
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction of ammonia with nitrous acid is to be completed. Also, the major product formed in the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction of ammonia with nitrous acid is shown below.
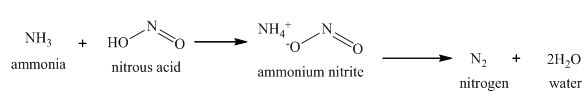
The major product formed is the nitrogen gas.
Explanation of Solution
When ammonia reacts with nitrous acid, diazotization occurs with the formation of ammonium nitrite intermediate which dissociates and liberates nitrogen gas along with the formation of water.
The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The reaction of ammonia with nitrous acid is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
The conversion of amines into
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The complete reaction between
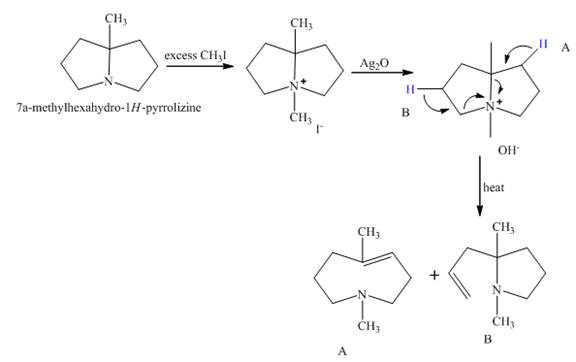
The major product will be compound
Explanation of Solution
Hofmann elimination reaction takes place when

Figure 2
The complete reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
The conversion of amines into alkenes can be achieved by Hoffmann elimination reaction. Amines have poor leaving groups. They react with excess of alkyl halides to form ammonium salts. These ammonium salts undergo
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction between
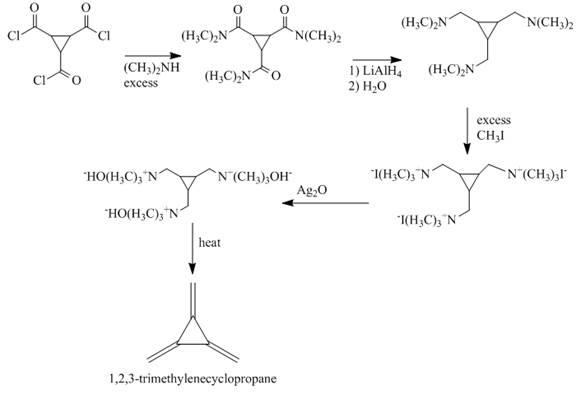
The major product formed is
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 3
The reaction between
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction of phenol with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite is to be completed. Also, the major product of the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction involves the substitution of an electrophile on an aromatic ring. The
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction of phenol with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite is shown below.
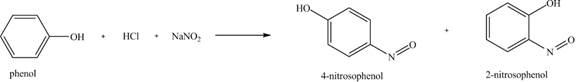
The major product formed is
Explanation of Solution
The compounds

Figure 4
The reaction of phenol with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic amines takes place using sodium nitrite and hydrohalide at low temperatures. This process is known as diazotization. Aryl diazonium salts undergo a variety of specific substitution reactions in which the nucleophilic Z group replaces (a very good leaving group) to form corresponding products.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction between
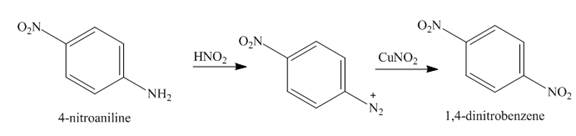
The major product in the corresponding reaction is
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 5
The reaction between
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction between butylamine with oxirane is to be completed. The major product of the corresponding reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction between butylamine with oxirane is shown below.
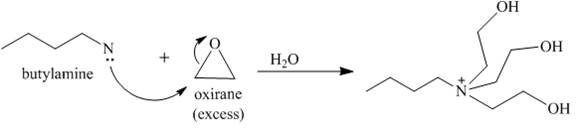
Explanation of Solution
Oxirane is a symmetrical molecule. Therefore, the nucleophile can attack at any carbon. Nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when butyl amine reacts with oxirane. The lone pair of electrons attacks the carbon atom of the oxirane which opens the ring. Since, the oxirane is in excess, so, the amine will react with oxirane till it’s all the hydrogen groups are replaced by the oxirane to yield a quaternary ammonium derivative as shown below.

