
Balance each of the following equations, and classify them as precipitation, acid-base, gas-forming, or
(a) CuCl2 + H2S →CuS + HCl
(b) H3PO4 + KOH → H2O + K3PO4
(c) Ca +HBr → H2 + CaBr2
(d) MgC12 + NaOH → Mg(OH)2 + NaCl
(a)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of reactant and product are shown below.
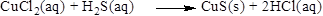
Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below,
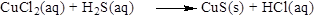
The given compound is copper chloride and hydrogen sulfide which is soluble in water. In this reaction copper chloride reaction with hydrogen sulfide to give copper sulfide and hydrochloric acidater. Most of the salts of
Therefore the given reaction is precipitation reaction
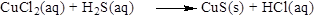
Balance the equation,
Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two hydrogen atoms in the left side and one hydrogen atoms in the right side. Therefore two molecule of hydrochloric acid is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
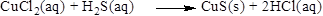
(b)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is acid - base reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is acid - base reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is potassium hydroxide and Phosphoric acid. In this reaction potassium hydroxide reaction with Phosphoric acid to give Tripotassium phosphate and formation of water is also the product.

Balance the equation,
Balance the potassium atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are three potassium atoms in the right side and one potassium atoms in the left side. Therefore three molecule of potassium hydroxide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation. There are six hydrogen atoms in the left side and two hydrogen atoms in the right side. Therefore three molecule of water is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

(c)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is oxidation and reduction reaction and the state of reactant and product is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is oxidation and reduction reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is calcium and hydrogen bromide. In this reaction hydrogen bromide reaction with calcium to give calcium bromide and hydrogen gas. Here the oxidation state of calcium is zero in the reactant and

Balance the equation,
Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two hydrogen atoms in the right side and one hydrogen atoms in the left side. Therefore two molecule of hydrogen bromide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

(d)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is magnesium chloride and sodium hydroxide. In this reaction magnesium chloride reaction with sodium hydroxide to give magnesium hydroxide and sodiumchloride. Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
the given reaction is precipitation reaction.

Balance the equation,
Balance the chlorine atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two chlorine atoms in the left side and one chlorine atoms in the right side. Therefore two molecule of sodium chloride is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Balance the oxygen atom in the given equation, there are two oxygen atoms in the right side and one oxygen atoms in the left side. Therefore two molecule of sodium hydroxide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Water is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid water evaporates in 30 min. Find the rate of heat transfer to the water (kW).arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the resonance structures that were given please.arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the question.arrow_forward
- please solve. If the answer is "no error" and it asks me to type something, and i typed a-helix, its always wrong.arrow_forwardCan you please solve and explain this for me in a simple way? I cant seem to comprehend this problem.arrow_forwardPart I. Problem solving. Include all necessary calculations 13 provide plots and graphs. Complexation wl diphenyl carbazide (OPC) in acidic media is another type of sensitive photometric method used for the analysis of aqueous. hexavalent chromium. At 540nm the cherry-red complex as a result of DPC reaction w/ chromium can be photometrically measured. at this wavelength. - a 25mL The UV-vis analysis for the determination of nexavalent chromium in ground water sample is given below. The experiment was based on external calibration method w/ each measurement sample prepared are as follows lab sample analysis contained the standard 100 ppb croy cor groundwater sample, volumes used as indicated below), 12.50 mL of 0.02 M H2Soy and 5.50 ml of 100 ppm DPC (wi water to adjust final volume to 25-ml). The main stripping method was square wave voltammetry, following the conditions set in the main ASV experiment. Standard 100 Volumetric Groundwater H2SO4 0.20 M, flask Sample, mL ppb CrO4*, 100…arrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions. Draw mechanism arrows for each step for a, b, and c. a.) HBr b.) HI H₂O H2SO4 d.) C12 HO H2SO4 1.) BH3 2.) H2O2, NaOHarrow_forwardK for the following reaction is 0.11 at constant temperature. If the equilibrium concentration of HCl is 0.5 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3. NH4CI(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCI(g)arrow_forward
- please help by Draw the following structures (Lewis or line-angle drawing).arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardConsider the reaction: 2 A (aq) ⇌ B(aq) Given the following KC values and starting with the initial concentration of A = 4.00 M, complete ICE diagram(s)and find the equilibrium concentrations for A and B.A) KC = 4.00B) KC = 200C) KC = 8.00 x10-3arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





