
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Amino group reacts faster with the
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is shown below.
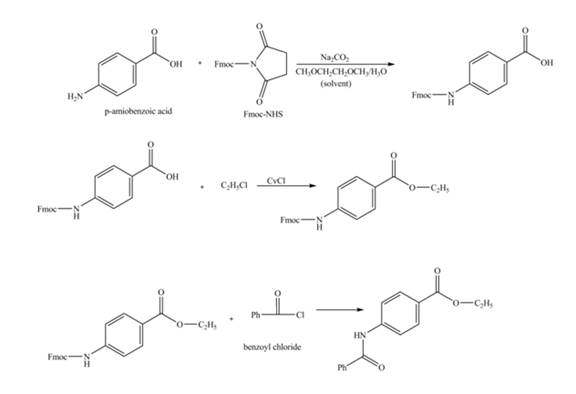
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
Figure 1
The amine group of the
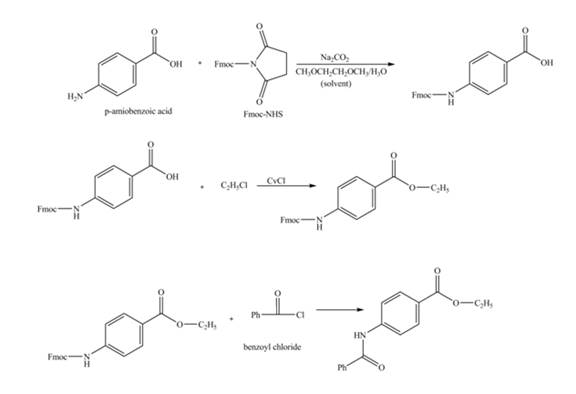
Figure 2
The complete synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Sodium borohydride is a strong reducing agent. The hydride ion of sodium borohydride acts as the nucleophile and gets attached to the carbonyl carbon.
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
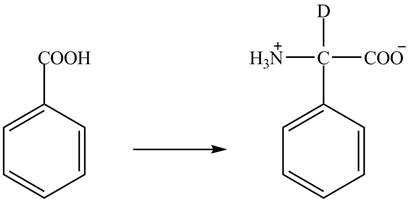
Figure 3
The benzoic acid reacts with
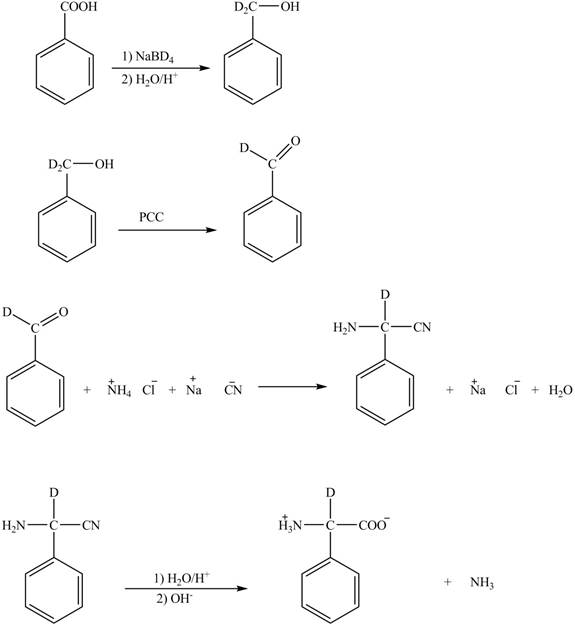
Figure 4
The complete synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes reacts with sodium cyanide to form nitrile compound. The nitrile compound reacts with ammonium chloride to form the
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is shown below.
