
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The peptide
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
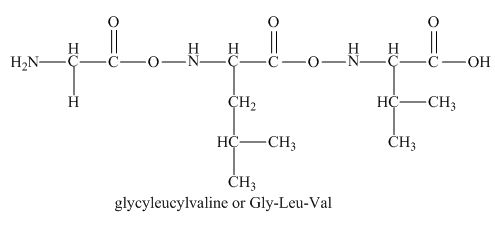
There will be no charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
The given peptide

Figure 1
This tripeptide contains one amino group and one carboxylic group. So, this amino acid is neutral in nature. The
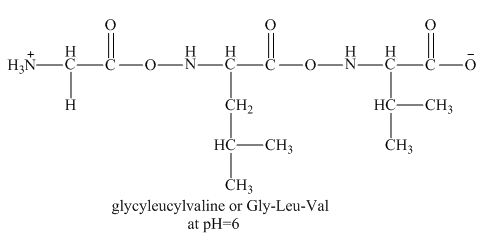
Figure 2
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
(b)
Interpretation:
The peptide,
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
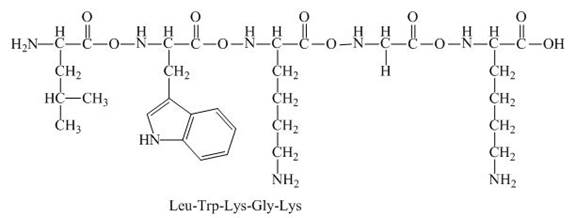
The peptide,
The net charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
The given peptide,

Figure 3
This given peptide contains three amino group in its chain and one carboxylic group. So, this amino acid is basic in nature. All the amine group of the given peptide having value of
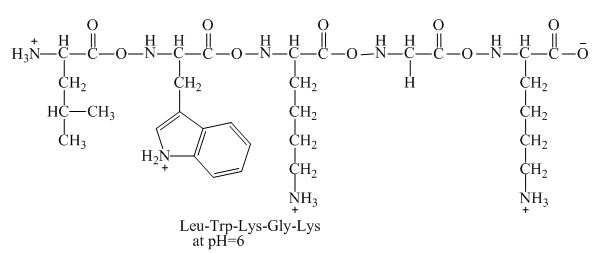
Figure 4
Therefore, the net charge of
The peptide,
(c)
Interpretation:
The peptide,
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
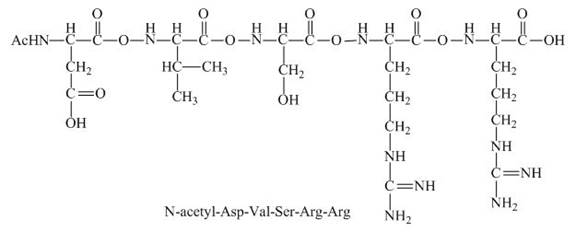
There will be no charge on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
The given peptide

Figure 5
This given peptide contains two amino groups in the side chain and two carboxylic groups. So, this amino acid is neutral in nature. All the amine groups of this peptide having
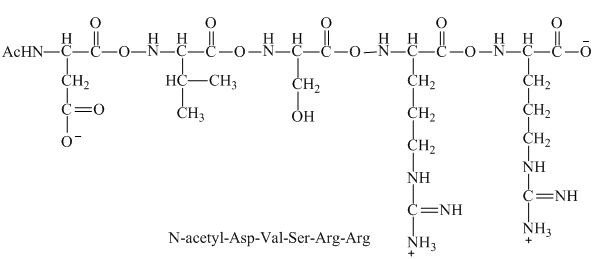
Figure 6
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
(d)
Interpretation:
The peptide
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic and neutral according to the functional group they possesses. Acidic amino acids are those which have one more than one carboxylic acid group in its side chain and basic amino acids are those which have one or more amino group present in their side chain. Isoelectric point of the amino acids is the pH of the dilute aqueous solution of the amino acid at which the total charge on all molecules of amino acid is zero.
Answer to Problem 27.10P
The peptide
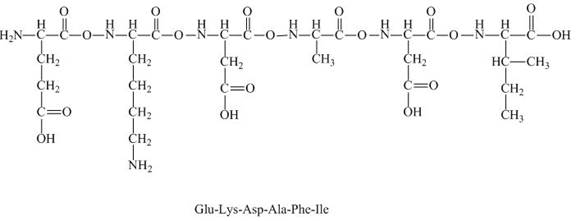
The charge present on the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
Peptides are classified as acidic, basic, or neutral according to the amino acids they contain. If they contain unbalanced basic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptide and if they contain unbalanced acidic amino acid then they are considered as basic peptides. If the basic and acidic amino acids are balanced or not at all present in the peptide then it is considered as neutral peptide.
The given peptide

