
Concept explainers
(a)
To Check: Whether the collision would occur or not.
(a)
Answer to Problem 101A
Yes, collision will occur.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For express train:
Velocity of train,
Deceleration of the train,
Time,
For local train:
Initial distance
Velocity,
Since it is moving with constant velocity. therefore, acceleration
Formula used:
Second equation of motion:
Where,
Calculation:
Table below represents the distance travelled by each train with time.
| Time(s) | Distance travelled by the express train | Distance travelled by the local train |
| Formula used | ||
| 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 1 | 34.5 | 111 |
| 2 | 66 | 122 |
| 3 | 94.5 | 133 |
| 4 | 120 | 144 |
| 5 | 142.5 | 155 |
| 6 | 162 | 166 |
| 7 | 178.5 | 177 |
| 8 | 192 | 188 |
| 9 | 202.5 | 199 |
| 10 | 210 | 210 |
| 11 | 214.5 | 221 |
| 12 | 216 | 232 |
Distance travelled by the express train is equal to distance travelled by the local train at
Therefore, collision will take place.
Conclusion:
Both the trains will be at same position at
(b)
The table for the position of each train and plot the graph for the same.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For express train:
Velocity of train,
deceleration of the train,
Time,
For local train:
Initial distance
Velocity,
Since it is moving with constant velocity. therefore, acceleration
Formula used:
Equation of motion:
Where,
Calculation:
Table below represents the distance travelled by each train with time.
| Time(s) | Distance travelled by the express train | Distance travelled by the local train |
| Formula used | ||
| 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 1 | 34.5 | 111 |
| 2 | 66 | 122 |
| 3 | 94.5 | 133 |
| 4 | 120 | 144 |
| 5 | 142.5 | 155 |
| 6 | 162 | 166 |
| 7 | 178.5 | 177 |
| 8 | 192 | 188 |
| 9 | 202.5 | 199 |
| 10 | 210 | 210 |
| 11 | 214.5 | 221 |
| 12 | 216 | 232 |
Graph below represents the distance travelled by each train with time:
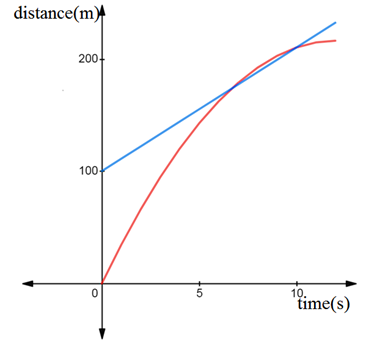
Red line represents the motion of express train.
Blue line represents the motion of local train
Conclusion:
Graph and table representing the motion of each train with time is shown above.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
- Part A Consider the mechanism shown in (Figure 1). If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle of the toggle clamp, determine the resulting clamping force at A. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure -235 mm- 30 mm 70 mm 30 mm/ 30 275 mm 1 of 1 > ΜΑ ? FA= Value Units Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardgot 4.67 for 1 then 9.33 for the rest then 21.33 for the input and output but it says all are wrongarrow_forwardmase as shown 2) A holy of once sty extually at rest & acted upon by bus mutually perpendicular forces 12 Nand 5N belowilf the particle moves in derection Calculato the magnitude of the acceleration of 12nt R 0 so A SNarrow_forward
- Required information Two speakers vibrate in phase with each other at 523 Hz. At certain points in the room, the sound waves from the two speakers interfere destructively. One such point is 1.45 m from speaker #1 and is between 2.00 m and 4.00 m from speaker #2. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. How far is this point from speaker #2? marrow_forwarda) Consider the following function, where A is a constant. y(x,t) = A(x — vt). Can this represent a wave that travels along? Explain. b) Which of the following are possible traveling waves, provide your reasoning and give the velocity of the wave if it can be a traveling wave. e-(a²x²+b²²-2abtx b.1) y(x,t) b.2) y(x,t) = = A sin(ax² - bt²). 2 b.3) y(x,t) = A sin 2π (+) b.4) y(x,t) = A cos² 2π(t-x). b.5) y(x,t) = A cos wt sin(kx - wt)arrow_forwardThe capacitor in (Figure 1) is initially uncharged. The switch is closed at t=0. Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the current through the resistor R1, R2, and R3? What is the final charge on the capacitor? Please explain all steps.arrow_forward
- Suppose you have a lens system that is to be used primarily for 620-nm light. What is the second thinnest coating of fluorite (calcium fluoride) that would be non-reflective for this wavelength? × nm 434arrow_forwardThe angle between the axes of two polarizing filters is 19.0°. By how much does the second filter reduce the intensity of the light coming through the first? I = 0.106 40 xarrow_forwardAn oil slick on water is 82.3 nm thick and illuminated by white light incident perpendicular to its surface. What color does the oil appear (what is the most constructively reflected wavelength, in nanometers), given its index of refraction is 1.43? (Assume the index of refraction of water is 1.33.) wavelength color 675 × nm red (1 660 nm)arrow_forward
- A 1.50 μF capacitor is charging through a 16.0 Ω resistor using a 15.0 V battery. What will be the current when the capacitor has acquired 1/4 of its maximum charge? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardIn the circuit shown in the figure (Figure 1), the 6.0 Ω resistor is consuming energy at a rate of 24 J/s when the current through it flows as shown. What are the polarity and emf of the battery E, assuming it has negligible internal resistance? Please explain all steps. I know you need to use the loop rule, but I keep getting the answer wrong.arrow_forwardIf you connect a 1.8 F and a 2.6 F capacitor in series, what will be the equivalent capacitance?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





