
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553278
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 45AP
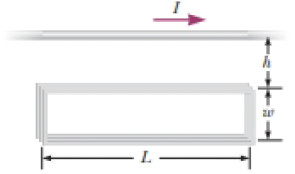
A long, straight wire carries a current given by I = Imax sin (ωt + ϕ). The wire lies in the plane of a rectangular coil of N turns of wire as shown in Figure P30.45. The quantities Imax, ω, and ϕ are all constants. Assume Imax = 50.0 A, ω = 200π s−1, N = 100, h = ω = 5.00 cm, and L = 20.0 cm. Determine the emf induced in the coil by the magnetic field created by the current in the straight wire.
Figure P30.45
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...?
a. Both rods have less mass
b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass
c. both rods have more mass
d. the masses of both rods are unchanged
e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe mass
8) 9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Ch. 30.1 - A circular loop of wire is held in a uniform...Ch. 30.2 - In Figure 30.8a, a given applied force of...Ch. 30.3 - Figure 30.12 Figure 30.12 shows a circular loop of...Ch. 30.5 - Prob. 30.4QQCh. 30 - A circular loop of wire of radius 12.0 cm is...Ch. 30 - An instrument based on induced emf has been used...Ch. 30 - Scientific work is currently under way to...Ch. 30 - A long solenoid has n = 400 turns per meter and...Ch. 30 - An aluminum ring of radius r1 = 5.00 cm and...Ch. 30 - An aluminum ring of radius r1 and resistance R is...
Ch. 30 - A coil formed by wrapping 50 turns of wire in the...Ch. 30 - When a wire carries an AC current with a known...Ch. 30 - A toroid having a rectangular cross section (a =...Ch. 30 - A small airplane with a wingspan of 14.0 m is...Ch. 30 - A helicopter (Fig. P30.11) has blades of length...Ch. 30 - A 2.00-m length of wire is held in an eastwest...Ch. 30 - A metal rod of mass m slides without friction...Ch. 30 - Prob. 14PCh. 30 - Prob. 15PCh. 30 - An astronaut is connected to her spacecraft by a...Ch. 30 - You are working for a company that manufactures...Ch. 30 - You are working in a laboratory that uses motional...Ch. 30 - You are working in a factory that produces long...Ch. 30 - You are working in a factory that produces long...Ch. 30 - Within the green dashed circle show in Figure...Ch. 30 - Prob. 22PCh. 30 - Prob. 23PCh. 30 - Figure P30.24 (page 820) is a graph of the induced...Ch. 30 - The rotating loop in an AC generator is a square...Ch. 30 - In Figure P30.26, a semicircular conductor of...Ch. 30 - Prob. 27PCh. 30 - Suppose you wrap wire onto the core from a roll of...Ch. 30 - A rectangular loop of area A = 0.160 m2 is placed...Ch. 30 - A rectangular loop of area A is placed in a region...Ch. 30 - A circular coil enclosing an area of 100 cm2 is...Ch. 30 - Consider the apparatus shown in Figure P30.32: a...Ch. 30 - A guitars steel string vibrates (see Fig. 30.5)....Ch. 30 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 30 - A conducting rod of length = 35.0 cm is free to...Ch. 30 - Magnetic field values are often determined by...Ch. 30 - The plane of a square loop of wire with edge...Ch. 30 - In Figure P30.38, the rolling axle, 1.50 m long,...Ch. 30 - Figure P30.39 shows a stationary conductor whose...Ch. 30 - Prob. 40APCh. 30 - Figure P30.41 shows a compact, circular coil with...Ch. 30 - Review. In Figure P30.42, a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 30 - An N-turn square coil with side and resistance R...Ch. 30 - A conducting rod of length moves with velocity v...Ch. 30 - A long, straight wire carries a current given by I...Ch. 30 - A rectangular loop of dimensions and w moves with...Ch. 30 - A thin wire = 30.0 cm long is held parallel to...Ch. 30 - An induction furnace uses electromagnetic...Ch. 30 - Prob. 49CPCh. 30 - A betatron is a device that accelerates electrons...Ch. 30 - Review. The bar of mass m in Figure P30.51 is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY