
Concept explainers
a)
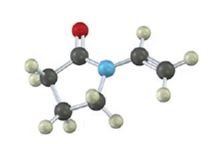
Interpretation:
Draw the structures of the
Concept introduction:
The term “polymer” is derived from the two words poly+mer. Where poly means ‘many’ and mer means ‘unit’, when combined known as polymer. The
The reaction mechanism may be classified into two categories:
Chain growth polymerization:
Chain growth polymers are produced by chain growth polymerization or addition polymerization. In this process an initiator is added to the reaction mixture. This initiator gets added to the carbon-carbon double bond and yields a reactive monomer (intermediate). This reactive intermediate reacts with the monomer and this process keeps on repeating to give rise to final polymeric product.
Step growth polymerization:
Step growth polymers are produced by step growth polymerization or condensation polymerization. In this process, each bond is formed in a step wise manner. In this the product of each is again a bi-
b)
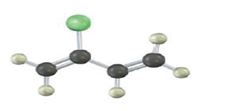
Interpretation:
Draw the structures of the polymers formed by the given monomer units.
Concept introduction:
The term “polymer” is derived from the two words poly+mer. Where poly means ‘many’ and mer means ‘unit’, when combined known as polymer. The polymerization is the process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to give rise to a polymer. If the reacting units are same then this type of polymer is known as homopolymer and if the reaction takes place between different molecules then it is called copolymer.
The reaction mechanism may be classified into two categories:
Chain growth polymerization:
Chain growth polymers are produced by chain growth polymerization or addition polymerization. In this process an initiator is added to the reaction mixture. This initiator gets added to the carbon-carbon double bond and yields a reactive monomer (intermediate). This reactive intermediate reacts with the monomer and this process keeps on repeating to give rise to final polymeric product.
Step growth polymerization:
Step growth polymers are produced by step growth polymerization or condensation polymerization. In this process, each bond is formed in a step wise manner. In this the product of each is again a bi-functional group and the condensation goes on.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 31 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- K Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward(2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic trisulfide anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. с [ ] - Garrow_forward1. Calculate the accurate monoisotopic mass (using all 1H, 12C, 14N, 160 and 35CI) for your product using the table in your lab manual. Don't include the Cl, since you should only have [M+H]*. Compare this to the value you see on the LC-MS printout. How much different are they? 2. There are four isotopic peaks for the [M+H]* ion at m/z 240, 241, 242 and 243. For one point of extra credit, explain what each of these is and why they are present. 3. There is a fragment ion at m/z 184. For one point of extra credit, identify this fragment and confirm by calculating the accurate monoisotopic mass. 4. The UV spectrum is also at the bottom of your printout. For one point of extra credit, look up the UV spectrum of bupropion on Google Images and compare to your spectrum. Do they match? Cite your source. 5. For most of you, there will be a second chromatographic peak whose m/z is 74 (to a round number). For one point of extra credit, see if you can identify this molecule as well and confirm by…arrow_forward
- Please draw, not just describe!arrow_forwardcan you draw each step on a piece of a paper please this is very confusing to mearrow_forward> Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? esc ? A O O •If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. olo 18 Ar Explanation Check BB Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Name the structurearrow_forward> For each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) C 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy A F10arrow_forwardHow to draw this mechanism for the foloowing reaction in the foto. thank youarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





