
Concept explainers
To calculate: The first and second derivative of the function
Answer to Problem 21E
The value of first derivative of the function is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function
Formula used:
Let a function g be continuous on closed interval
If first derivative of the function is greater than zero that is
If first derivative of the function is less than zero that is
If second derivative of the function is greater than zero that is
If second derivative of the function is less than zero that is
The point where the graph changes it nature is known as the point of inflection.
Power rule of differentiation,
Calculation:
Consider the provided function
Simplify the function, multiple the terms of second and third bracket first,
Now, multiply the terms of both the brackets together,
Evaluate the first derivative of the function,
Apply sum rule of differentiation,
Apply the power rule of differentiation,
Evaluate the second derivative of the function, differentiate the first derivative again with respect to x .
Apply the power rule of differentiation,
Recall if first derivative of the function is greater than zero that is
If first derivative of the function is less than zero that is
If second derivative of the function is greater than zero that is
If second derivative of the function is less than zero that is
The point where the graph changes it nature is known as the point of inflection.
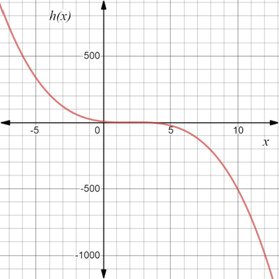
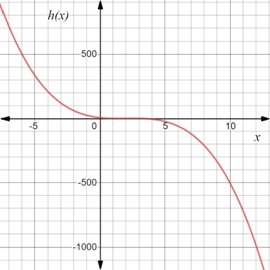
To sketch the graph of the function
Observe that first derivative of the function
The derivative of the function has solutions,
Simplify it further as,
Next observe that second derivative of the function
The function
Next observe that second derivative of the function
The function
At
Therefore, the graph of the function
Thus, the value of first derivative of the function is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Modeling the Dynamics of Life: Calculus and Probability for Life Scientists
- A straight-line H is tangent to the function g(x)=-6x-3+ 8 and passes through the point (- 4,7). Determine, the gradient of the straight-line Choose.... y-intercept of the straight-line Choose... + which of the following is the answers -1.125 -6.72 1.125 7.28 0.07 - 7.28 6.72arrow_forwardYou are required to match the correct response to each statement provided. Another term/word that can be used synonymously to Choose... gradient. A term/phrase that is associated with Arithmetic Progression. Common difference → An identity matrix can be referred to as a Choose... ÷ What is the inequality sign that represents "at most"? VIarrow_forwardAffect of sports on students linked with physical problemsarrow_forward
- 26.1. Locate and determine the order of zeros of the following functions: (a). e2z – e*, (b). z2sinhz, (c). z*cos2z, (d). z3 cosz2.arrow_forwardQ/ show that: The function feal = Se²²²+d+ is analyticarrow_forwardComplex Analysis 2 First exam Q1: Evaluate f the Figure. 23+3 z(z-i)² 2024-2025 dz, where C is the figure-eight contour shown in C₂arrow_forward
- Q/ Find the Laurent series of (2-3) cos around z = 1 2-1arrow_forward31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardUsing FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward
- 1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward7. The demand for a product, in dollars, is p = D(x) = 1000 -0.5 -0.0002x² 1 Find the consumer surplus when the sales level is 200. [Hints: Let pm be the market price when xm units of product are sold. Then the consumer surplus can be calculated by foam (D(x) — pm) dx]arrow_forward4. Find the general solution and the definite solution for the following differential equations: (a) +10y=15, y(0) = 0; (b) 2 + 4y = 6, y(0) =arrow_forward

 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning