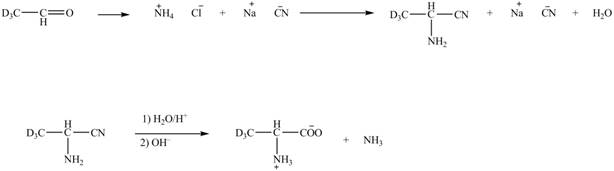
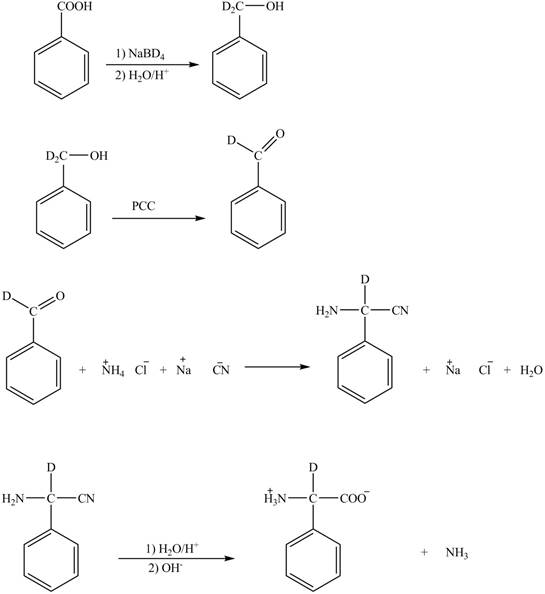
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
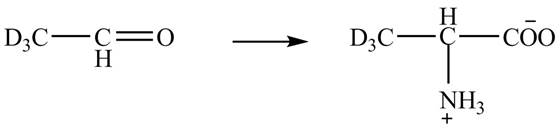
Figure 5
The deuteriated acetaldehyde reacts with ammonium chloride and sodium cyanide to form deuteriated
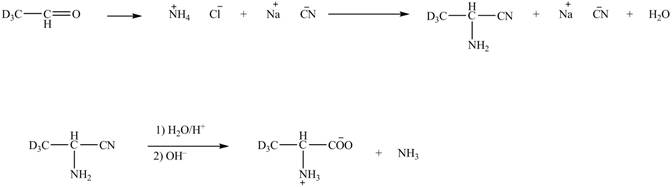
Figure 6
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Amino group reacts faster with the alkyl halides than the carboxylic group. The reaction of carboxylic acid can be performed only by protecting the amine group. Fmoc compound is used as the protecting agent for amine group. Amine and acid chloride reacts to form amide bond.
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
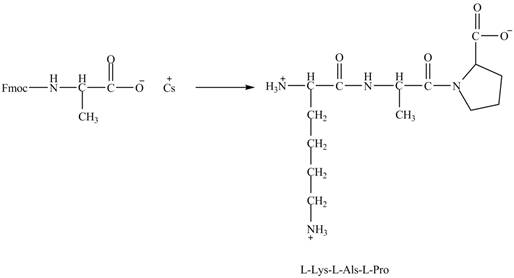
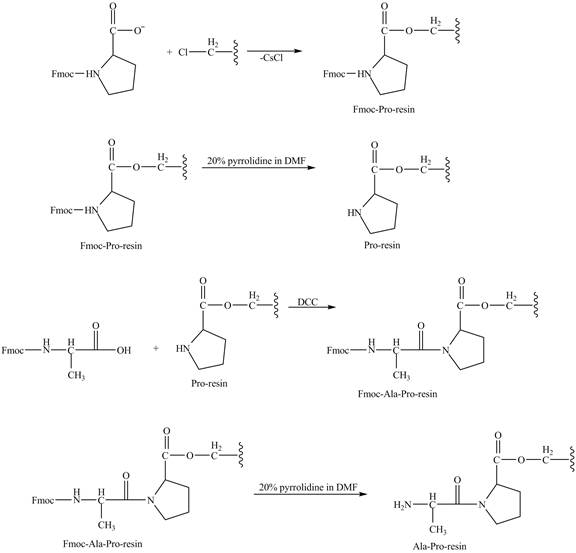
Figure 7
The cesium salt of Fmoc-proline is reacted with the resin linker. The amine is deprotecteed in pyrrolidine. Fmoc-alanine reacts with the prolin resin in presence of