Figure 7
This given peptide contains two amino groups in the side chain and four carboxylic groups. So, this amino acid is acidic in nature. All the amine groups of this peptide having
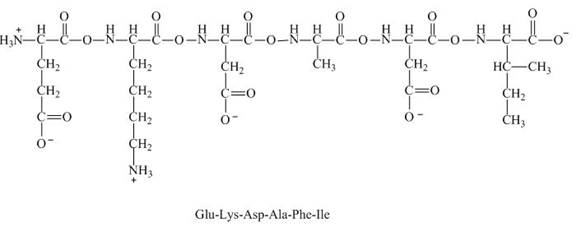
Figure 8
Therefore, the net charge on the peptide,
The peptide
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Label all absorptions over 1500 cm-1. Please be specific and mark IR if needed for explanation. Compound OH sp^3 C-H C=O C-O Triglyceridearrow_forwardIdentify the intermediate that is INITIALLY formed in a saponification reaction (hydrolysis of an ester). III -OH H₂O HO OH HO O || A B C III D IV IVarrow_forwardHelp me answer this practice sheet I found for an answer guidearrow_forward
- show the retrosynthesis of this molecule step by step starting with 1,3-dimethoxy benzene H3CO OH OH OCH 3arrow_forwardConsider the reaction of a propanoate ester with hydroxide ion shown below. A series of four alcohol leaving groups were tested to determine which would be the best leaving group. Based on the pKa values of the alcohols, predict which alcohol would produce the fastest hydrolysis reaction. HO FOR A Alcohol I, pKa =16.0 B Alcohol II, pKa =10.0 C Alcohol III, pKa = 7.2 + ROH D Alcohol IV, pKa = 6.6arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: NaOH, H₂O 00:4 Na O heat NaO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows :0: Na a NaOH, H2O :0: NaOH, H2O heat heat Na ONH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H CH3NH3+ :0: :0: HO CH3NH2 HH iSelect to Add Arrows i Select to Add Arrows i HH CH3NH3+ CH3NH2 Select to Add Arrows i CH3NH3 CH3NH2 ايكدا HH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardThe reaction is carried out with gases: A → B + C at 300 K. The total pressure is measured as a function of time (table). If the reaction order is 2, calculate the rate or kinetic constant k (in mol-1 L s¹) Ptotal (atm) 492 676 760 808 861 t(s) 0 600 1200 1800 3000arrow_forwardcan someone give a description of this NMR including whether its a triplt singlet doublet where the peak is around at ppm and what functional group it representsarrow_forward
- 1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6 points, 2 points each). OH OH OH A-A OH HOT HO- ACHN and HO- ACHN OH HO HO ° OH and OH OH SH and ...SHarrow_forward20,0 Complete the electron pushing mechanism to y drawing the necomery unicaciones and carved on for Step 1: Add curved arms for the tint step, traiment with NalilĻ. The Nation 458 Step 2: Added for the second step, inalment with), how the "counterion bar Step 3: Daw the products of the last simplom organic and one incoganic spacient, including all nonbondingarrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank you!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





