
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321973610
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 29, Problem 29.17E
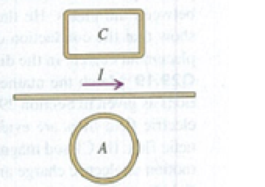
Two closed loops A and C are close to a long wire carrying a current I (Fig. E29.17). (a) Find the direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current induced in each loop if I is steadily decreasing. (b) While I is decreasing, what is the direction of the net force that the wire exerts on each loop? Explain how you obtain your answer
Figure E29.17
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:18
Students have asked these similar questions
metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity along two parallel metal rails, connected with a strip of metal at one end across a magnetic field (B) of 0.5 T, pointing out of the page. The rod is of length 45 cm and the speed of the rod is 70 cm/s. The rod has a resistance of 10 Ω and the resistance of the rails and connector is negligible. What is the rate at which energy is being transferred to thermal energy?
a) 0.225 W
b) 22.55 W
c) 2.25 × 10-4 W
d) 2.25 × 10-3 W
I got 0.1981686061 V
A current runs in a long solenoid of a radius 3 cm and 437 turns per meter. The current in the solenoid is increased at a rate of 2 A/s. A single circular loop of wire of radius 5 cm and resistance 2 Ω surrounds the solenoid. Find the electrical current induced in the single loop. Give your answer in units of microamperes.
Chapter 29 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 29.2 - The accompanying figure shows a wire coil being...Ch. 29.3 - (a) Suppose the magnet in Fig. 29.14a were...Ch. 29.4 - The earths magnetic field points toward (magnetic)...Ch. 29.5 - If you wiggle a magnet back and forth in your...Ch. 29.6 - Prob. 29.6TYUCh. 29.7 - Prob. 29.7TYUCh. 29 - A sheet of copper is placed between the poles of...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.2DQCh. 29 - Prob. 29.3DQCh. 29 - Prob. 29.4DQ
Ch. 29 - A long, straight conductor passes through the...Ch. 29 - A student asserted that if a permanent magnet is...Ch. 29 - An airplane is in level flight over Antarctica,...Ch. 29 - Consider the situation in Exercise 29.21. In part...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.9DQCh. 29 - Prob. 29.10DQCh. 29 - Example 29.6 discusses the external force that...Ch. 29 - In the situation shown in Fig. 29.18, would it be...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.13DQCh. 29 - Small one-cylinder gasoline engines sometimes use...Ch. 29 - Does Lenzs law say that the induced current in a...Ch. 29 - Does Faradays law say that a large magnetic flux...Ch. 29 - Can one have a displacement current as well as a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.18DQCh. 29 - Match the mathematical statements of Maxwells...Ch. 29 - If magnetic monopoles existed, the right-hand side...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.21DQCh. 29 - A single loop of wire with an area of 0.0900 m2 is...Ch. 29 - In a physics laboratory experiment, a coil with...Ch. 29 - Search Coils and Credit Cards. One practical way...Ch. 29 - A closely wound search coil (see Exercise 29.3)...Ch. 29 - A circular loop of wire with a radius of 12.0 cm...Ch. 29 - CALC A coil 4.00 cm in radius, containing 500...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.7ECh. 29 - CALC A flat, circular, steel loop of radius 75 cm...Ch. 29 - Shrinking Loop. A circular loop of flexible iron...Ch. 29 - A closely wound rectangular coil of 80 turns has...Ch. 29 - CALC In a region of space, a magnetic field points...Ch. 29 - In many magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems,...Ch. 29 - The armature of a small generator consists of a...Ch. 29 - A flat, rectangular coil of dimensions l and w is...Ch. 29 - A circular loop of wire is in a region of...Ch. 29 - The current I in a long, straight wire is constant...Ch. 29 - Two closed loops A and C are close to a long wire...Ch. 29 - The current in Fig. E29.18 obeys the equation I(t)...