
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin formed at the same time
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center. The structure of the heme group is:
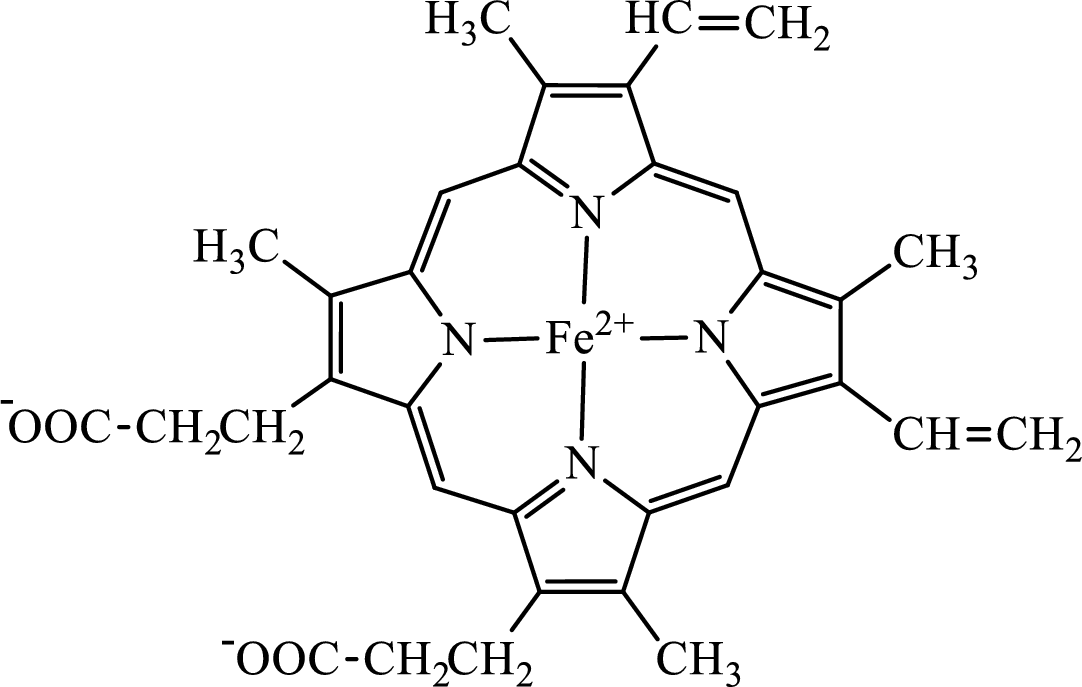
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin associated with the condition called jaundice.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The structure of the heme group is:
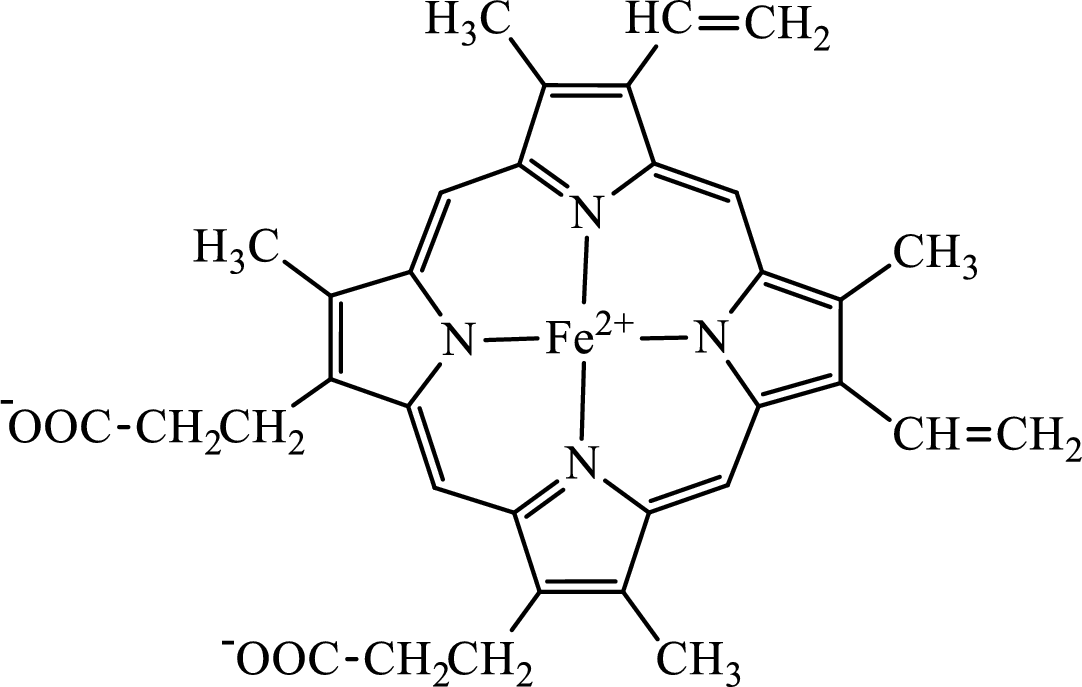
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin for which molecular oxygen is used as a reactant.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The structure of the heme group is:
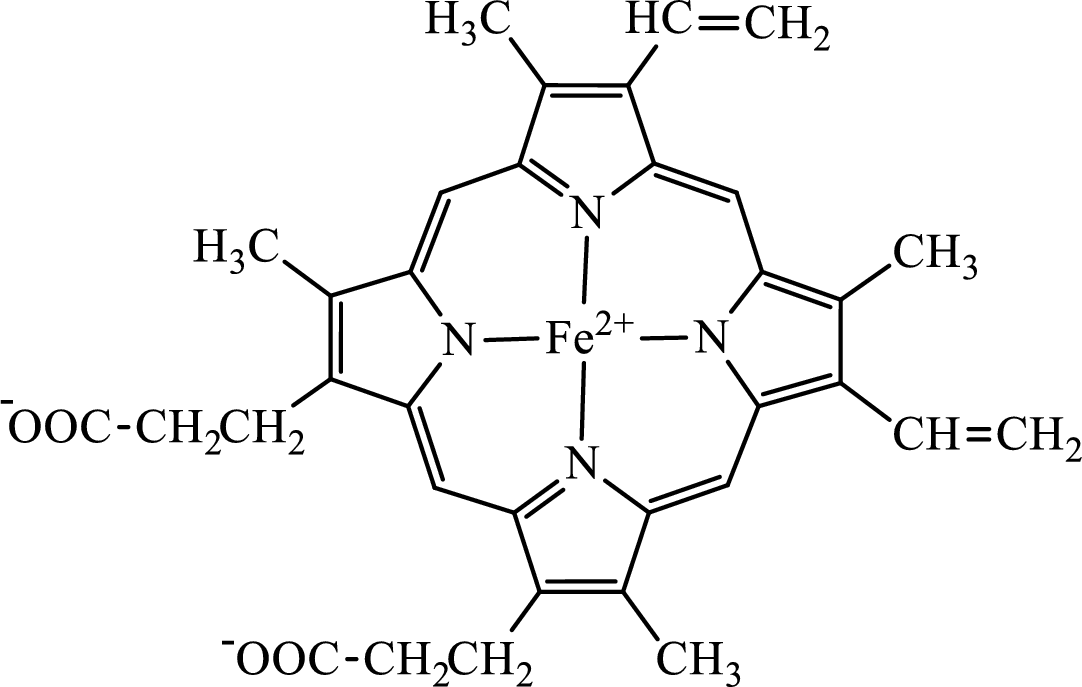
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the heme degradation product (1) bilirubin, (2) biliverdin, (3) stercobilin, and (4) urobilin which is bile pigment and has a brownish color.
Concept introduction: Hemoglobin is a heme protein present in the red blood cells. The protein part is called globin and the non-protein part is heme. Heme is the prosthetic group that contains 4 pyrrole groups bonded together and has an iron atom in the center.
