
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin riboflavin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.116EP
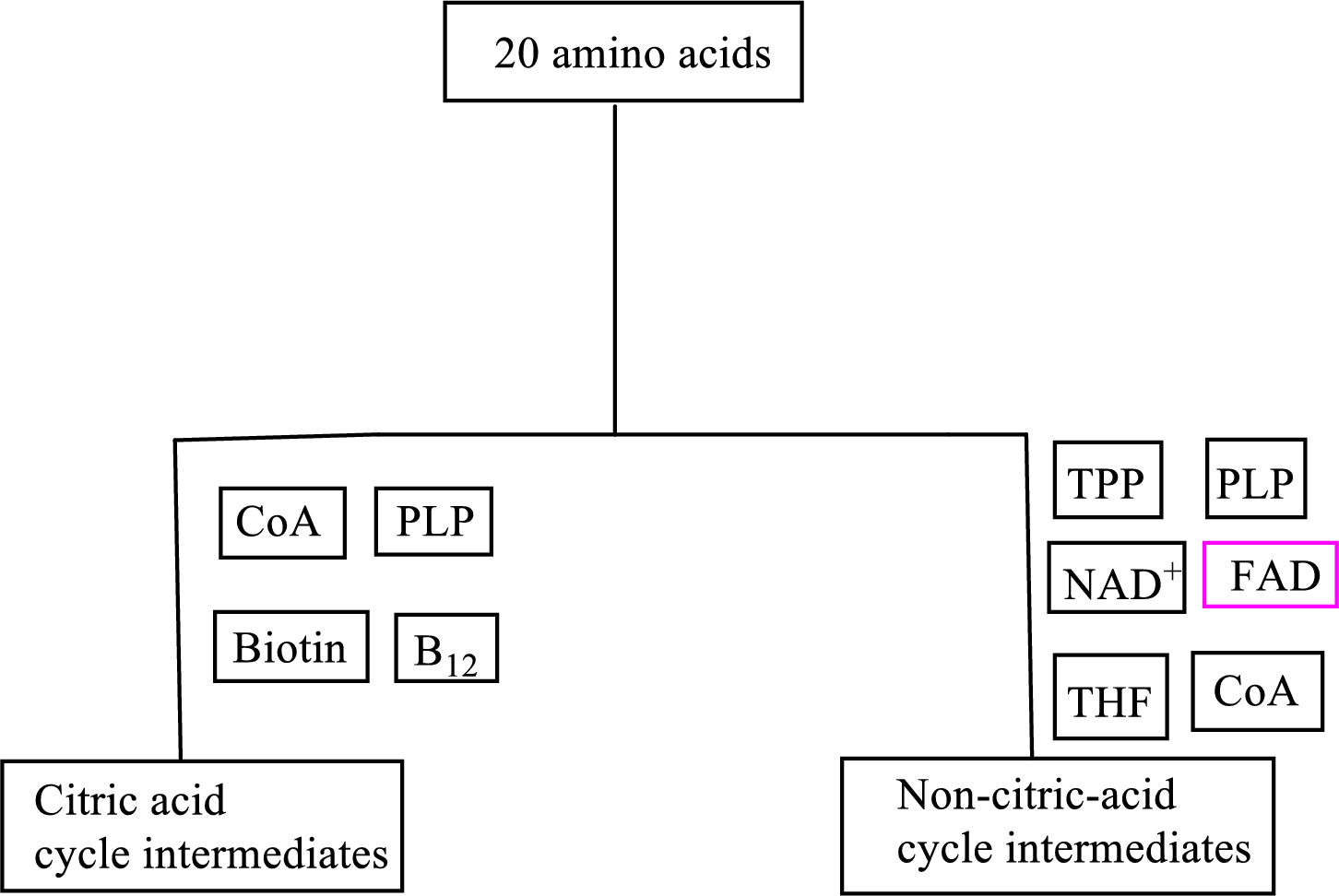
B vitamin riboflavin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
(b)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin thiamin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.116EP
