
A Figure P32.74 shows an N-turn rectangular coil of length a and width b entering a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude Bout directed out of the page. The velocity of the coil is constant and is upward in the figure. The total resistance of the coil is R. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil a. when only a portion of the coil has entered the region with the field, b. when the coil is completely embedded in the field, and c. as the coil begins to exit the region with the field?
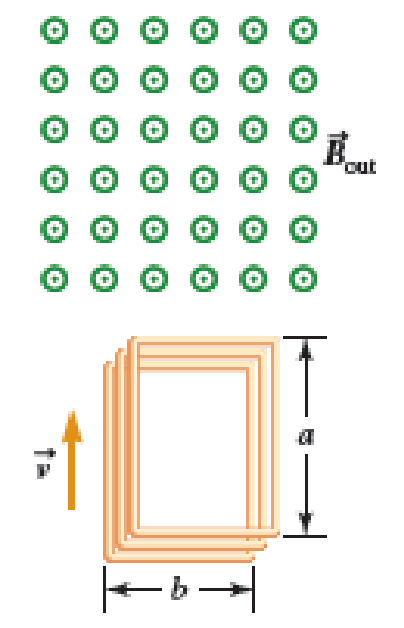
(a)
The magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil when a portion of the coil enters the region of the field.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The magnitude of the magnetic force on the coil when a portion of the coil enters the region of the field is
Explanation of Solution
Faraday’s law states that an emf is induced in a coil when the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes.
The direction of the induced emf is given by Lenz law. Lenz law states that the current induced in a circuit due to change or a motion in the magnetic field, opposes the change in flux and exerts a mechanical force opposing the motion.
A current carrying conductor experiences a force in a magnetic field. Thus, the conductor experiences a force due to the current induced in it.
A coil ABCD of
The coil moves with a constant velocity
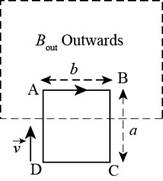
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the induced emf entering the magnetic field.
Write the expression for magnitude of the induced current in the coil.
Here,
Substitute equation (I) in the above equation to find
The flux entering the coil increases, as the coil enters the magnetic field. According to Lenz law, the current in the segment which enters the field, flows towards the right, from point A to point B.
Write the expression for force experienced by the segment due to current flowing in the coil.
According to the right hand screw rule, the force acts perpendicular to both the direction of current and the magnetic field. Therefore, the force acts downwards.
Write the expression for magnitude of the force.
Substitute equation (II) in the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic force on the coil, when a portion of the coil enters the region of the field is
(b)
The magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil when the coil is completely embedded in the field.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The magnitude of the force on the coil when it is completely embedded in the magnetic field is
Explanation of Solution
As shown in Figure-(2), the coil is completely embedded in the field.
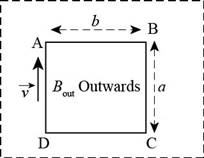
Figure-(2)
According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, the emf induced in the coil is
There is no current flow in the coil, when the induced emf is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force on the coil when it is completely embedded in the magnetic field is
(c)
The magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil as the coil begins to exit the region of the field.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The magnitude of the magnetic force on the coil, when a portion of the coil exits the region of the field is
Explanation of Solution
The outward flux through the coil decreases, as the coil begins to exit the field. The current flows in the counter clockwise direction in the coil. The current flows from point D to point C as shown in figure-(3).
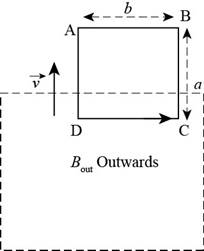
Figure-(3)
The magnitude of the current in the coil remains the same as it is when the coil enters the field, as the coil moves with the same constant speed. The direction of the current flowing in the coil, when it exits the field, is opposite to the direction of the current when the coil enters the field.
Write the expression for the current in the coil when it exits the magnetic field.
Write the expression for magnitude of the force experienced by the coil.
The magnitude of the force experienced by the coil, when it exits the field is same as, when it enters the field.
The force acts downwards along the plane of the paper.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic force on the coil, when a portion of the coil exits the region of the field is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
- When the motorcyclist is at A, he increases his speed along the vertical circular path at the rate of = (0.3t) ft/s², where t is in seconds. Take p = 360 ft. (Figure 1) Part A 60° Ρ B If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his velocity when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer ་ Part B ? Units If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his acceleration when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 11 ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forwardThe car starts from rest at s = 0 and increases its speed at a₁ = 7 m/s². (Figure 1) Part A = 40 m Determine the time when the magnitude of acceleration becomes 20 m/s². Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? t = Value Units Part B At what position s does this occur? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. s = Value Submit Request Answer ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





