines absolute convergence or fails. For the ¿th series, if the test is inconclusive then let Mi = 4, while if the test determines absolute convergence let Mi 1 : 2: ∞ Σ(−1)"+¹ sin(2n); n=1 Σ n=1 Σ ((−1)”. COS n² 3+2n4 3: (+ 4: 5 : n=1 ∞ n 2+5n3 ПП n² 2 5+2n3 пп n² Σ(+)+ n=1 ∞ n=1 COS 4 2 3+8n3 П ηπ n- (−1)+1 sin (+727) 5 + 2m³ 4 = 8. Then the value of cos(M₁) + cos(2M2) + cos(3M3) + sin(2M) + sin(M5) is -0.027 -0.621 -1.794 -1.132 -1.498 -4.355 -2.000 2.716arrow_forwardi need help with this question i tried by myself and so i am uploadding the question to be quided with step by step solution and please do not use chat gpt i am trying to learn thank you.arrow_forwardi need help with this question i tried by myself and so i am uploadding the question to be quided with step by step solution and please do not use chat gpt i am trying to learn thank you.arrow_forward
- 1. 3 2 fx=14x²-15x²-9x- 2arrow_forwardNo it is not a graded assignment, its a review question but i only have the final answer not the working or explanationarrow_forwardClass, the class silues, and the class notes, whether the series does alternate and the absolute values of the terms decrease), and if the test does apply, determine whether the series converges or diverges. For the ith series, if the test does not apply the let Mi = 2, while if the test determines divergence then M¿ = 4, and if it determines convergence then M¿ = 8. 1: 2: 3 : 4: 5 : ∞ n=1 ∞ (−1)n+1. Σ(-1) +1 n=1 ∞ п 3m² +2 Σ(-1)+1 sin(2n). n=1 ∞ 2n² + 2n +3 4n2 +6 1 e-n + n² 3n23n+1 9n² +3 In(n + 1) 2n+1 Σ(-1) +1 n=1 ∞ Σ(-1)". n=1 Then the value of cos(M₁) + cos(2M2) + cos(3M3) + sin(2M4) + sin(M5) is 1.715 0.902 0.930 -1.647 -0.057 ● 2.013 1.141 4.274arrow_forward
- 3. FCX14) = x²+3xx-y3 +.arrow_forwardA cylindrical chemical storage tank with a capacity of 950m3 is going to be constructed in a warehouse that is 11m by 14m with a height of 10m. The specifications call for the case to be made of sheet metal that costs $90/m2, the top to be made from sheet metal that costs $45/m2 and the wall to be made of sheet metal that costs $80/m2. If you want to minimize the cost to make the storage house, how much would you end up spending to build the tank?arrow_forwardCalculate the max value of the directional derivatearrow_forward
- Calculus III May I please have the example, definition semicolons, and all blanks completed and solved? Thank you so much,arrow_forwardA company estimates that the revenue (in dollars) from the sale of x doghouses is given by R(x) = 12,000 In (0.02x+1). Use the differential to approximate the change in revenue from the sale of one more doghouse if 80 doghouses have already been sold. The revenue will increase by $ if one more doghouse is made. (Round to the nearest cent as needed.)arrow_forwardThe population of bacteria (in millions) in a certain culture x hours after an experimental 20x nutrient is introduced into the culture is P(x) = - 2 Use the differential to approximate the changes in population for the following changes in x. 8+x a. 1 to 1.5 b. 3 to 3.25 a. Use the differential to approximate the change in population for x=1 to 1.5. Between 1 and 1.5 hours, the population of bacteria changes by million. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