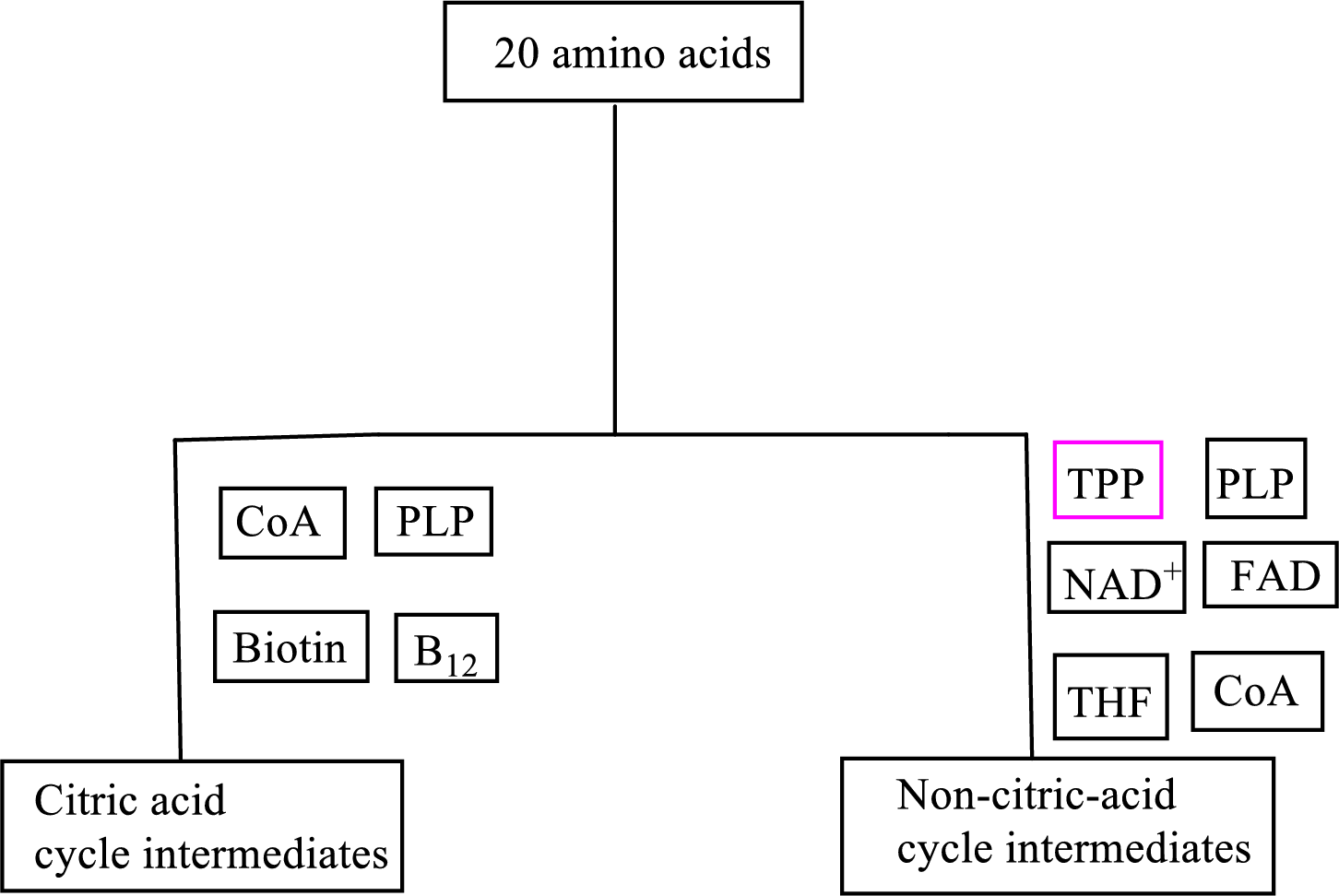
B vitamin thiamin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme thiamin pyrophosphate
Thiamin pyrophosphate
(c)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin pantothenic is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.116EP
