
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutamate can be converted to
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
Yes, glutamate can be converted to
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
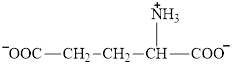
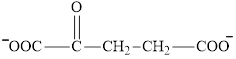
Both glutamate and
(b)
Interpretation: To determine whether
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
Yes,
Explanation of Solution
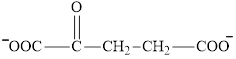
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
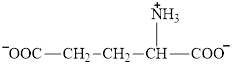
Both glutamate and
(c)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutamate can be converted to aspartate via a transamination reaction or not.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
No, glutamate cannot be converted to aspartate by transamination.
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
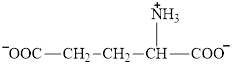
Aspartate is an amino acid and its structure is:
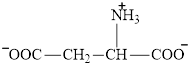
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of an amino group from an
(d)
Interpretation: To determine whether
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(d)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
No,
Explanation of Solution
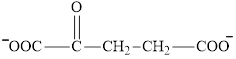
Oxaloacetate is a keto acid and its structure is:
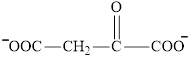
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of an amino group from an
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- A unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alanine and histidine write the amididation reaction mechanism using arrows then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction and the one letter code for the product of the reaction.arrow_forwardWrite the amididation reaction mechanism of p-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophen please use arrows.arrow_forward
- Write the amididation reaction mechanism of a-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophenarrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forward
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