The structure of the heme group is:
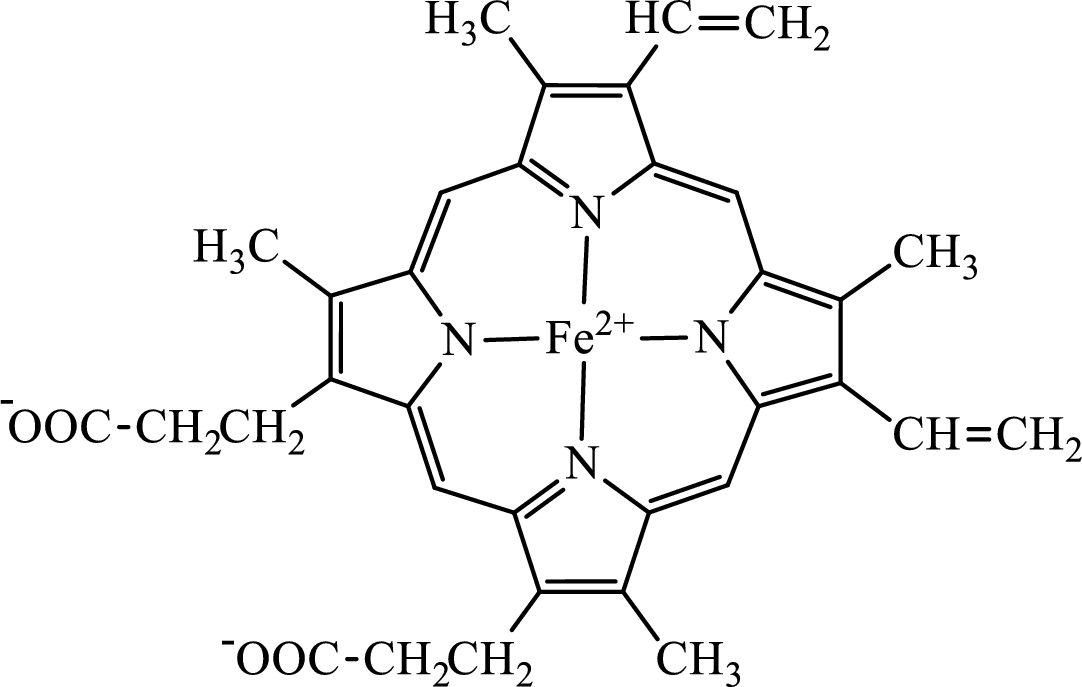
The first step of degradation of heme involves opening of pyrrole ring with the release of the iron atom and production of biliverdin. The iron atom released becomes part of ferritin protein. Biliverdin produced is converted bilirubin in the spleen. Bilirubin is then transported to the liver where attachment of sugar residues to the propionate side chains of the bilirubin occurs to make it more soluble. Then more solubilized bilirubin is excreted in bile and finally to the small intestine. In the small intestine, it is converted into stercobilin for excretion in feces or urobilin for excretion in urine.
Bile pigments are the colored degradation product of tetrapyrrole carbon arrangement of heme portion of hemoglobin. These are excreted in bile and give characteristic color to urine and feces.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- For the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning