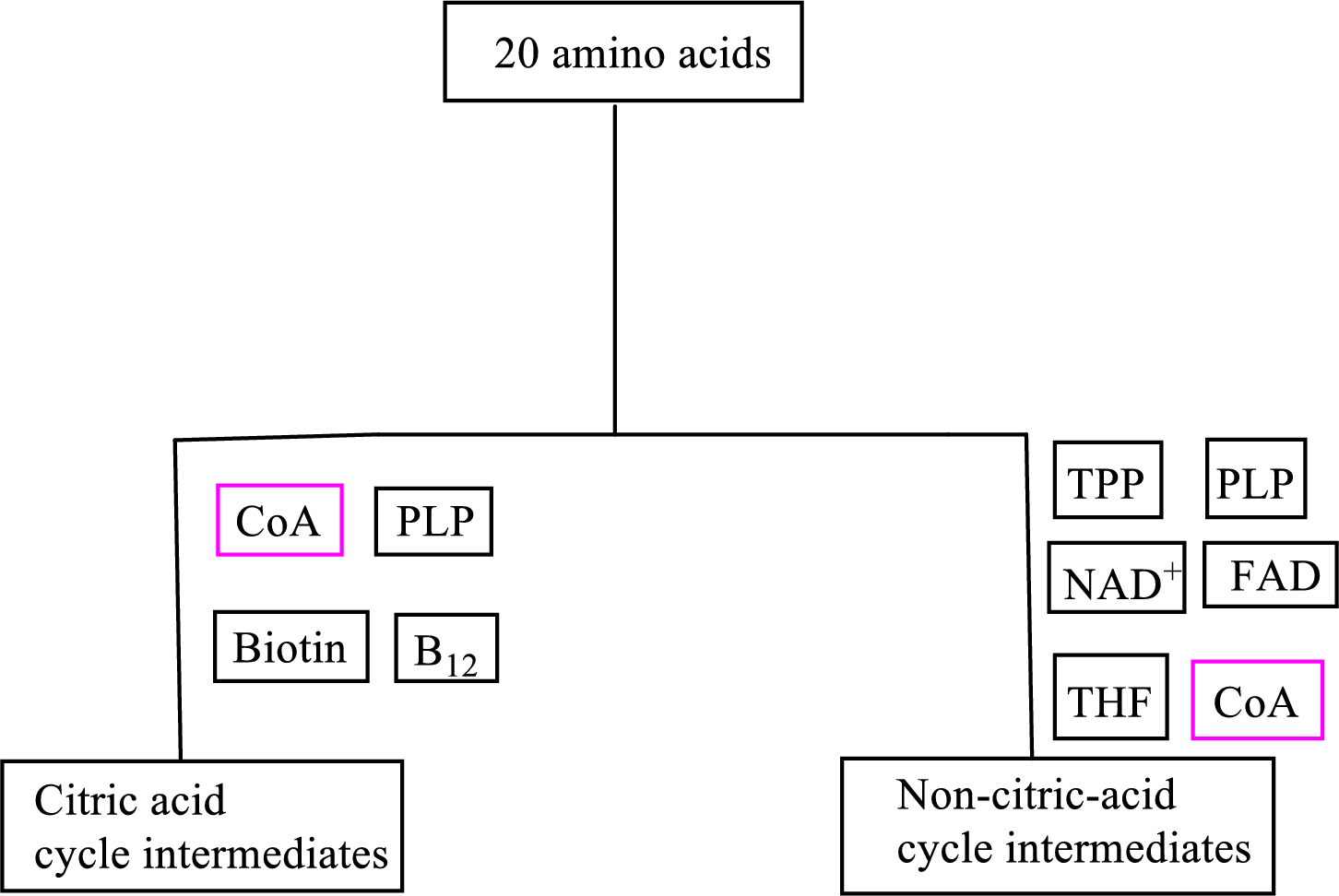
B vitamin pantothenic acid is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC and CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
(d)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(d)
Answer to Problem 26.116EP
Explanation of Solution
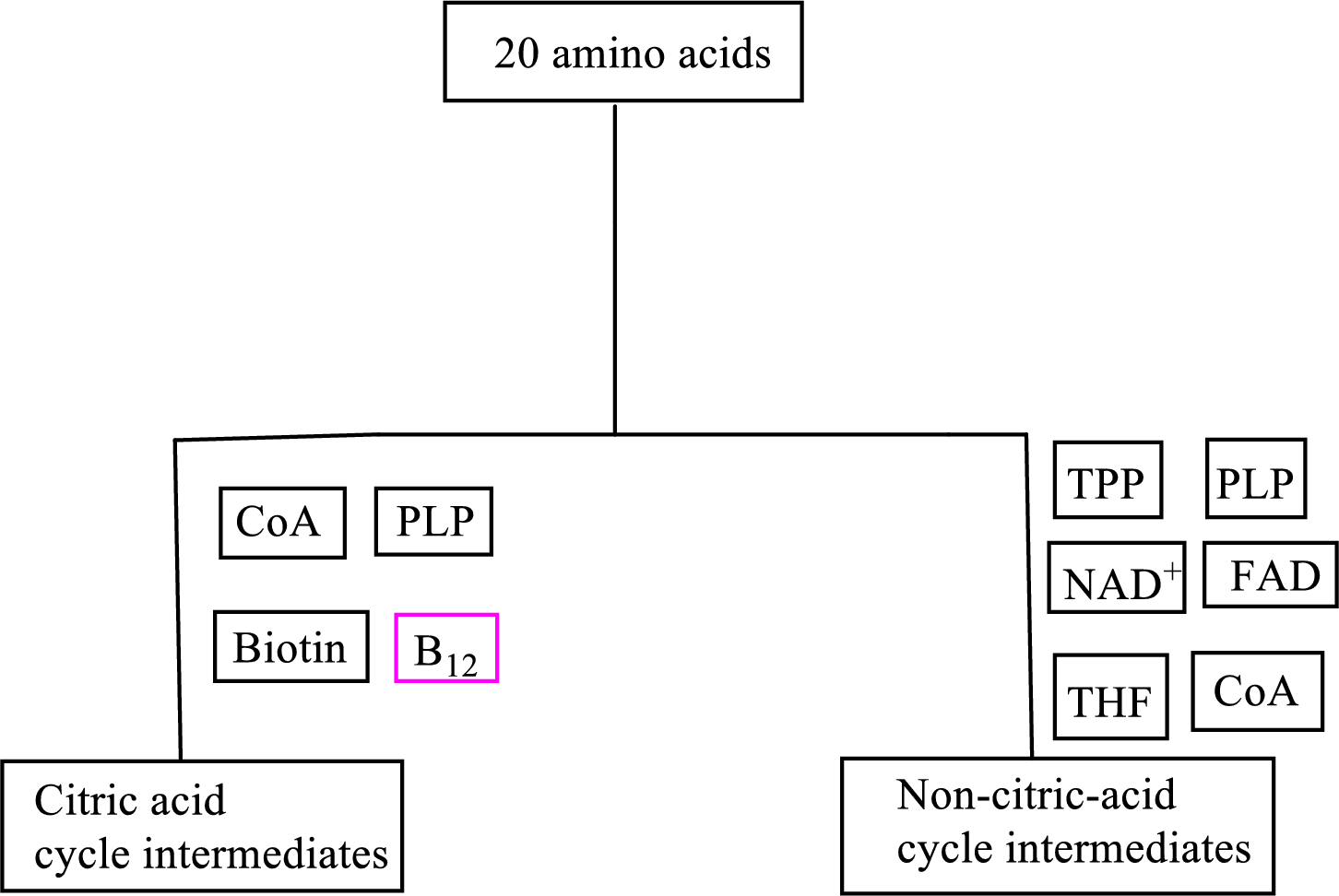
Coenzyme methylcobalamin contains the B vitamin
Coenzyme methylcobalamin is involved in the carbon skeleton degradation pathway to CAC intermediates.
An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forwardName the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forward
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




