
A thin wire ℓ = 30.0 cm long is held parallel to and d = 80.0 cm above a long, thin wire carrying I = 200 A and fixed in position (Fig. P30.47). The 30.0-cm wire is released at the instant t = 0 and falls, remaining parallel to the current-carrying wire as it falls. Assume the falling wire accelerates at 9.80 m/s2. (a) Derive an equation for the emf induced in it as a function of time. (b) What is the minimum value of the emf? (c) What is the maximum value? (d) What is the induced emf 0.300 s after the wire is released?
Figure P30.47
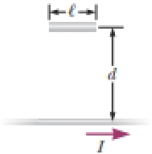
(a)
Answer to Problem 47AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Length of wire is
The speed of the wire according to Newton’s law of motion can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
The distance covered by the wire can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
The total distance covered by wire can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
The magnetic field at a distance
Here,
The emf induced in the wire can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equation for emf induced in the wire as function of time is
(b)
Answer to Problem 47AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Length of wire is
The expression for emf can be given as in equation (1),
At
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum value of emf is
(c)
Answer to Problem 47AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Length of wire is
The expression for emf can be given as in equation (1),
From the above equation, at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum value of emf is
(d)
Answer to Problem 47AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Length of wire is
The expression for emf can be given as in equation (1),
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the induced emf
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