Figure 6
The reaction between butylamine with oxirane is show in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction of
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction of
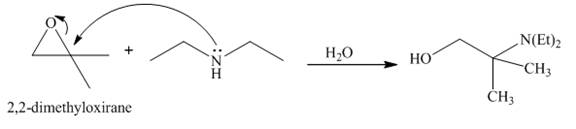
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between

Figure 7
The reaction between
(h)
Interpretation:
The reaction between phthalimide and
Concept introduction:
Gabriel synthesis is a reaction in which a primary amine is formed when a phthalimide anion is alkylated and then undergoes hydrolysis. It is the best method to prepare primary aliphatic amines. Aromatic amines cannot be prepared by this reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction between phthalimide and
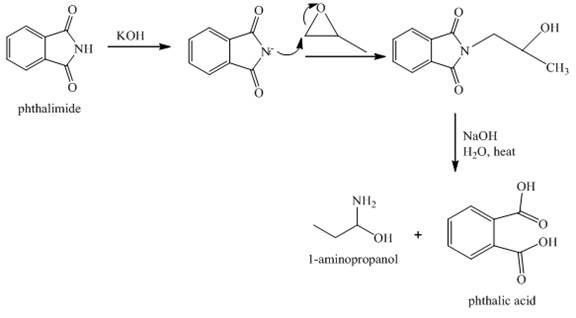
Explanation of Solution
Gabriel phthalimide reaction occurs when phthalimide reacts with

Figure 8
The reaction between phthalimide and
(i)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The nucleophilic substitution reaction between
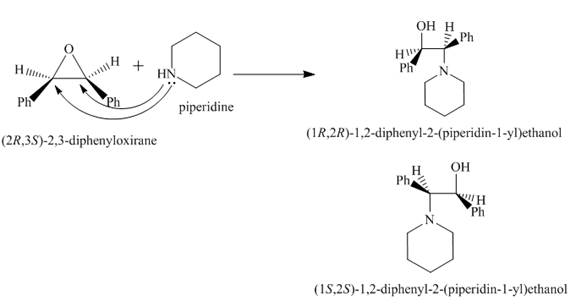
Two enantiomeric products will be formed in equal proportions because the substrate is symmetrical, so, the attack of nucleophile is feasible equally at both the carbon sites in substituted oxirane.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when

Figure 9
The reaction between
(j)
Interpretation:
The reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic center and a substituted product is formed. It takes place by the generation of an electrophilic intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction between
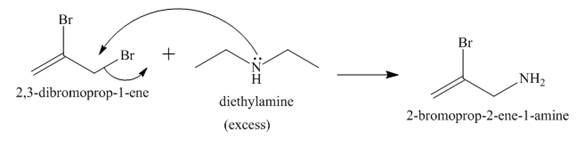
Explanation of Solution
The nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when diethyl amine reacts with

Figure 10
The reaction between
(k)
Interpretation:
The reaction of nitrobenzene with
Concept introduction:
Catalytic hydrogenation is a reduction process of addition of hydrogen atoms in an alkene or an
Answer to Problem 23.65AP
The reaction of nitrobenzene with
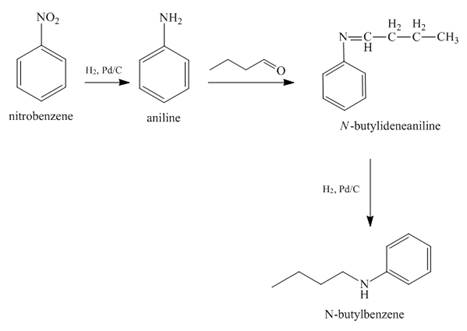
Explanation of Solution
When nitrobenzene is catalytically hydrogenated with
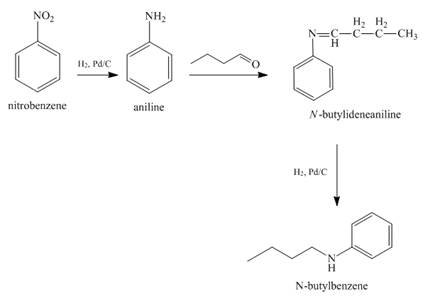
Figure 11
The reaction of nitrobenzene with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
