
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution should be written.
Concept introduction:
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water but some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
(a)
Answer to Problem 28PS
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution is,
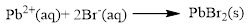
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is lead nitrate and potassium bromidewhich is soluble in water. In this reaction Pb2+ and K+ cations exchange the anions (NO3- and Br-) to give lead bromide and potassium nitrate.
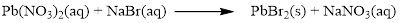
Balance the equation,
Balance the bromine atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There are two bromine atoms in the right side and one bromine atom in the left side. Therefore two molecule of sodium bromide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
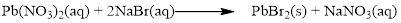
Balance the sodium atom in the given equation, there are two sodium atoms in the left side and one sodium atom in the right side. Therefore two molecule of sodium nitrate is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
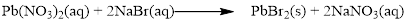
Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
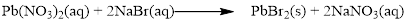
Almost all the salts of
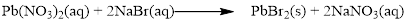
In this reaction, all the soluble ionic dissociates and forms the ions in solution.
The ionic equation is given below,

To get the net ionic equation, remove the spectator ions. Therefore the net ionic equation is given below,
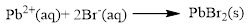
(b)
Interpretation:
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution should be written.
Concept introduction:
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water but some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
(b)
Answer to Problem 28PS
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution is,
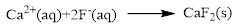
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is calcium nitrate and potassium fluoride which is soluble in water. In this reaction Ca2+ and K+ cations exchange the anions (NO3- and F-) to give calcium fluoride and potassium nitrate.
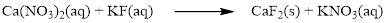
Balance the equation,
Balance the fluorine atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There are two fluorine atoms in the right side and one fluorine atom in the left side. Therefore two molecule of potassium fluoride is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
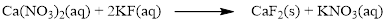
Balance the potassium atom in the given equation, there are two potassium atoms in the left side and one potassium atom in the right side. Therefore two molecule of potassium nitrate is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
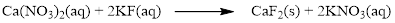
Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
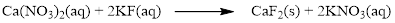
Almost all the salts of
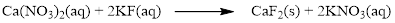
In this reaction, all the soluble ionic dissociates and forms the ions in solution.
The ionic equation is given below,
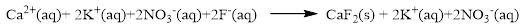
To get the net ionic equation, remove the spectator ions. Therefore the net ionic equation is given below,
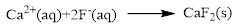
(c)
Interpretation:
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution should be written.
Concept introduction:
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water but some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
(c)
Answer to Problem 28PS
Product and balanced net ionic equation for the given aqueous solution is,
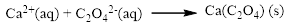
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is calcium nitrate and sodium oxalatewhich is soluble in water. In this reaction Ca2+ and Na+ cations exchange the anions (NO3- and C2O42-) to give calciumoxalate and sodium nitrate.
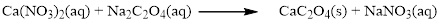
Balance the equation,
Balance the sodium atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There are two sodium atoms in the left side and one sodium atom in the right side. Therefore two molecule of sodium nitrate is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
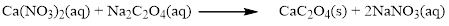
Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
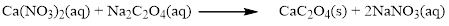
Almost all the salts of
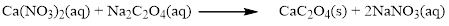
In this reaction, all the soluble ionic dissociates and forms the ions in solution.
The ionic equation is given below,
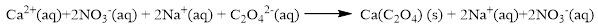
To get the net ionic equation, remove the spectator ions. Therefore the net ionic equation is given below,
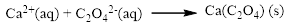
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





