
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:
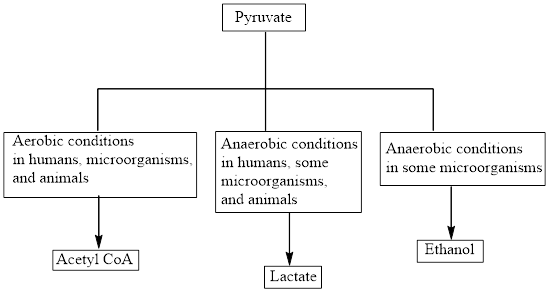
Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
(a)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
Carbon dioxide
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to
The process of ethanol fermentation takes place in two steps. In step 1, the pyruvate molecule is converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes. Carbon dioxide molecule is produced in this step. In step 2, acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore,
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for lactate fermentation is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: To identify NADH is a reactant in which the fate of pyruvate-
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions.
The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the
A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the
(b)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
NADH is encountered as a reactant in the lactate and ethanol production from pyruvate.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Ethanol fermentation process occurs in some microorganisms (for example yeast) under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore, NADH is encountered as a reactant in the lactate and ethanol production from pyruvate.
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
Therefore, NADH is formed along with
(c)
Interpretation: To identify
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the redox reactions in metabolism. Its reduced form is NADH and oxidized form is
A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the chemical reaction and gets consumed to form a new substance.
(c)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
In the production of
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
Therefore,
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to lactate is as follows:
Ethanol fermentation process occurs in some microorganisms (for example yeast) under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore,
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the end product is a
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Pyruvate
(d)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. This anaerobic reduction is called lactate fermentation. The chemical reaction for the formation of lactate is as follows:

Lactate contains three carbon atoms. Therefore, lactate is a
Reason for incorrect choice:
In the ethanol fermentation process, pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide by enzymes under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Ethanol
Pyruvate is converted to
Acetyl group
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