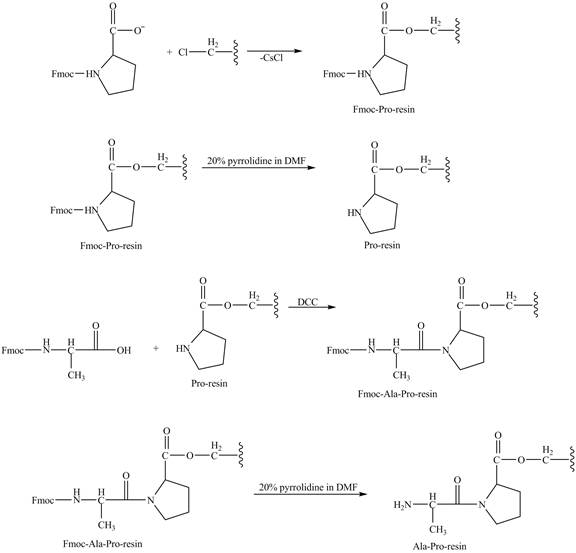
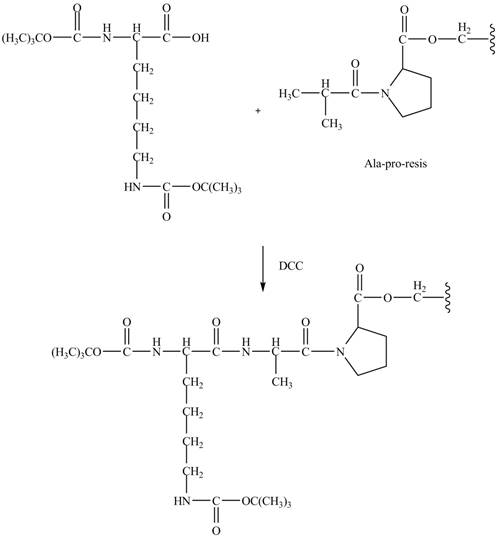
Figure 8
The alanine-proline resin reacts with the Boc protected lysin to form the
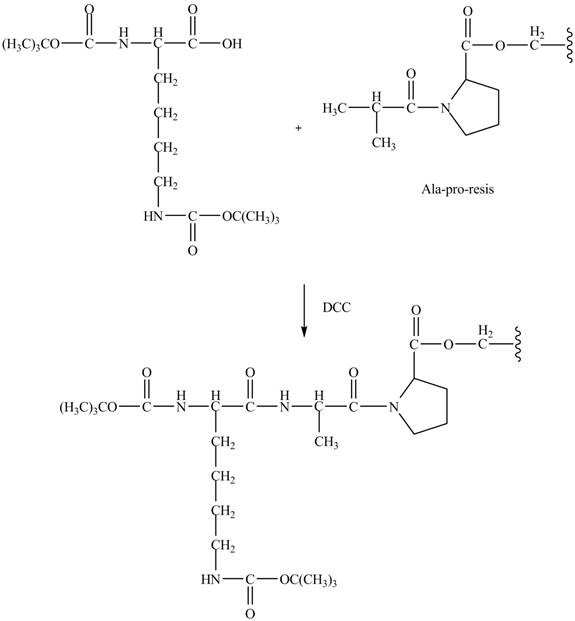
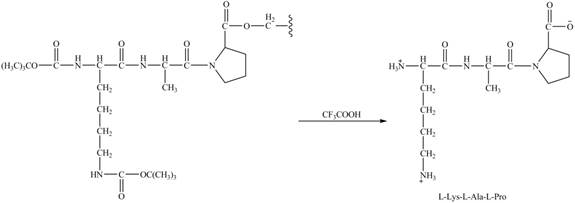
Figure 9
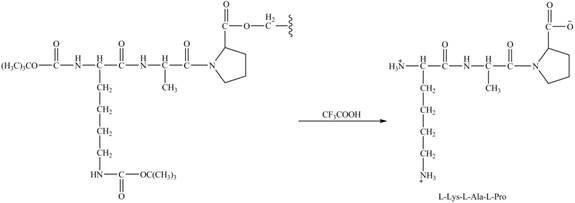 Figure 10
Figure 10
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9 and Figure 10.
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes reacts with sodium cyanide to form nitrile compound. The nitrile compound reacts with ammonium chloride to form the
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The complete synthesis of given compound is shown below.
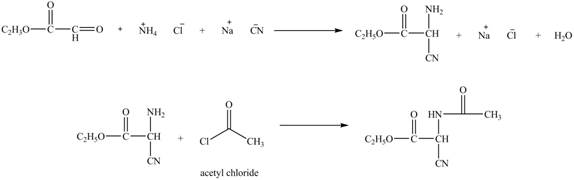
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
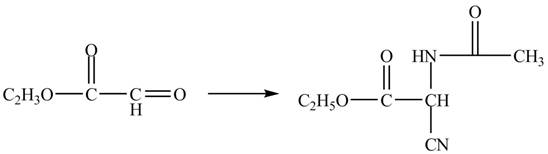
Figure 11
The compound
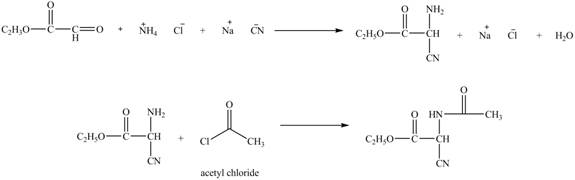
Figure 12
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 12.