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.19ECh. 29 - A cardboard tube is wrapped with two windings of...Ch. 29 - A small, circular ring is inside a larger loop...Ch. 29 - A circular loop of wire with radius r = 0.0480 m...Ch. 29 - CALC A circular loop of wire with radius r =...Ch. 29 - A rectangular loop of wire with dimensions 1.50 cm...Ch. 29 - In Fig. E29.25 a conducting rod of length L = 30.0...Ch. 29 - A rectangle measuring 30.0 cm by 40.0 cm is...Ch. 29 - Are Motional emfs a Practical Source of...Ch. 29 - Motional emfs in Transportation. Airplanes and...Ch. 29 - The conducting rod ab shown in Fig. E29.29 makes...Ch. 29 - A 0.650-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at...Ch. 29 - A 0.360-m-long metal bar is pulled to the left by...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.32ECh. 29 - A 0.250-m-long bar moves on parallel rails that...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.34ECh. 29 - Prob. 29.35ECh. 29 - A metal ring 4.50 cm in diameter is placed between...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.37ECh. 29 - Prob. 29.38ECh. 29 - A long, thin solenoid has 400 turns per meter and...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.40ECh. 29 - A long, straight solenoid with a cross-sectional...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.42ECh. 29 - Prob. 29.43ECh. 29 - CALC In Fig. 29.23 the capacitor plates have area...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.45ECh. 29 - A very long, rectangular loop of wire can slide...Ch. 29 - CP CALC In the circuit shown in Fig. P29.47, the...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.48PCh. 29 - CALC A very long, straight solenoid with a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.50PCh. 29 - In Fig. P29.51 the loop is being pulled lo the...Ch. 29 - Make a Generator? You are shipwrecked on a...Ch. 29 - A flexible circular loop 6.50 cm in diameter lies...Ch. 29 - CALC A conducting rod with length L = 0.200 m,...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.55PCh. 29 - CP CALC Terminal Speed. A bar of length L = 0.36 m...Ch. 29 - CALC The long, straight wire shown in Fig. P29.57a...Ch. 29 - CALC A circular conducting ring with radius r0 =...Ch. 29 - CALC A slender rod, 0.240 m long, rotates with an...Ch. 29 - A 25.0-cm-long metal rod lies in the .xy-plane and...Ch. 29 - CP CALC A rectangular loop with width L and a...Ch. 29 - CALC An airplane propeller of total length L...Ch. 29 - The magnetic field B, at all points within a...Ch. 29 - CP CALC A capacitor has two parallel plates with...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.65PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.66PCh. 29 - DATA You are conducting an experiment in which a...Ch. 29 - DATA You measure the magnitude of the external...Ch. 29 - A metal bar with length L, mass m, and resistance...Ch. 29 - CP CALC A square, conducting, wire loop of side L,...Ch. 29 - BIO STIMULATING THE BRAIN. Communication in the...Ch. 29 - BIO STIMULATING THE BRAIN. Communication in the...Ch. 29 - It may be desirable to increase the maximum...Ch. 29 - Which graph in Fig. P29.74 best represents the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
38. A 70 W electric blanket runs at 18 V.
a. What is the resistance of the wire in the blanket?
b. How much cur...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
The force, when you push against a wall with your fingers, they bend.
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
42. (II) A box is given a push so that it slides across the floor. How far will it go, given that the coefficie...
