
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of basicity of propylamine, ammonia, and dipropylamine in aqueous solution is to be arranged.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.7P
The increasing order of basicity of propylamine, ammonia, and dipropylamine in aqueous solution is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the order of basicity of amines in aqueous solution is
The increasing order of basicity of propylamine, ammonia, and dipropylamine in aqueous solution is shown below.
(b)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of basicity of
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.7P
The increasing order of basicity of
Explanation of Solution
It is known that the order of basicity of amines in aqueous solution solution is
The increasing order of basicity of
(c)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of basicity of aniline, methyl m-aminobenzoate, and methyl p-aminobenzoate in aqueous solution is to be arranged.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.7P
The increasing order of basicity of aniline, methyl m-aminobenzoate, and methyl p-aminobenzoate in aqueous solution is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of aniline, methyl m-aminobenzoate, and methyl p-aminobenzoate is shown below.
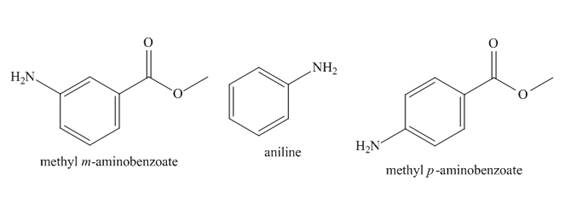
Figure 1
Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
The basicity of aniline substituted compound depends on the group that is attached to benzene ring. If the group attached to benzene ring is electron withdrawing group, it will decrease the basicity of the compound. If the group attached to benzene ring is electron donating group, it will increase the basicity of the compound.
There is no group attached in case of aniline. Therefore, it is most basic. In case of methyl m-aminobenzoate and methyl p-aminobenzoate, the
The increasing order of basicity of aniline, methyl m-aminobenzoate, and methyl p-aminobenzoate in aqueous solution is shown below.
(d)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of basicity of benzylamine, p-nitrobenzylamine, cyclohexylamine, aniline in aqueous solution is to be arranged.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.7P
The increasing order of basicity of benzylamine, p-nitrobenzylamine, cyclohexylamine, aniline in aqueous solution is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzylamine, p-nitrobenzylamine, cyclohexylamine, aniline is shown below.
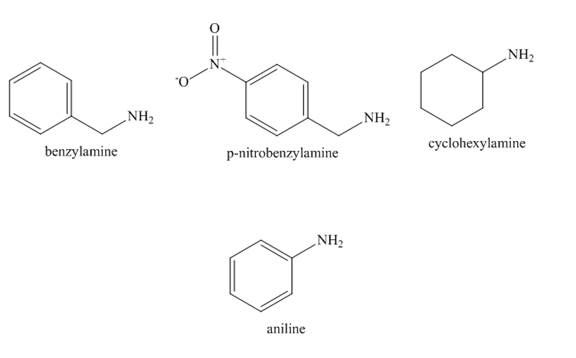
Figure 2
Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and also the ability of the nitrogen to accept the proton in water.
In case of aniline, the lone pair present at nitrogen atom is resonate with the benzene ring. Therefore, the electron density on nitrogen is decreased. Therefore, it is least basic.
In case of cyclohexylamine, there is no resonance. The cyclohexyl group is an electron donating group which increases the electron density on nitrogen atom. Therefore, the basicity of cyclohexylamine increased.
In case of benzylamine there is also no resonance because
In case of p-nitrobenzylamine there is also no resonance because
The increasing order of basicity of benzylamine, p-nitrobenzylamine, cyclohexylamine, aniline in aqueous solution is shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


