
Concept explainers
a.
Use a graphical utility to create a sactter plot of the data.
a.
Answer to Problem 23PS
The
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
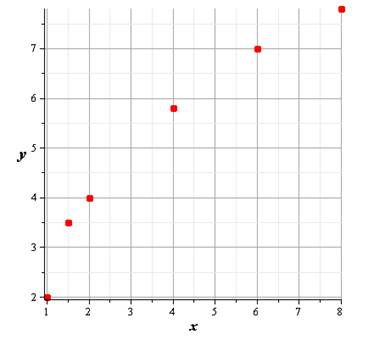
The scatter plot of the data is given as
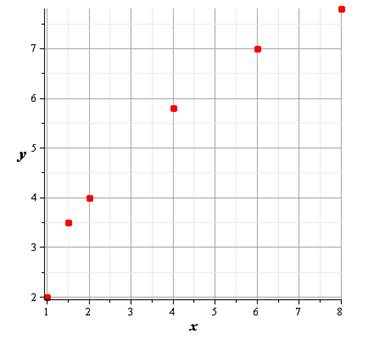
Hence, the graph is shown above.
b.
Decide the model for data .
b.
Answer to Problem 23PS
logarithmic model.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The best model for these points is logarithmic model
Hence, the data could be modelled by a logarithmic model
c.
Explain the model of part
c.
Answer to Problem 23PS
From the graph, we can see that points are increasing non-linearly, so, we cannot use a model linear model for this. We can also see that points are not growing rapidly,so, exponential model is not suitable.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the graph, we can see that points are increasing non-linearly, so, we cannot use a model linear model for this. We can also see that points are not growing rapidly,so, exponential model is not suitable.
Hence, we chose logarithmic model.
d.
find the model you chose in part (b) for the data and graph the model with scatter plot.
d.
Answer to Problem 23PS
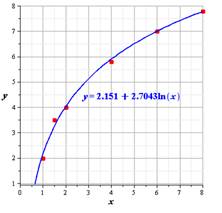
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Now, by using the values of and from the data and graphing utility we get,
Hence, the required model is
Now, the graph of scatter plot is,
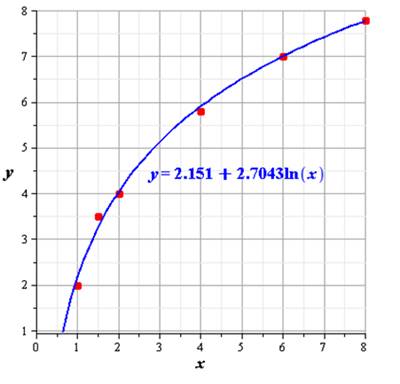
Hence, the graph is shown above.
e.
Determine if the model you chose fits the data.
e.
Answer to Problem 23PS
From the graph we can see that the model we get fits the data very well.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the graph we can see that the model we get fits the data very well.
Hence, logarithmic model fits the data very well.
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- DO NOT GIVE THE WRONG ANSWER SHOW ME ALL THE NEEDED STEPS 11: A rectangle has a base that is growing at a rate of 3 inches per second and a height that is shrinking at a rate of one inch per second. When the base is 12 inches and the height is 5 inches, at what rate is the area of the rectangle changing?arrow_forwardplease answer by showing all the dfalowing necessary step DO NOT GIVE ME THE WRONG ANSWER The sides of a cube of ice are melting at a rate of 1 inch per hour. When its volume is 64 cubic inches, at what rate is its volume changing?arrow_forwardSox & Sin (px) dx 0arrow_forward
- 8 L 8 e ipx dxarrow_forwardFind the Taylor polynomial T³(×) for the function f centered at the number a. f(x) = xe-2x a = 0 T3(x) =arrow_forwardFor each graph in Figure 16, determine whether f (1) is larger or smaller than the slope of the secant line between x = 1 and x = 1 + h for h > 0. Explain your reasoningarrow_forward
- Points z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forwardA polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forwardA curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forward
- New folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward1. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: t X== y = t +1 2 te(-∞, ∞) 42,369 I APR 27 F5 3 MacBook Air stv A Aa T 4 DIIarrow_forwardMiddle School GP... Echo home (1) Addition and su... Google Docs Netflix Netflix New folder 9. Find the area enclosed by x = sin²t, y = cost and the y-axis.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