Physics: Principles with Applications
A foul ball leaves the bat going straight up at 23 m/s. (a) How high does it rise? (b) How long is it in the ai...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A coil with a self-inductance of 3.0 H and a resistance of 100 2 carries a steady current of 2.0 A. (a) What is the energy stored in the magnetic field of the coil? (b) What is the energy per second dissipated in the resistance of the coil?arrow_forwardIn Figure P20.65 the rolling axle of length 1.50 m is pushed along horizontal rails at a constant speed v = 3.00 m/s. A resist or R = 0.400 is connected to the rails at points a and b, directly opposite each other. (The wheels make good electrical contact with the rails, so the axle, rails, and R form a closed-loop circuit. The only significant resistance in the circuit is R.) A uniform magnetic field B = 0.800 T is directed vertically downward. (a) Find the induced current I in the resistor. (b) What horizontal force F is required to keep the axle rolling at constant speed? (c) Which end of the resistor, a or b. is at the higher electric potential? (d) Alter the axle rolls past the resistor, does the current in R reverse direction? Explain your answer. Figure P20.65arrow_forwardA Figure P32.74 shows an N-turn rectangular coil of length a and width b entering a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude Bout directed out of the page. The velocity of the coil is constant and is upward in the figure. The total resistance of the coil is R. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil a. when only a portion of the coil has entered the region with the field, b. when the coil is completely embedded in the field, and c. as the coil begins to exit the region with the field?arrow_forward
- The bar in Figure OQ23.10 moves on rails to the right with a velocity v, and a uniform, constant magnetic field is directed out of the page. Which of the following statements are correct? More than one statement may be correct. (a) The induced current in the loop is zero. (b) The induced current in the loop is clockwise. (c) The induced current in the loop is counterclockwise. (d) An external force is required to keep the bar moving at constant speed. (e) No force is required to keep the bar moving at constant speed.arrow_forwardA piece of insulated wire is shaped into a figure eight as shown in Figure P23.12. For simplicity, model the two halves of the figure eight as circles. The radius of the upper circle is 5.00 cm and that of the lower circle is 9.00 cm. The wire has a uniform resistance per unit length of 3.00 Ω/m. A uniform magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the two circles, in the direction shown. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate of 2.00 T/s. Find (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of the induced current in the wire. Figure P23.12arrow_forwardFigure P23.58 is a graph of the induced emf versus time for a coil of N turns rotating with angular speed ω in a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular to the coil’s axis of rotation. What If? Copy this sketch (on a larger scale) and on the same set of axes show the graph of emf versus t (a) if the number of turns in the coil is doubled, (b) if instead the angular speed is doubled, and (c) if the angular speed is doubled while the number of turns in the coil is halved. Figure P23.58arrow_forward
- A loop of wire in the shape of a rectangle of width w and length L and a long, straight wire carrying a current I lie on a tabletop as shown in Figure P23.7. (a) Determine the magnetic flux through the loop due to the current I. (b) Suppose the current is changing with time according to I = a + bt, where a and b are constants. Determine the emf that is induced in the loop if b = 10.0 A/s, h = 1.00 cm, w = 10.0 cm, and L = 1.00 m. (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the rectangle? Figure P23.7arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire with a radius of 4.0 cm is in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.060 T. The plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. In a time interval of 0.50 s, the magnetic field changes to the opposite direction with a magnitude of 0.040 T. What is the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop? (a) 0.20 V (b) 0.025 V (c) 5.0 mV (d) 1.0 mV (e) 0.20 mVarrow_forwardReview. Figure P31.31 shows a bar of mass m = 0.200 kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance = 1.20 m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle = 25.0 with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is R = 1.00 and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.500 T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground, over the entire region through which the bar moves. With what constant speed v does the bar slide along the rails?arrow_forward
- A thin wire = 30.0 cm long is held parallel to and d = 80.0 cm above a long, thin wire carrying I = 200 A and fixed in position (Fig. P30.47). The 30.0-cm wire is released at the instant t = 0 and falls, remaining parallel to the current-carrying wire as it falls. Assume the falling wire accelerates at 9.80 m/s2. (a) Derive an equation for the emf induced in it as a function of time. (b) What is the minimum value of the emf? (c) What is the maximum value? (d) What is the induced emf 0.300 s after the wire is released? Figure P30.47arrow_forwardA 500-turn coil with a 0.250m2 area is spun in Earth’s 5.00105T magnetic field, producing a 12.0-kV maximum emf. (a) As what angular velocity must the coil be spun? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumption or premise is responsible?arrow_forwardYou wish to move a rectangular loop of wire into a region of uniform magnetic field at a given speed so as to induce an emf in the loop. The plane of the loop must remain perpendicular to the magnetic field lines. In which orientation should you hold the loop while you move it into the region of magnetic field so as to generate the largest emf? (a) with the long dimension of the loop parallel to the velocity vector (b) with the short dimension of the loop parallel to the velocity vector (c) either way because the emf is the same regardless of orientationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY