
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To determine whether denaturation of protein is associated with the (1) mouth, (2) stomach, (3) small intestine or (4) intestinal lining.
Concept introduction: Proteins are natural biopolymers. Amino acids are the main building block of protein molecules. A large number of amino acids condense together to form a polypeptide chain. A large polypeptide chain is called protein.
Denaturation of protein is defined as the process in which the quaternary, tertiary and secondary structure of the protein is disrupted except the primary structure with the help of external sources. Denaturation disrupts the intermolecular forces responsible for the protein structure. Denaturation of proteins can be carried out by treatment of protein with strong acid or bases, solvents, reducing and oxidizing agents.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.1EP
Protein is denatured in the stomach.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
Denaturation of proteins can be effected by treatment of protein with strong acid or bases, solvents, reducing and oxidizing agents. When dietary protein enters the stomach it triggers the release of gastrin hormone by mucosa cells of the stomach. Gastrin secretion, in turn, causes secretion of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid and thus result in the denaturation of the protein.
Reason for incorrect option:
Digestion of protein starts in the stomach, not in the mouth. Salive present in the mouth just helps to swallow down the food it does not affect the protein. Hence, denaturation of protein is not associated with the mouth.
In the small intestine, bicarbonate ion is secreted by secretin hormone. Bicarbonate is weakly basic and thus does not denatures protein rather in small intestine peptide bonds are hydrolyzed by the pancreatic enzymes. Hence, denaturation of protein is not associated with the small intestine.
Protein digestion is completed in the small intestine. The free amino acids released are absorbed through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream. Hence, denaturation of protein is not associated with the intestinal lining.
(b)
Interpretation: To determine whether active trypsin is associated with the (1) mouth, (2) stomach, (3) small intestine or (4) intestinal lining.
Concept introduction: Proteins are natural biopolymers. Amino acids are the main building block of protein molecules. A large number of amino acids condense together to form a polypeptide chain. A large polypeptide chain is called protein. The digestion of dietary protein starts in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. It does not start in the mouth because saliva present in the mouth does not contain an effective enzyme to break down the protein. The flow chart for protein digestion in the human body is as follows:
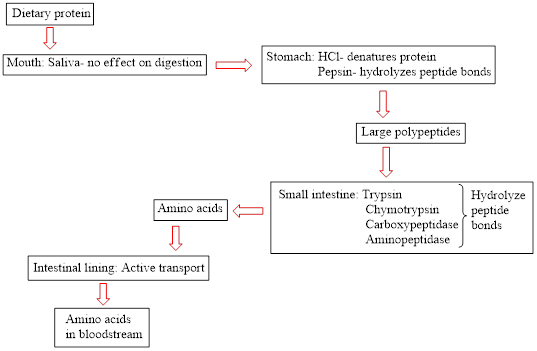
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.1EP
Trypsin is active in the small intestine.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
Trypsin is an example of a proteolytic enzyme. The basic environment in the small intestine stimulates the production of pancreatic digestive enzyme trypsin. Trypsin is active in the small intestine and attacks the peptide bond of the proteins.
Reason for incorrect option:
The only enzyme present in the mouth is salivary amylase. Pepsin is present in the stomach and no enzyme is present in the intestinal lining.
(c)
Interpretation: To determine whether active breaking of peptide bonds is completed in the (1) mouth, (2) stomach, (3) small intestine or (4) intestinal lining.
Concept introduction: Proteins are natural biopolymers. Amino acids are the main building block of protein molecules. A large number of amino acids condense together to form a polypeptide chain. A large polypeptide chain is called protein. The digestion of dietary protein starts in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. It does not start in the mouth because saliva present in the mouth does not contain an effective enzyme to break down the protein. The flow chart for protein digestion in the human body is as follows:

(c)
Answer to Problem 26.1EP
The breaking of peptide bonds is completed in the small intestine.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
The partially digested polypeptides are passed into the small intestine from the stomach. In small intestine trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, and aminopeptidase digestive enzyme are present. These attack and hydrolyzes the peptide bond of the protein and breaks the long polypeptide chains into free amino acid residues resulting in the complete digestion or breaking of the peptide bonds.
Reason for incorrect option:
Digestion of protein starts in the stomach, not in the mouth. In the stomach hydrochloric acid present denatures or unwind the globular protein and the enzyme pepsin hydrolyzes only
(d)
Interpretation: To determine whether hydrochloric acid is secreted in the (1) mouth, (2) stomach, (3) small intestine or (4) intestinal lining.
Concept introduction: Proteins are natural biopolymers. Amino acids are the main building block of protein molecules. A large number of amino acids condense together to form a polypeptide chain. A large polypeptide chain is called protein. The digestion of dietary protein starts in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. It does not start in the mouth because saliva present in the mouth does not contain an effective enzyme to break down the protein. The flow chart for protein digestion in the human body is as follows:

(d)
Answer to Problem 26.1EP
Hydrochloric acid is secreted in the stomach.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
Hydrochloric acid secretion is stimulated by the production of gastrin hormone which in turn is released by mucosa cells of the stomach. Thus, hydrochloric acid is secreted in the stomach.
Reason for incorrect option:
Hydrochloric acid is secreted in the stomach and is responsible for denaturation of the protein. Protein denaturation is the first step of protein digestion that occurs in the stomach. Hence, hydrochloric acid is not associated with the mouth, small intestine or intestinal lining.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning