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The complete synthesis of given compound is shown below.
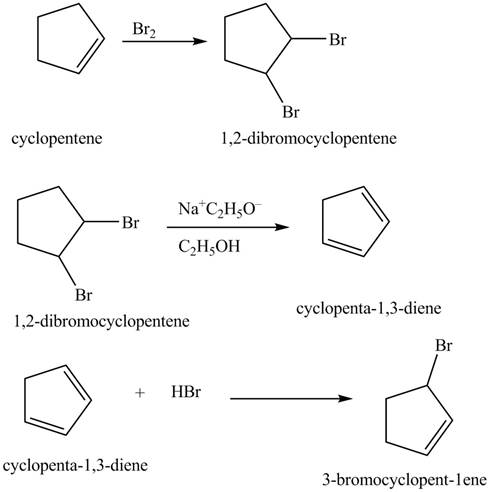
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
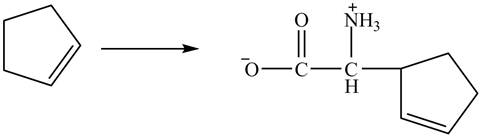
Figure 13
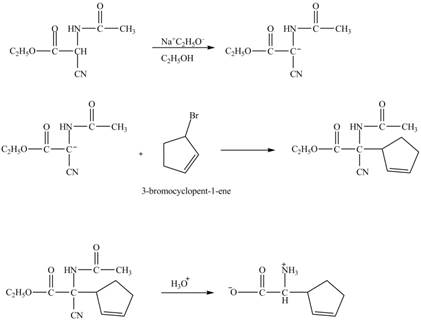
The compound cyclopentene undergo bromination reaction to form
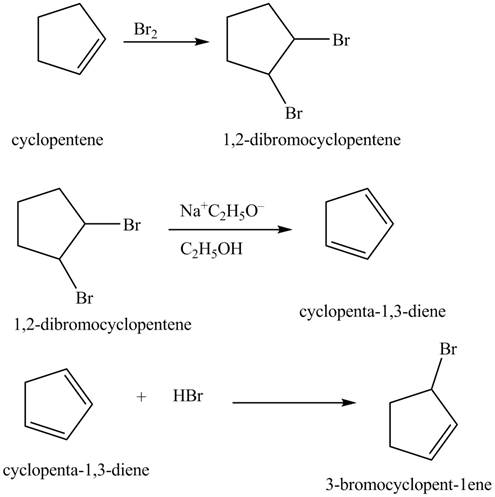
Figure 14
The given nitrile compound upon reaction with sodium ethoxide forms anion. The formed anion reacts with
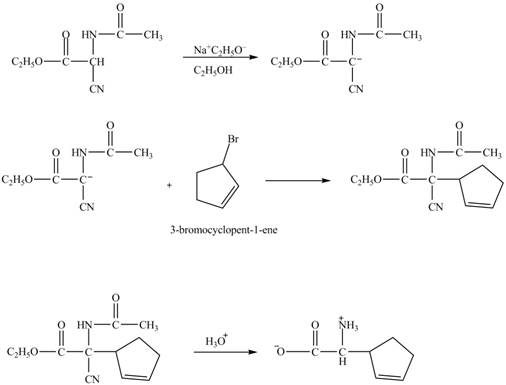
Figure 15
The complete synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15.
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The reaction of carboxylic acid and amines to form amide is not possible. Amines are very basic so it abstracts acidic proton from the carboxylic acid. The reaction is performed in the presence of
Answer to Problem 27.71AP
The complete synthesis of given compound is shown below.
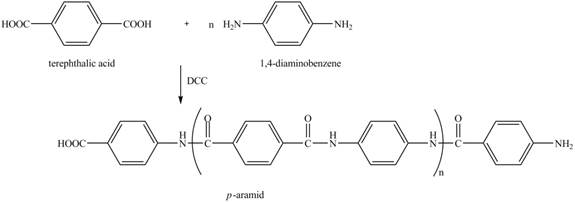
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
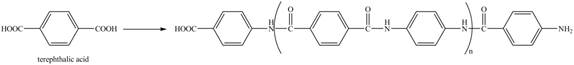
Figure 16
The reaction between terephthalic acid and

Figure 17
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 17.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

